In what cases are barrier and protective membranes applied?
Membrane linings perform several functions:
- Protective - protect the operated area from external factors.
- The role of the reinforcing material is to fix the osteoplastic material in a suitable position.
Applicable:
- when strengthening mobile units;
- to protect bone from atrophy after tooth extraction;
- when it is necessary to fix granules of osteoplastic material during osteoplasty before or during implantation;
- when building up the jaw bone with blocks.
The decision to use barrier membranes is made by the dentist after a preliminary examination.
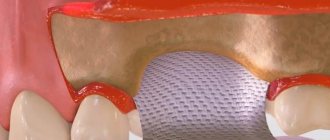
To increase bone
An osteoplastic material is fixed under the gum, on top of which a protective pad is placed. It protects the bed and its contents from growing soft tissues. Eliminates washing out of the bone graft from the wound through the suture line. More reliable treatment results are provided by the use of a bone substitute along with two types of membranes. One of them covers the defect and osteoplastic material, and a collagen plate is placed on top of it.
Gum extension (augmentation) during gum recession
Deficiency of soft tissues as a result of atrophy is characteristic of patients with long-term absence of teeth. Significant bone loss in such cases is accompanied by a proportional decrease in gum volume, which causes significant discomfort. Augmentation is more expensive and more difficult to install an implant. Gum augmentation can be performed with non-resorbable membranes, usually based on a non-porous material and resorbable, with a high rate of tissue compatibility. The method promotes rapid healing, reduces the risk of relapse and soft tissue swelling.
Indications and contraindications
The collagen membrane is used for delayed or immediate cell regeneration in the following cases:
– for defects of bone walls caused by incorrect activities of the surgeon;
– to maintain a stable state of the mucous sinuses;
– with resorption of the jaw ridge;
– to eliminate periodontal pathologies;
– with atypical manifestations of alveolar bone loss;
– after removing the apex of the tooth root;
– when removing affected bone tissue;
– after tooth extraction.
Collagen membrane is not used in the presence of the following diseases:
– acute infectious processes in the oral cavity;
– in the presence of general contraindications;
– in case of intolerance to the components of the substance.
Types of biomaterials used
The method of directed tissue regeneration in surgical dentistry is based on the use of two main groups of membranes: resorbable (collagen, vicryl, polylactic acid, etc.) and non-resorbable (Gore-tex or titanium mesh, with titanium reinforcement, Teflon and others).
Resorbable
Installation of absorbable membranes prevents their removal after the osteoplastic material has engrafted. Such linings do not always remain stable over a long period. To enhance the prolonged action, their composition is supplemented with slowly resorbing substances. One of the main advantages of membrane linings is the possibility of enriching their structure with drugs that enhance osteogenesis, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial agents, etc.
Types of resorbable membranes:
- Synthetic polymers (polyactides, polyglycolides) and their chemical modifications (for example, Guidor, EpiGuide, Vicryl) - decomposition into microscopic fragments that undergo phagocytosis occurs under the influence of hydrolysis. Among the disadvantages of the products, weak tissue integration and a high likelihood of developing swelling during resorption due to changes in pH in the tissues are noted. Advantages of polymer plates:
- no risk of transmitting an infectious disease;
- hypoallergenic;
- long-term effect (5-6 months).
Non-resorbable
They contribute to the effective restoration of bone in a given volume and trajectory, there are:
- Frameless - for restoration of bone tissue less than 4 mm.
- With a titanium frame - for bone restoration in large volumes, in all directions.
Main advantages:
- high mechanical strength;
- pronounced barrier properties.
These types of pads should be removed after 6-9 months . Consisting of titanium, they are effective in situations where there is a large load on the bone and it is necessary to protect implants or osteoplastic material. The most common indication for use is vertical ridge augmentation. They are removed after restoration of soft and bone tissues damaged during the operation.
Main disadvantages:
- risk of exposure - during suturing of the flap, the insert must be completely closed;
- absence of the process of periosteum formation under the overlay;
- the patient needs to visit the dentist frequently (every 2 weeks).
Statistics show that the most effective membranes are polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) GoreTex and aliphatic polyetherurethane (Bone-up). Less commonly used are mesh forms made of calcium sulfate (Capset) or titanium (Frios, BoneShield, Tiomesh).
Materials for osteoplasty
Bone tissue is not capable of growing in volume on its own, so bone replacement materials, grafts and growth stimulants are used to generate this process. All of them are divided into several types:
- alloplastic - synthetic substances that serve as a framework for the formation of new bone tissue;
- autogenous - donor materials taken from the patient himself;
- allogeneic - similar to autogenous, but taken from donors. They are not used often due to the existing risk of rejection;
- xenogeneic – replacement materials without a protein component. Biocompatible, do not provoke an allergic response in the body. They are most often used in dental practice.
