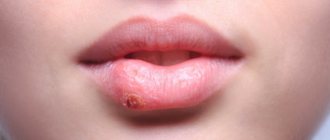
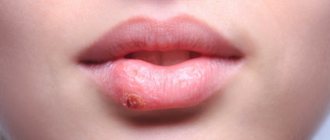
Angulitis – sticking in the corners of a child’s mouth – occurs as a result of disturbances in certain processes in the body or the influence of external factors. It is imperative to combat this phenomenon, since open wounds are an additional source of infection and inconvenience for the child.
Symptoms and treatment of lip jams in adults and children
The popular name for angulite is zaeda.
The disease is characterized by the presence of cracks in the corners of the mouth, erosion and irritation. In some cases, slight bleeding may occur. Common causes of sticking at the corners of the mouth include infection, irritation, and damage to the skin at the corners of the lips. Angulitis is rare in children. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in adults. Predisposing factors:
- decreased general immunity;
- deficiency of B vitamins;
- the presence of a bacterial infection;
- habit of licking lips, malocclusion;
- hypothermia;
- long-term use of corticosteroid drugs;
- eating unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- presence of caries;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, HIV, liver disease).
Your pediatrician will tell you at your appointment what causes seizures in babies.
How to care for children's skin with jams?
Regardless of the cause of the appearance of seizing, skin care is based on the same principles.
Avoid flare-up triggers.
Try to protect your child from anything that could cause seizures. These could be certain products, hygiene products or decorative cosmetics.
Wash your baby in warm (not hot) water for no longer than 10 minutes.
Hot water evaporates moisture from the skin and makes it dry and defenseless. Therefore, dermatologists advise children and adults to wash themselves in warm water for no longer than 5-10 minutes to protect the skin’s protective barrier from drying out.
Opt for gentle cleansers.
Pay attention to drugstore brands for baby skin care and the labels “for sensitive/atopic skin.” These products usually do not contain harsh cleansers and do not cause irritation or redness.
Moisturize your baby's skin regularly.
Caring for any skin is based on hydration, and if it is dry and prone to inflammation, then this stage should not be skipped under any circumstances. Apply moisturizer to your baby's skin after each wash, and cover your hands and lips several times a day to prevent dryness.
To prevent seizures and relieve discomfort when they occur, smear your child’s lips with Morozko® hygiene lipstick - it was developed specifically for children’s skin.
It protects the skin from the elements and prevents dryness, cracking and seizing. The lipstick contains a complex of healing oils, vitamins A and E, as well as chamomile extract. Together they soften and restore dry lips. Apply lipstick to children's lips before and during a walk.
Types of angulite
Considering the etiology, seizures can be primary and secondary. In turn, the primary ones are divided into: streptococcal, viral and candidiasis.
Viral seizures. They are caused by a viral infection (herpes virus). In this case, a doctor will help you choose an ointment for sticking in the corners of an adult’s lips.
Streptococcal seizures are caused by streptococcal infection. A characteristic manifestation is the formation of a yellowish-red crust.
Candidiasis angulitis. The cause is a fungal infection. This type is characterized by a chronic course and the absence of a crust.
Thrush as a cause of white plaque
Thrush in the mouth of newborns appears in 15% of children under one year of age. The causative agent of the disease is the Candida fungus. It enters the child’s body from the outside or during childbirth/breastfeeding (provided that the fungus is in the body of a nursing woman), actively affecting the oral mucosa.
Causes of thrush in newborns
Candidiasis is more common in premature babies
Candidiasis will not occur without a fungus - that’s for sure. And the factors due to which the disease will receive an impetus for development are varied.
- Anatomical features of the structure of mucous membranes in newborns. The protective function of the oral mucosa in babies is just developing, so the ability to repel germs is imperfect. In the first months after birth, children have low salivation, and the amount of antifungal components in saliva is extremely small.
- Any damage to the inner shell greatly increases the risk of catching a fungal infection.
