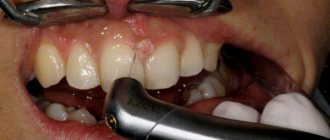
From this article you will learn:
- why do gums bleed during pregnancy,
- what is pregnancy gingivitis,
- how to carry out treatment correctly.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is a process characterized by bleeding gums, as well as hypertrophy of the gingival papillae, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This condition is usually called the term “gingivitis in pregnant women”, and according to statistics, it is observed in 75% of women - for a period of 2 to 8 months. Most often, gingivitis occurs in the area of the front teeth, and it affects only the gingival margin at the necks of the teeth (including the gingival papillae).
Clinical studies show that more than half of all women with gingivitis during pregnancy already had a mild form of chronic catarrhal gingivitis at the beginning of pregnancy, which is practically asymptomatic. Thus, an increase in the content of estrogen and progesterone in most cases led to an exacerbation of pre-existing gingivitis, and was not the root cause of its development. We will tell you more about the causes of inflammation below, because... there are other factors to consider.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis –
But pregnant women can experience not only gingivitis, but also a more serious gum disease, in which inflammation spreads from the superficial part of the gums to deeper tissues. This disease is called periodontitis, and with it there is destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, destruction of the dental-gingival attachment, suppuration from periodontal pockets, and over time, tooth mobility also occurs. And this disease already indirectly affects the fetus, which requires mandatory treatment.
Why does gingivitis occur during pregnancy?
Tens of millions of microorganisms live in the oral cavity. Slight swelling of the gums leads to an increase in periodontal pockets, which become an excellent reservoir for the life and reproduction of bacterial microflora. In addition, microorganisms do not lack nutrition, since pregnant women like to pamper themselves with sweets, and carbohydrate foods are the best substrate for the development of bacteria.
Swelling of the gums, leading to an increase in periodontal pockets, excessive salivation, an acidic environment in the mouth, an increased feeling of hunger - these features that accompany pregnancy are the main factors contributing to the rapid growth of oral microflora. And this, in turn, provokes inflammation of the gum tissue - gingivitis.
Different forms of gingivitis, features of manifestation in pregnant women
There are different forms of inflammation, they are characteristic of different trimesters of pregnancy:
- Catarrhal disease is characteristic of the first half of the period, manifested by bleeding, swelling of the marginal zone of the gums, painful symptoms during the cleansing process, as well as visually - a change in the color of the inflamed areas.
- Hypertrophic is less common, when mild manifestations of inflammation can worsen and lead to polypous growth of gingival tissue. The pathology is more pronounced in places where fillings adhere and crowns overhang, which have an additional traumatic effect.
Painful sensations can occur with any mechanical impact, when the gums are at rest. A “gentle” regimen to reduce gum trauma during pregnancy leads to an even greater accumulation of plaque, which only intensifies the visible manifestations of gingivitis.
Whims or symptoms of gingivitis during pregnancy?
The first symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women begin to appear between 8 and 12 weeks. Expectant mothers, as a rule, suffer from two forms - catarrhal and hypertrophic; ulcerative gingivitis develops less often.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease is manifested by the formation of a fairly large amount of soft yellow plaque on the surface of the teeth, swelling of the gums, their soreness and significant bleeding when pressed with a sharp object. Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by the spread of inflammation over the entire surface of the gums, sometimes the process affects the tissues of both the upper and lower jaws.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
The first symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis usually appear no earlier than the twentieth week of pregnancy. Inflammation affects the lower jaw, gums in the area of incisors, canines and small molars. The hypertrophic form of gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the volume of gum tissue, an inflammatory process in it and bleeding. Gum pockets also appear - grooves formed between the tooth and gum due to the growth of gum tissue.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most severe form of gingivitis occurs in pregnant women. It occurs against the background of serious health problems accompanying pregnancy, in the last trimester, or under the influence of stressful situations. The main signs of ulcerative gingivitis are severe itching, burning, bleeding of the gums, swelling and ulceration.
