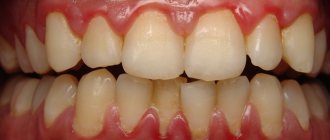
Bad breath and bleeding gums are considered common symptoms among potential dental patients. The unpleasant sensations accompanying the patient disturb not only him, but also those around him, because the smell from the mouth when the soft periodontal tissues are bleeding cannot be removed for a long time.
The cause of regular bleeding in the mouth and severe odor can be several diseases, and not all of them are directly related to dentistry. In this material we will consider in detail the symptoms of diseases and methods of treating these ailments.
note
- Privacy Policy
What is bleeding gums?
If, when brushing your teeth, the paste on the brush becomes pinkish, this may indicate bleeding gums. According to the frequency of manifestation, it can be situational or chronic. In the first case, blood on the mucous membrane appears as a result of mechanical damage and usually does not cause alarm. If the gums bleed regularly, there is a high probability of infection and inflammation of the soft tissue.
Statistics show that almost all people aged 30 years and older experience inflammatory processes in the periodontal area. The reason lies in the imbalance of microorganisms, which occurs against the background of poor ecology, poor hygiene, poor nutrition and bad habits. Under the influence of external factors, the immune defense of the mucous membrane deteriorates, which contributes to the development of dental diseases.
If a person experiences bleeding when brushing his teeth, doctors recommend not leaving the pathology unattended. The problem is not only often accompanied by discomfort and bad breath, but if left untreated, it leads to many complications, including tooth loss.
Children's gums bleed
Young children enjoy brushing their teeth the least. If parents do not control the quality of oral hygiene, gingivitis occurs. In this case, the main symptom of the disease is bleeding gums.
The physiological cause of this condition in children is the process of teething. In this case, the integrity of the gum is compromised and it can bleed.
Problems with the gums are also caused by an incorrect bite. In this case, soft tissues are injured by teeth that are incorrectly positioned relative to each other.
Wearing orthodontic appliances can damage the integrity of the gums. This especially happens when wearing braces with uneven edges. To prevent injury, locks must be treated with special wax. But children often forget to do this; as a result, braces damage soft tissues, causing bleeding.
“Disease of dirty hands” - stomatitis, also more often affects children. They take less care of hygiene, which provokes the appearance of characteristic ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Some parents believe that children do not need to treat their baby teeth, because they will still be replaced by molars. This opinion is erroneous, because caries is caused by bacteria, and their constant presence in the mouth leads to periodontitis. The disease is characterized not only by bleeding gums, but also by the appearance of bumps with pus. This condition requires immediate medical intervention, otherwise serious complications arise.
Main symptoms
The main sign of pathology is the appearance of blood while eating or brushing teeth. When gums become inflamed, they become more vulnerable to injury, their capillaries become highly permeable, and the tissue becomes thinner, so bleeding occurs much more easily. Additional symptoms depend on the specific disease. Most often, bleeding is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unpleasant odor;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of a metallic taste;
- redness of the gums, formation of white plaque;
- exposure of the neck of the tooth;
- discomfort when brushing teeth or pressing on the gums;
- uneven height of the gingival margin.
If these signs appear, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor. It is much easier to treat bleeding gums at an early stage than in an advanced form.
How to say goodbye to bad breath?
The problem can be eliminated only after its cause is determined. If the problem is diseases of the teeth and gums, it is necessary to cure all inflammatory and necrotic processes, put fillings, and, if necessary, replace dentures. Sometimes patients experience an unpleasant odor after tooth extraction: such a symptom may indicate the onset of complications, so it is better to see a dentist as quickly as possible. Periodontitis and periodontal disease give off a particularly strong putrid odor. The doctor will remove the deposits with ultrasound and prescribe therapy.
Since tonsillitis, bronchitis, sinusitis and other ENT diseases are a common cause of unpleasant odor in children, a treatment strategy should be chosen with an otolaryngologist. Komarovsky also recommends correcting mouth breathing - the cause of dryness and halitosis.
Reasons for appearance
First of all, the doctor makes a diagnosis and finds out the reasons that led to the bleeding. Let's look at what diseases can cause blood on the gums.
Gingivitis
With gingivitis, inflammation of the gum mucosa develops. The cause of the disease is the accumulation of soft plaque near the gingival margin, which is associated with poor hygiene. Bacteria contribute to the development of the inflammatory process and the appearance of bleeding, which increases when brushing your teeth. Blood on the mucous membrane may be accompanied by symptoms:
- redness or bluishness of soft tissues;
- swelling;
- swelling of the gingival papillae;
- itching, pain.