- Immunodeficiency in the body. A lack of immune cells and insufficient activity of all other defense mechanisms is observed in all babies at the beginning of life. But the period when the immune system is weakened is the optimal time for the development of diseases, including candidiasis.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora. For the first time after birth, healthy microflora in the intestines is at the formation stage. An imbalance of microflora and further thrush can cause intestinal infections.
- Candidiasis can develop after taking antibacterial agents. The intestinal microbial community is not able to recover after therapy, which means Candida fungi can become more active.
- Prematurity. The risk of candidiasis is greatest in premature babies - due to the fact that they are less resistant to all of the above factors.
There are 3 forms of candidiasis in a child:
- Easy. White grains with the consistency of cottage cheese form in the mouth. Typical location: tongue, cheek area. The condition does not cause concern for the baby.
- Moderate weight. A coating of cheesy consistency partially affects the oral cavity. Redness of the mucous membrane is observed, attempts to remove plaque are accompanied by bruising.
- Heavy. High-density plaque covers almost the entire oral cavity and cannot be removed. The baby cries and may refuse to feed.
It is necessary to visit a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease to prevent its development. In the initial stages, thrush responds well to treatment.
How to treat thrush
Therapy for thrush includes the use of local (ointments, suppositories, creams) and general (tablets, injections) agents.
Medicines are chosen exclusively by a pediatrician - drugs that are effective for treating an adult can negatively affect a child due to the risk of adverse reactions.
Of the entire list of drugs against candidiasis, only 2 are used to treat young children:
- Fluconazole;
- Nystatin.
The dosage will be chosen by a specialist taking into account the baby’s weight and the severity of the disease. Timely treatment starts guarantees a quick recovery.
Angulitis during pregnancy: how to get rid of it
Pregnant women are very vulnerable to various infections. Risk factors in this case are vitamin deficiency and increased stress on the body.
Causes of angulitis during pregnancy:
- licking lips in the cold;
- allergic reactions;
- caries;
- dry lips;
- general decrease in immunity.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information on this issue. Here you can make an appointment with a doctor, who will tell you how to get rid of the jam and which ointment is best to use in your case.
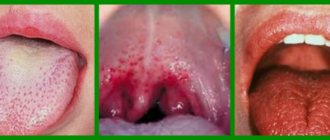
Causes of white plaque in a child
Young mothers panic when they see a white coating on their baby’s tongue. First of all, this is due to ignorance of the causes of the condition, which are divided into natural and dangerous to health.
When there is no reason to worry
Babies may experience a white coating after feeding
Babies who are breastfed may develop a white coating in their mouth after feeding. This is normal.
The same situation is observed in babies who are fed artificial formulas.
In both cases, the plaque disappears 10–15 minutes after finishing the meal. The oral cavity again acquires a healthy pink tint.
Such plaque on the tongue, inner surface of the cheeks and palate also forms after regurgitation. It is lumps of undigested milk and looks like cottage cheese.
Important! Plaque can be easily removed. To do this, wrap a clean finger in a bandage and rub it over the surface covered with the white formation.
When to see a doctor
When white plaque is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, you need to consult a doctor.
You need to visit a pediatrician in the following cases:
- the baby refuses to eat, is capricious, sleeps restlessly;
- there are diaper rashes on the body;
- there is an increase in body temperature;
- there is a lot of plaque in the oral cavity, it is difficult, but still not completely, to be removed;
- white mass appears regularly;
- plaque forms on the genitals.
The reasons for this lie in diseases.
Diseases of infectious and dental origin
Such diseases include:
Angulitis: clinical manifestations
The symptoms of angulitis are very similar to the manifestations of herpes, so it is extremely important to promptly contact a specialist who will make the correct diagnosis and tell you how to quickly cure angulitis.
Symptoms of seizure:
- redness in the corners of the mouth;
- cracks;
- multiple blisters with purulent contents;
- slight bleeding (not always);
- purulent crusts.