BLEEDING GUM DURING PREGNANCY: HOW TO TREAT AND WHAT TO DO
Every girl who experienced pregnancy remembers how unstable her emotional state was at that time. Often, the expectant mother reminds herself of the heroine of some soap opera, because she can burst into tears at the slightest reason. If in such a situation a girl notices that her gums are bleeding when brushing her teeth, there will be another reason for worry and a bad mood. Is bleeding gums dangerous during pregnancy? In this case, the fears will not be unfounded. By the way, bleeding gums during pregnancy, yes and in general, this is a signal that an inflammatory process is occurring in the oral cavity. If you do not pay attention to the fact that your gums bleed heavily, then gingivitis, which is common during pregnancy, will develop into a more serious disease - periodontitis. It develops if the infection affects the tissues surrounding the tooth and can even lead to its loss. Many expectant mothers put the baby's health first. They are afraid to solve this problem and are ready to endure the fact that their gums are bleeding; treatment, on the contrary, can be completely harmless for the child. But the development of an infectious process in the oral cavity can affect it negatively, because the child is very closely related to the mother. They bleed gums during pregnancy for a number of reasons: Firstly, hormonal changes in a woman’s body manifest themselves in this case. The gums become soft as their connective tissue weakens, which ultimately causes bleeding gums. The reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon also lie in the lack of vitamins and minerals, the need for which is increased many times over. Calcium deficiency can especially affect the health of teeth and cause bleeding gums; treatment is impossible without a sufficient supply of this important substance in the body. Calcium is extremely necessary in the second half of pregnancy, when the skeleton and foundation for the baby’s baby teeth begin to form. Gums are bleeding: how to treat and what to do. Pregnancy is almost always an exciting and difficult time for any woman. Therefore, you shouldn’t ruin your mood by wondering why your gums bleed or how to treat bleeding gums. It’s better to focus only on pleasant experiences and get ready to meet your baby! And the competent dentists of our center will carefully and professionally examine the oral cavity and select an absolutely safe remedy for bleeding gums for both the expectant mother and the child.
Safe treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women
The dentist is included in the list of mandatory specialists to visit during pregnancy. He will be able to detect the disease in time and prescribe safe treatment for gingivitis. The peculiarities of therapy for pregnant women are that measures aimed at eliminating gingivitis include only the removal of tartar and plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy and the prevention of re-development of inflammation, that is, therapeutic measures only imply relief of symptoms.
The first stage of treatment that the dentist will perform will be professional teeth cleaning. Dental plaque will be removed mechanically using Air Flow or ultrasound. The idea that ultrasound, which is used in this procedure, harms the fetus is absolutely groundless: throughout pregnancy, a woman undergoes scheduled ultrasound examinations at least three times. As an anti-inflammatory therapy, the doctor will select drugs that can act as gently as possible on the vulnerable body of a pregnant woman. Their use comes down to a local effect on the gum tissue: rinsing, baths, irrigation.
How can oral health affect a child?
Recent research shows that severe gum disease, accompanied by red, swollen or bleeding gums, can harm the health of an unborn baby.
Scientists have found that women with severe gum disease are 7 times more likely to have preterm birth before 32 weeks than women with healthy gums. Another study looked at women with gingivitis and more severe gum disease and found a threefold increase in the risk of giving birth before 37 weeks.
Current research into gum disease during pregnancy shows a risk of prematurity comparable to that of alcohol consumption and slightly higher than that of smoking. Premature babies may have a wider range of health problems immediately after birth than full-term babies.
Women with gingivitis may also have low birth weight babies during pregnancy. Studies have shown that if you have gingivitis during pregnancy, you are 3 times more likely to have a low birth weight baby. This estimate is comparable to the risk associated with smoking during this period.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Treatment of disorders associated with bleeding gums at any stage of pregnancy
The lack of proper treatment leads to complicated forms of inflammation:
- edematous, in which the soft tissues have a loose structure and polypous growths;
- fibrous, when enlarged areas of the gums - edges, papillae become dense.
The microflora in dental plaque releases toxins, which, after being absorbed into the blood, can negatively affect the contractility of the uterus, placenta and fetus. The degree of risk of pathologies and even premature birth is directly proportional to the severity of the inflammatory process.
Providing adequate treatment for gums during pregnancy is not easy, especially in the early trimester. It is recommended to carry out conservative treatment in a local form in the second half of the period, and only in a clinical setting. In severe cases of hypertrophic pathology, surgical correction of the marginal part of the gums may be necessary.
Treatment in dentistry
The order of therapy depends on the type and extent of the disease. For catarrhal inflammation, the following manipulations are performed:
- initial examination, office cleaning using gentle methods;
- selection of anti-inflammatory drugs, applications to relieve tissue inflammation;
- treatment of gingival papillae and margins using special preparations.
In the hypertrophic form, examination and treatment of tissue surfaces and a course of sclerosing injections are carried out. If the case is advanced and the therapy undertaken does not bring results, surgical removal of the affected tissue will be indicated.
The choice of treatment methods also depends on the stage of pregnancy; in the early stages, preference is given to gentle and preventive methods. Ultrasound methods are not used, like many medications. The optimal time to visit a doctor and start treatment is the second trimester. At this time, the use of applications and antibiotics is allowed. But only the dentist selects the treatment regimen and medications, based on the condition of the Patient and her condition.
Prevention
After completing the course of treatment, the Patient must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Using recommended brushes, toothpastes, and mouthwashes;
- giving up alcohol and smoking (for pregnant women this rule is general and necessary to preserve the baby’s health and its proper development);
- training the gums by including solid foods in the diet;
- good nutrition, avoiding excessive chewing of sweet gum (it provokes tissue inflammation);
- Instead of toothpicks, use special dental floss or irrigators.
