Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Inflammation of the periosteum (periostitis) is a disease that brings many painful symptoms. As a rule, acute pain and severe swelling immediately bring the patient to the dentist, and rightly so: not only the condition of the oral cavity, but also health in general depends on the timeliness of treatment.
Typical symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are quite pronounced:
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- increasing severe pain radiating to the ear, temple and other areas, depending on the location of the inflammation;
- swelling of the face on one side (cheeks, lips, cheekbones);
- high body temperature;
- symptoms of general intoxication (headache, dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue and weakness, general loss of strength);
- white or gray plaque on the gums;
- change in tooth position, tooth mobility;
- in some cases, the appearance of purulent discharge.
With a prolonged inflammatory process, a fistula can form: pus finds its way into the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood, but the pain and fever temporarily subside. This is due to the fact that the contents stop accumulating in the tissues and begin to flow out, but you should definitely consult a doctor.
Biomechanics of injury
The main difference between running and walking is the absence of a double support phase (when both legs are on the ground at the same time), as a result of which the body weight falls on one limb when landing, which leads to 1) a sharp increase in the impact load on the leg; 2) the need to increase the activity of the foot stabilizer muscles. That is, muscles that provide not so much power (like the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles), but rather the correct position of the landing and pushing off foot, adaptation to uneven surfaces.
As a result of increased load, the stabilizer muscles become clogged and shortened, just like any muscle after training. And here the second mechanism that causes injury is activated - the distribution of the shock load.
When we land on our foot, the muscles, ligaments and bones absorb and dissipate the shock. If the muscle is elastic and in normal tone, then most of the blow is absorbed by the lengthening of its abdomen (central part), and the tendons and places of attachment to the bone take on the rest of the blow. If the muscles are shortened and not elastic, much more shock load falls on the attachment site.
periosteum (a dense layer of connective tissue that covers the entire bone). When receiving a blow, the muscles seem to pull the periosteum, which leads to its microtrauma and inflammation.
Structural disorders of the foot can also increase the shock load on the lower leg muscles, such as an excessively high arch of the foot (Figure 3), which reduces its shock-absorbing ability, and flat-valgus feet, which often lead to hyperpronation (excessive roll of the ankle joint and the foot inwards when landing ) and, consequently, additional load on the tibialis posterior muscle.
Causes of tire splint:
- Weak and clogged foot stabilizer muscles
- High impact load.
High impact loads may be caused by:
- overweight;
- structural features of the foot - hyperpronation, high rigid arch of the foot;
- shoes with low cushioning;
- hard surface for running;
- hard contact with the surface (excessively high tension of the feet upon contact);
- acceleration or running down an inclined surface;
- running on uneven surfaces.
Moreover, you can clog up your muscles one day, for example, when training in the park, and damage the periosteum during the next workout when running on your usual hard surface, simply by shortening the muscles.
Why does inflammation of the periosteum occur?
There are three ways that pathogenic bacteria enter the periosteum:
- odontogenic factor - dental diseases become the source of inflammation: caries, cysts and granulomas of the tooth root, pulpitis. Bacteria penetrate deep into soft tissues. Quite often, periostitis is observed as a result of a long and complicated process of eruption of “eights”;
- hematogenous factor - infection occurs as a result of bacteria entering the tissues from the bloodstream or lymph flow. As a rule, this happens in connection with ENT diseases, furunculosis of the face, neck, abscesses, etc.;
- traumatic factor - mechanical damage to the periosteum during fractures, impacts, complex tooth extractions leads to inflammation.
Causes of shin pain
After physical effort or minor injury, the pain usually goes away on its own and does not require specialist intervention. If the pain does not go away within 2-3 days, you need to visit an orthopedist or traumatologist who will help establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
One of the causes of pain is flat feet. With this pathology, the shape of the foot is flattened and irregular. Its functioning is impaired, and the shock-absorbing function of the foot is not fulfilled. As a result, muscles and ligaments experience additional stress, and fatigue appears after walking. In this case, you need to use orthopedic shoes or special insoles.
Varicose veins can cause discomfort in the lower leg. This disease is accompanied by stagnation of blood in the vessels. Its microcirculation is disrupted, the walls of blood vessels are greatly stretched. With venous stagnation, discomfort and pain occur.