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it can transform into a destructive form of periodontal pathology – periodontitis.
Periodontitis
With this disease, periodontal tissue becomes inflamed. During the course of the disease, the structure of the alveolar part of the jaw is destroyed, which threatens the loss of teeth. Initially, the disease manifests itself by bleeding, the formation of plaque and viscous saliva. Over time, teeth become mobile and begin to loosen. In the acute form of periodontitis, the patient complains of pain and purulent discharge from the periodontal pockets. Sometimes fistulas may form and submandibular lymph nodes may enlarge.
Stomatitis
With stomatitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs, caused by the body's reaction to allergens and irritants. The disease can also develop due to poor hygiene and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. A person’s mucous membranes become swollen, hyperemic, and covered with a yellow or white coating. A common symptom of the disease is bleeding gums, which is accompanied by increased salivation and an unpleasant odor.
Tartar
Tartar is hardened particles of food and soft plaque resulting from the activity of bacteria. When it forms, the gums are injured, which contributes to the appearance of blood. Stones can be supragingival or subgingival. Any of these types can cause pathology and lead to the development of more serious diseases.
Avitaminosis
In some cases, bleeding indicates that the body lacks minerals and vitamins. Typically, the appearance of blood on the gums is associated with a deficiency of the following elements:
- Tocopherol – when there is a lack of it, excessive lipid oxidation occurs, which contributes to cell damage and the development of inflammation. Periodontal dystrophy may indicate a lack of vitamin E.
- Ascorbic acid – vitamin C deficiency leads to deterioration of vascular permeability and decreased elasticity of vascular walls. The gums become loose and prone to inflammation.
- Phylloquinone - its main task is to improve the processes of prothrombin synthesis. With vitamin K deficiency, blood may appear both after an injury and spontaneously.
Blood diseases
Mucous membranes may bleed due to pathologies of the hematopoietic system, such as coagulopathy or anemia. Against the background of a low platelet level, bleeding occurs both immediately after mechanical damage to the gums, and for no apparent reason. Many people are afraid to visit the dentist and get rid of symptomatic manifestations by regular teeth cleaning. As a result, bacteria begin to multiply more intensively, which entails additional problems - the development of caries or periodontitis.
Diabetes
It has long been noted that bleeding from the gums is a common phenomenon in people with diabetes. Against the background of the disease, there is a deficiency of saliva, a bacterial imbalance in the oral cavity, and a deterioration of immunity, which together leads to the appearance of blood on the gums and the development of periodontitis.
Sometimes the causes of pathology are more banal. So, it can be caused by an incorrectly selected toothbrush with too hard bristles. In pregnant women, the appearance of blood on the mucous membrane is associated with changes in the body and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy.
We know how to treat bleeding gums
Mistakes in self-medication
When trying to get rid of bleeding gums on their own, patients make a number of mistakes. Never worth it:
- start taking antibiotics without a prescription - they may not be needed, but the blow to the body will be dealt;
- Stop brushing your teeth - this will only lead to a worsening of the condition;
- getting too carried away with oral hygiene - this will not save you from complications and will not cure, but will only aggravate the situation due to systematic injury to soft tissues;
- be afraid to go to the dentist - modern treatment methods are painless and do not cause discomfort, unlike purulent complications.
Lack of timely and competent treatment of bleeding gums leads to the spread of inflammation to bone formations. As a result, teeth become loose and fall out, requiring implants to be inserted. This is much more expensive than contacting a specialist in time to solve a gum problem.
You should not let the disease progress and self-medicate; come to the Matisse Dent clinic and receive competent medical care.
How and with what to treat pathology?
If you have an oral problem, you should contact your dentist. Before prescribing treatment, the doctor will conduct an examination and understand the causes of bleeding. Diagnosis may include laboratory tests or instrumental examinations. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to specialists.
Treatment of pathology is carried out in a complex and depends on the specific disease. For tartar, gingivitis or periodontitis, teeth are ultrasonic cleaned and gum ointments and medicated toothpastes are prescribed. If the disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Vitamin deficiency is treated with vitamin complexes based on the results of a laboratory examination. If there is a lack of vitamins associated with impaired absorption in the intestines, oral administration may not give the desired effect, so problems with the gastrointestinal tract are first eliminated. If the gums bleed due to leukemia and other pathologies of the circulatory system, medications are prescribed that prevent platelet aggregation.
How can you tell if your breath smells?
Determining the freshness of your own breath is not at all easy. We adapt to the aromas that we smell all the time and stop noticing them. In addition, the oral cavity and nasopharynx are a single system, and this makes testing difficult. But there are several simple and visual ways to understand if there is a bad smell.