PFR membranes are used as a means of improving the engraftment of bone material. This means that the top layer during the operation is a platelet mass formed from the patient’s own blood. This stimulates active cell growth and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Fixing elements of different types
The membrane is adjusted to the size of the defect, or the required dimensions are transferred to it using sterile templates in the package. The edges should overlap the boundaries of the bone defect by at least 2-3 mm . Fixation can occur in one of several ways:
- Before installation, the resorbable pad is pierced and placed on the implant using the rubber dam principle. The edges are secured with screws or pins into the bone, in which holes are previously created with burs. Additionally secured with sutures to the periosteum. When used on the upper jaw, titanium pins with a wide head are used for fastening.
- The self-curing mixture or film with an adhesive composition is fixed directly to the alveolar process.
- Non-resorbable plates are fixed with titanium pins or microscrews. The edges of the barrier must be tightly adjacent to the bone to prevent soft tissue ingrowth. When suturing the mucosa, small diameter suture material is used. The thread should pass along the edge of the membrane in contact with the neck of the implant. The stitching is done in the middle of the overlay between the edge stitches.
Opinion of a dentist-implantologist : “The success of implantation depends on how accurately patients follow medical recommendations. The operated area should be protected from hard, hot foods. Hygiene must be regular. Medications are taken only in consultation with a doctor.”
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
Properties
The ability of collagen membranes to be completely absorbed is used to create a barrier that prevents epithelial particles from entering the organ cavity. Thus, collagen creates conditions for independent regeneration of bone tissue in the sinus lift area. In this case, soft particles almost do not participate in the recovery processes.
The membrane, in contact with a humid environment, loses color and becomes translucent. The dense fiber layer prevents the penetration of connective tissue cells from the gums and promotes the proliferation of bone cells.
Pork collagen is characterized by low antigenicity and tensile strength.
How membranes take root during dental implantation
Collagen membrane overlays reduce the risk of complications due to loss of soft tissue. Non-stitched - due to the healing of soft tissues by secondary intention, the wounds are protected from the general inflammatory process. Both types integrate well into the jaw tissue. The bone under the surface of the barrier plate is regenerated in a manner similar to fetal bone growth.
When using absorbable overlays, the postoperative wound heals without the use of additional medications. Often the healing process of non-resorbable membranes is accompanied by complications, in particular, exposure of the structure. This can lead to infection and inflammation, which means it will have to be removed prematurely.
Often, under the barriers a favorable background is created for the development of microbes, so it is not always possible to achieve the desired result.
Types of dental membranes
Types of dental membranes are divided into two groups - resorbable and non-resorbable.
Non-resorbable membranes must be removed at the end of treatment, as they do not resorb. And repeated surgical intervention, which is obvious, always means repeated trauma and, as a consequence, an increased period of tissue restoration until complete healing, the risk of possible complications and inflammatory reactions, increased time and cost of dental treatment.
Resorbable membranes do not need to be removed. They completely dissolve. Accordingly, the risk of tissue trauma and treatment time are significantly reduced, the regeneration process is accelerated, and therefore the overall recovery time for the patient and the cost of dental treatment.
Membrane exposure after bone grafting - consequences and treatment
The non-resorbable membrane pad is exposed in 1% of cases , causing the following consequences:
- wound infection with the development of purulent inflammation;
- rejection of osteoplastic material during vascularization of the mucous membrane (in 40-50% of cases).
In such situations, it is recommended to remove the implanted materials, carry out treatment, and then repeat bone grafting. Typically, a second layer of soft tissue is formed under the incision using a mucoperiosteal flap. To do this, it is peeled off, split, modeled, and then sutured in layers.
The exposed resorbable pad should be treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide and 0.12% chlorhexidine. Sometimes this allows you to postpone the removal procedure by 8 weeks.
Opinion of a dental surgeon : “Most of my patients are smokers. Many people do not immediately realize the complexity of the situation caused by their bad habit. Smoking causes a sharp narrowing of the blood vessels in the mouth. This weakens the flow of blood filled with oxygen and nutrients. Due to their lack, the healing process is delayed. Therefore, you need to completely stop smoking at least a couple of weeks before implantation and for several months after it.”
General overview
From a technical point of view, Bio Gide belongs to the category of resorbable materials and is a two-layer membrane, the use of which makes it possible to implement a protocol for directed regeneration of periodontal tissue and bone structure. Practical studies have shown that the material used is completely biologically compatible, eliminating the development of an allergic reaction or rejection during use, and is also an effective solution to the problem of restoring the natural state of the oral cavity after surgery.
The functional properties of the membrane provide the ability to predict and control the rate of tissue regeneration at all stages of the protocol, stabilizing and protecting the structure from negative external factors. Upon achieving the intended result, the removal mechanism is activated - the membrane remains in the structure for 4-6 months, undergoing gradual enzymatic resorption. The measured resorption process eliminates the formation of local areas of irritation on the surface of mucous tissues.
Bio Gide is fastened using pins (small pins) or, depending on the clinical indications and the dimensions of the product, a suture tie. Collagen fibers, forming a special structure, gradually increase in size, which makes it possible to create a full-fledged base covering the flap area and stimulating tissue adaptation.