To reduce the severity of discomfort, it is recommended to wear special compression products. Vein thrombosis and obliterating atherosclerosis are also diseases of the vascular system. Their development is accompanied by circulatory disorders, blood stagnation, and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Other causes of pain in the lower leg include:
- decrease in the concentration of magnesium, calcium, potassium in the blood. Long-term use of diuretics can provoke such conditions;
- improper use of statins, a side effect is deformation of muscle tissue;
- spasms in muscle tissue after prolonged physical activity;
- ruptures or cracks in the tendons after an injury;
- broken bones, cracked joints;
- meniscal deformation, previous trauma;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- inflammatory process in tendons;
- atherosclerotic disease of the circulatory system with the formation of cholesterol plaques, deterioration of blood outflow;
- infectious processes in tissues;
- damage to nerve fibers, ruptures, sprains or trauma to fibers;
- severe injury or muscle strain, which is accompanied by the development of trap syndrome, compression of the lower leg;
- development of muscle contracture under severe tension or loads;
- inflammatory process in the periosteum of the tibia;
- tears of various types in the muscular system of the lower leg;
- tears of the popliteal ligaments;
- inflammatory process in the kneecap, in the tuberous surface;
- neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature in any part of the leg;
- the use of glucocorticosteroid drugs, in this case pain is a side effect;
- compression of muscle tissue or neurons in tissue.
People who smoke more than two packs of cigarettes a day often experience pain in the lower leg. After quitting the bad habit, the pain of smokers stops on its own. This may be a consequence of stress on the vascular system.
Types of inflammation
Symptoms of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth depend on the form of the process. In the acute form, pain and swelling are severe, difficulty swallowing, spreading of swelling to the face and neck, and enlarged lymph nodes may be observed. Acute inflammation occurs over several days.
The chronic form may bother the patient for several months. Symptoms are more moderate; a fistula may appear - an opening through which inflamed tissues get rid of purulent contents.
There are also two types of both acute and chronic inflammation:
- serous - more often provoked by traumatic injury, swelling forms quickly, but the pain is more moderate and tolerable, relief occurs, on average, after 5 days;
- purulent - more dangerous, characterized by severe throbbing pain, severe swelling and redness of soft tissues, and higher body temperature.
In both cases, you should definitely consult a doctor, since the risk of complications is very high.
MBST therapy
With the help of magnetic radiation supplied by the MBST device, the following goals can be achieved:
- improve blood circulation and vascular condition;
- get rid of pain;
- prevent further development of the pathological process.
You can sign up for ankle treatment in Moscow at ArthroMedCenter. A completed course of MBST therapy is a good prevention of arthritis, arthrosis, atherosclerosis, and osteoporosis. After the procedure, blood circulation improves and the walls of blood vessels are strengthened. When undergoing MBST therapy, tissues begin to better absorb calcium, and damage and microcracks are restored faster.
Thanks to an integrated approach to treatment and prevention, you can get rid of unpleasant symptoms and prevent further development of diseases.
Features of treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth should only be carried out by a doctor. The specialist chooses tactics depending on the type and form of the disease.
Drug treatment is only advisable if you consult a doctor immediately at the first symptoms of the disease. Therapy includes:
- taking antibiotics prescribed by a specialist: this will stop inflammation and prevent the spread of infection;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers;
- local effect: use of antiseptic rinses, chlorhexidine baths, ointments and gels with an anti-inflammatory effect.
The course of treatment is at least 5-7 days. If relief does not occur, surgical methods are used.
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are individual. In case of advanced inflammation, ineffectiveness of conservative methods and other indications, the doctor performs a tissue opening - periostotomy. It is carried out in several stages:
- anesthesia: local infiltration or conduction anesthesia is sufficient.
- Making an incision in the gum in the projection of the source of inflammation.
- Washing and cleaning tissues.
- Treatment of the wound with antiseptic agents.
- Installation of drainage - a small rubber band in order to prevent premature fusion of the mucous membrane and the re-formation of pus inside.
The drainage is removed by a doctor after a few days; you should not do this yourself. The specialist must make sure that the contents of the inflamed tissue are released and the wound can be allowed to heal. If the incision is small, no stitches will be required.