Treatment of lip jams in adults depends on the etiology and form (acute or chronic). It is very important to start treatment on time, because without it, the affected area can increase, causing significant discomfort to the patient.
When should parents take their child to the doctor for seizures?
There are clear criteria by which atopic dermatitis can be suspected. First of all, the child should be bothered by itching and flaking of the skin over the past 12 months, plus at least 3 signs from the list below:
- age - signs of atopy usually appear before the age of 2 years, a little less often - up to 4 years and in adolescence;
- noticeable redness of the skin in its folds - for example, on the inside of the elbows, outside of the knees, on the cheeks or the front of the legs;
- constant irritation - itching, peeling - in the areas indicated above;
- constant dry skin;
- the child has close relatives with asthma - these could be parents, brothers or sisters.
If you have counted all the signs in your child, then he probably has atopic dermatitis. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact your local pediatrician. Usually, examination of the child’s skin is sufficient, but the doctor may also prescribe additional examinations.
These are usually allergy tests to check if there is something triggering the flare-up. To do this, they perform a prick test - in which a tiny amount of allergen is applied pointwise to the skin and the reaction is monitored. The appearance of redness and irritation is a signal that there is an allergy to the substance.
Diagnosis of the disease
Unfortunately, patients with angulitis very rarely turn to a specialist for help, but in vain. After all, the acute form of the disease is easier to cure, thereby preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Required research:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood sugar test;
- biochemical analysis and liver tests;
- ELISA blood test for herpes viruses;
- blood test for syphilis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Consultation with highly specialized specialists may also be required.
Treatment of streptoderma
Even if the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, a dermatologist should prescribe treatment for streptoderma in children.
A specialist in this profile is aware of narrow-spectrum drugs that will help to quickly cope with the disease. The first step is to transfer the child to a therapeutic diet with restrictions on sweets, fatty and salty foods. The course of therapy involves avoiding bathing: water procedures contribute to the spread of the disease. It is recommended to wash healthy areas with chamomile decoction, and never touch inflamed areas.
It is important to choose the right clothes for a sick child. Synthetic and wool items should be excluded from your wardrobe. These tissues cause discomfort and contribute to the spread of the disease.
Doctors recommend opening the blisters that form on the skin with a sterile needle, then treating the opening erosions with brilliant green 2 times a day. Areas of skin not infected with bacteria are wiped with a boron solution. Weeping erosions are lubricated with silver nitrate or resorcinol.
If crusts form on the skin, they are treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In severe cases, a number of other oral medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series;
- anti-allergy medications;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes;
- antipyretic drugs.
The list of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. Only a specialist knows how to treat streptoderma in children correctly. Self-medication can provoke the pathology to become chronic. With an adequate course of therapy, the symptoms disappear after 7 days, but after curing the deep form of the pathology, scars remain on the skin. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible.
Treatment of lip jams in adults
After examining the patient and studying the test results, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, usually consisting of medications (local or general action) and vitamin-mineral complexes. It is extremely important to give up bad habits and avoid irritating factors during treatment.
If there is an infection, the patient will be prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy (taking into account the type of pathogen). For a viral infection, antiviral drugs are recommended, and for candidiasis angulitis, antimycotic drugs, such as nystatin and lamicon. Trimistin and tetracycline are prescribed for mixed forms of the disease. All this applies to the treatment of the disease in adults. Your pediatrician will tell you how to treat jams in the corners of the mouth in children. After examining the baby, the pediatrician will prescribe drug therapy and suggest the most effective traditional medicine.
General information
Streptoderma is a disease caused by streptococci.
Damage to the skin is characterized by the appearance of a rash. Blisters and ulcers form on the surface of the skin, which itch and cause discomfort. Streptoderma in children can be acute or chronic. The first is characterized by an aggressive course with severe symptoms. Chronic is characterized by periodic exacerbations and periods of subsidence of the inflammatory process.
Based on the depth of the lesion, streptoderma is divided into superficial, deep and intertriginous (the rash develops in the skin folds). Each of the forms has its own characteristics.