- Lick your wrist with the tip of your tongue and wait 15-20 seconds until the saliva dries. The scent left on the skin will give you some idea of the freshness of your breath. However, the tip of the tongue collects the smallest amount of bacteria, so the results will not be completely true.
- The main breeding ground for microflora that causes an unpleasant odor is located at the root of the tongue. Run your finger or a cotton swab in the area and smell: if the “sample” smells strong, there is a high chance that your breath may be spoiled too.
- Take a plastic cup, place it on your lips and release the air through your mouth. The smell inside the container will help determine if you are suffering from halitosis.
- Ask a loved one if he notices a specific “smell” when he communicates with you. Sometimes this is the most reliable way to find out the answer to a sensitive question.
Medicines
The choice of medications is determined based on the type and stage of the disease. Miramistin, chlorhexidine, furatsilin can be used for rinsing the mouth. In the presence of inflammation, you can use ointments that have anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effects. Infections are treated with the following:
- antibiotics;
- antiseptic drugs;
- antifungal agents;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins.
Home treatments can be used as aids. Good results are shown by rinsing with herbal infusions of calendula, chamomile, and yarrow. To eliminate pain and strengthen soft tissues, use propolis tincture or a solution of soda and sea salt.
Diagnosis of gingivitis
It is always important to collect a complete history of the disease, because gingivitis is often a chronic disease that occurs in childhood.6
It is also worth paying attention to the general condition of the body; the dentist may refer you to other specialists.
Consultation with an endocrinologist – in diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands), gum inflammation is more active.
Consultation with a hematologist – in case of blood diseases, gum inflammation is only a symptom of the underlying disease. Consultation with a hematologist is required for differential diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist – gingivitis is usually accompanied by chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Related doctors, in turn, prescribe a number of other tests to treat pathology, for example, a general blood test, biochemical blood test, gastroscopy, ultrasound, etc.
The dental office conducts diagnostic tests such as:
- Probing is a diagnostic method in which the characteristics of the attachment of the gums to the teeth are determined.
- Staining the gums with iodine-containing solutions: this shows whether the gums are inflamed. With gingivitis, the gums turn shades of brown.
- Determining the level of hygiene, that is, how well a person brushes his teeth.
- Panoramic X-ray of the teeth: This is necessary to see whether the inflammation has affected the bone or not, and also shows the condition of all teeth, fillings and crowns.
Prevention
An important condition for preventing gum bleeding is regular prevention. To avoid pathology, it is advisable to adhere to the following recommendations:
- To eliminate oral dysbacteriosis, special hygiene products should be used, such as brushes, dental floss, and therapeutic and prophylactic pastes.
- If you have bleeding gums, your toothbrush should have soft bristles. It should be selected together with the dentist.
- An important condition is regular hygiene. Teeth should be brushed at least twice a day, spending at least 2 minutes on the procedure.
- After each meal you should rinse your mouth with plain water.
- To slow down the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the mouth, it is recommended to improve nutrition and reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed in the diet.
- Do not forget about minerals and vitamins, which can be obtained both with food and as part of vitamin complexes.
- It is advisable to avoid those products that can injure the mucous membrane (crackers, caramel, seeds, etc.).
You should visit the dentist twice a year. Even if a person does not have visible problems with his teeth, a visit to the doctor is necessary for preventive cleaning, elimination of bacterial plaque and examination for hidden pathologies. With regular prevention and timely treatment of dental diseases, you can avoid bleeding gums and keep your teeth healthy for many years.
What do different types of smell mean?
Unpleasant odors are caused by several types of volatile compounds produced by anaerobic bacteria. They use food debris on the tongue, between teeth and in carious cavities as a nutrient medium. Depending on the predominant compound, the character of the odor changes. Some of them suggest the pathology that caused halitosis:
- sour aroma – stomach diseases, gastritis or ulcers;
- feces, rotten cabbage - oral pathology, caries;
- smell of urine - kidney failure;
- the smell of ammonia or rotting apples – diabetes;
- rot, rotten meat - esophageal diverticulum.
You can find additional symptoms that will accurately indicate the cause of halitosis. If you have stomach pathology, you will experience pain between snacks. Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by excessive urination, dry mouth and thirst. Caries may not appear for a long time, but in advanced forms toothache appears.
Given the variety of causes, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of halitosis can be performed by doctors of different specialties. You need to see a dentist to get rid of dental diseases, but in other cases you will need to consult an endocrinologist, therapist or nephrologist.