If the cause of the disease was a damaged tooth, it is treated: restoring its shape using filling materials, filling root canals. Sometimes removal is required; it is performed simultaneously with surgical treatment of periostitis.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures may be recommended. They will speed up inflammation relief and healing. These include UHF, darsonval therapy, infrared radiation, and magnetic therapy. During the healing period, it is advisable to use vitamins and restorative medications.
What structures can become inflamed in the lower leg?
Pain in the lower leg and ankle occurs suddenly after an injury - bruise, sprain, fracture, dislocation. It can also be caused by a chronic illness. The following structures can become inflamed in the lower leg:
- Ligaments. They may become inflamed or stretched. When a tendon or muscle is sprained, severe tension occurs. Severe trauma also causes muscle or tendon rupture.
- Joints. Arthritis or arthrosis is a common pathological condition that affects the joints and is accompanied by pain. Ankle pain also often accompanies the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Tendons. The most common inflammatory tendon pathology is tendonitis. Also, with constant friction of the tendons and a deficiency of interarticular fluid, bursitis develops. This is accompanied by irritation and discomfort.
- Bones. After an injury, the integrity of the bone is often compromised. This is a fracture or crack. In this case, it is very important to visit a doctor as soon as possible. Only through timely and correct treatment will the bone heal and there will be no consequences of the injury.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome. It develops when the tarsal tunnel is not pinched. This is a nerve located along the entire length of the lower leg.
- Arch. There are tendons in the leg that work synchronously. This is how the arch is formed. When the tendons are connected correctly, a regular and symmetrical arch is formed. If they are connected asymmetrically, an arch of a small size is formed or it is completely absent. With this condition, discomfort or pain occurs.
- Connective tissue. Connective tissue elements are located on the bottom of the foot. When they become inflamed, it is called plantar fasciitis. This happens when wearing incorrectly selected shoes, too narrow and uncomfortable, or with poor posture.
How to help yourself before visiting a doctor
If the periosteum of the jaw is inflamed, you should forget about such traditional methods as heating: any hot compresses will aggravate the situation. If you open the formation, take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription, or remove the pus yourself, this can lead to dire consequences.
You can alleviate your condition by doing the following:
- rinse your mouth with a weak saline solution at room temperature or an antiseptic with an analgesic effect;
- apply a cool compress to the cheek on the side of the inflammation;
- Take an over-the-counter pain reliever.
These measures will help relieve pain and slightly reduce swelling, but you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. As an antiseptic rinse, you can use ACTIVE mouthwash. It does not contain alcohol, so there is no risk of burning inflamed tissues, and the chlorhexidine and benzydamine in the composition will help relieve the condition before you see a doctor.
Fibrous periostitis
It develops gradually and is chronic. It occurs under the influence of irritations lasting for years and is manifested by a callous fibrous thickening of the periosteum, tightly fused to the bone. is observed on the tibia in cases of chronic leg ulcers, bone necrosis, chronic inflammation of the joints, etc. Significant development of fibrous tissue can lead to superficial bone destruction. In some cases, with a long duration of the process, new bone formation is observed. After eliminating the stimulus, a reverse development of the process is usually observed.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
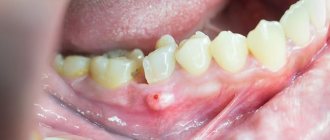
Signs of the disease
If the tissue is damaged, acute pain occurs in the area of the affected tooth, the mucous membranes swell, and a white coating appears on the tongue. Other symptoms of the disease include:
- an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- deterioration in physical well-being, weakness, decreased performance;
- decreased jaw mobility;
- separation of pus from the gums.
Pain during periosteum can radiate to the ear, chin, temple, and neck. If the disease occurs in a purulent form, after the abscess breaks through and the necrotic masses come out, the pain symptoms disappear almost immediately. But this does not mean that the inflammation has passed. It just went into a “calm” phase for a while. If a person continues to put off visiting the doctor, he may lose a tooth.
Prevention and relapse prevention
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to strengthen the stabilizing muscles of the foot with non-impact loading.
If you ride the subway, you can hold the handrail, slightly raise one leg and ride 1-2 stations on one leg and another 1-2 stations on the other leg. It is important to start the exercise after the train has accelerated and do not raise the second leg high from the floor so as not to fall during braking. The metro is generally an excellent trainer for stabilizer muscles.
You can train the muscles by performing amplitude rotations of the ankle clockwise and counterclockwise with a weight in the area of the instep weighing from 500 g to 1 kg 40 times in each direction, keeping the foot suspended. If you do such exercises every day for two months, this will greatly strengthen your ankle and prevent not only inflammation of the periosteum, but also a number of other running injuries.
Special balancing pillows are also used, exercises on which for 5-10 minutes a day give results within 3-4 weeks.
Another part of prevention is good stretching of the ankle and stabilizer muscles, as well as massaging them after high loads.
Execution: stand on the edge of a step or curb, remaining on the support, with the inside of your foot lower your heel as far as possible down and out. When performing the stretch, bend your knee slightly to increase the stretch in your calf muscles and reduce strain in your hamstrings and calf muscles. Hold the position for 40 seconds. Can be repeated 5-7 times.
For prevention and treatment, shoes with protection against overpronation are also used (selected by specialists, preferably using video recording on a treadmill) and/or special running individual insoles.
Attention! Do not combine insoles and specialized shoes without the advice of a specialist, since the anti-overpronation mechanisms built into the insole and the sneaker, when superimposed on each other, can have the opposite effect, completely extinguish pronation, or even put the foot in the opposite position!
How to deal with ankle pain
You shouldn’t fight this joint pain on your own: it’s better to get diagnosed and follow the recommendations of an orthopedist or rheumatologist. The specialist will conduct a physiological examination and collect anamnesis, and prescribe stress tests of the foot. During the examination, the condition and functioning of the nerve roots will also be assessed. If necessary, the patient will be sent for an X-ray or MRI.
The treatment regimen for osteoarthritis is fundamentally different from the treatment for gout or recovery from injury.
In case of injury, the doctor’s actions depend on the type of injury:
- in case of a fracture, a plaster cast is applied to the damaged area, but before this, surgical displacement of the bones is sometimes performed;
- the dislocation is first reduced, then an orthosis with rigid lateral parts or a plaster cast is applied to prevent swelling and properly fix the leg;
- When sprained, soft orthoses or fixing bandages are relevant.
For ankle injuries, it is important to reduce the load on the limb
Diagnostic measures
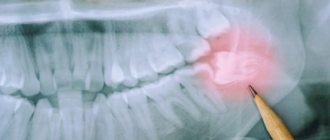
The doctor conducts an examination. It is not difficult to understand that a bone is damaged. This is indicated by external signs:
- redness of the gums;
- pain when pressing;
- the presence of a cushion containing pus;
- mobility of the incisor, canine, molar (noted if the disease is advanced).
To determine the stage of the disease and the depth of damage to bone formations, the doctor performs an X-ray or radiovisiography of the jaw.
Classification
Dentists classify pathology into the following types:
- Simple. It is the result of bruises and injuries. The lesion is found in close proximity to mechanical action. A person complains of aching pain and swelling.
- Fibrous. A consequence of prolonged irritation of the periosteum, for example, as a result of necrosis. During palpation, a painful thickening of the bone is detected. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the tumor can greatly increase in size and become malignant.
- Purulent. The result of an infection that penetrated from the outside after damage to the integrity of the mucosa. This form is often found with abscess, osteomyelitis, and phlegmon. Its causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci. Serous exudate is actively released from the abscess. An abscess occurs. Further, several options for the development of pathology are possible. The first is that pus destroys a separate area of the bone structure and breaks into the soft tissue. The second is that pus contributes to the exfoliation of a separate section of the periosteum. Then the bone stops receiving the necessary nutrition and dies. This type of inflammation always manifests itself clearly. The patient's body temperature rises. The cheek swells and an abscess forms in the mouth.
- Serous. May form after injury. A large amount of serous mucus is discharged. It accumulates. As a result, the periosteum may peel off and die.
- Ossifying. Bone tissue gradually grows. The problem occurs due to prolonged irritation of bone structures. For example, chronic osteomyelitis leads to it.
- Tuberculosis. This form is characterized by the formation of fistulas, inside which pus accumulates.
- Syphilitic. Found in patients with syphilis. The bones of the jaw and skull are affected. Pain is the main symptom. It intensifies at night. If fistulas form and break through, your health temporarily improves.
To understand how to treat pathology, it is important to determine what caused the abnormal process. That is why, before starting therapy, the dentist collects anamnesis and conducts diagnostics.