Regular visits to the doctor are also necessary to prevent diseases and monitor the condition of the gums. During pregnancy, it is safer to prevent many problems than to begin complex treatment, fraught with many complications.
Price
Prices for eliminating gum pathologies depend on the following factors:
- oral health, compliance with care rules;
- causes of the disease, the presence of other diseases of the teeth and gums;
- selected treatment methods, drugs, diagnostic measures;
- the effectiveness of the measures taken, the frequency of doctor visits.
The dentist can name the exact cost only after an initial examination and diagnostics. The price is based on the chosen treatment methods, drugs and techniques, and the frequency of visits to the dentist.
About our clinic
Magenta Dental Clinic offers gum treatment for pregnant women in the offices of our network. We provide our patients with the following benefits:
- comprehensive services;
- use of modern diagnostic and treatment techniques;
- comfortable conditions and individual approach to everyone;
- guarantee of quality and effectiveness of treatment;
- affordable prices.
We are open daily from 09:00 to 21:00, to make an appointment please call, leave a request on the website or send a request by email
Therapy
| Service | price, rub. |
| Primary consultation and examination with a doctor | For free |
| Initial consultation with an implantologist, orthodontist, orthopedist (orthopantomogram is required) | For free |
| Repeated examination without prescribing treatment | For free |
| Examination by a doctor with prescription of medication | 500 |
| Help for antenatal clinics, hospitals, sanatoriums | 500 |
| TREATMENT OF CARIES | |
| Treatment of caries “without drilling” ICON technology – 1 tooth | 3000 |
| Treatment of caries (filling, anesthesia, lining) | 2700 — 4200 |
| Treatment of deep caries (filling, anesthesia, x-ray, lining) | 3800 — 5100 |
| Artistic tooth restoration (frontal group of teeth) | 4800 — 6700 |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth (filling, gasket, anesthesia, x-ray, pin) | 3600 — 4600 |
| NERVE REMOVAL – CANAL TREATMENT (depulpation) is carried out in two visits, payment in stages, includes x-rays, anesthesia, canal treatment, temporary filling | |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 1-canal tooth, without the cost of a filling | 4400 — 5500 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 2-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 6500 — 7600 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 3-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 8600 — 9700 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 4-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 10700 — 11800 |
| Installing a seal | 3200 — 3600 |
Consultation is free.
Postpartum period
This period includes the lactation period. During the period of feeding a child, a woman also loses a huge amount of minerals, such as calcium, fluorine, phosphorus and many others. And again, the main source for “washing out” them is teeth. After the baby is born, it is important to continue remineralization of dental tissues. During the year, a nursing mother must undergo at least 4 procedures. After completing feeding, the impregnation of dental tissues with microelements can be reduced to 2 times a year by combining remineralization with professional hygiene and a routine dental examination.
Pregnancy and childbirth are the most wonderful period in the life of every woman. Our goal is to make it easy for you and your teeth remain strong and healthy! We are ready to help you with this.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of gingivitis during pregnancy are hormonal changes, disturbances in the blood supply to tissues, and an increase in the acidity of saliva. All this causes the formation of positive conditions for pathogenic microflora and the appearance of areas of soft tissue damage. Other causes of gum inflammation include:
- toxicosis in the early stages;
- lack of minerals, vitamins;
- poor oral hygiene;
- disrupted diet;
- the diet is dominated by foods high in carbohydrates;
- metabolic disorders, weakened immunity.
Why do a pregnant woman's gums bleed?
Main reasons:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- lack of vitamins such as: A, B1, E and C;
- calcium deficiency;
- abuse of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates;
- poor quality oral care, as a result of which hard deposits form on the teeth;
- decreased immunity during gestation;
- nervous conditions, stress.
The exact reason why the periodontium began to bleed can be determined by the doctor after an examination and the history of the expectant mother.
What to do if your gums bleed during pregnancy?
First, rinse your mouth with infusions of medicinal herbs, which are allowed during pregnancy. For example, an infusion of walnut leaves, linden blossom, chamomile, and a decoction of the herb cinquefoil should be taken with caution. You can buy a ready-made Rotokan rinse solution at the pharmacy. In addition, rinse the mouth with a solution of chlorhexidine (0.05%).
Secondly, treatment and prevention of gum inflammation involves the use of Kalanchoe juice, which is rubbed into the gums. For these purposes, you can also use a mixture of honey and salt (1:4). It will not hurt to use ready-made dosage forms, for example, Metrogil-denta or Cholisal. Of course, before using any medicine, you should consult with your doctor about possible contraindications.
Thirdly, you shouldn’t hope that everything will go away on its own. This is wrong. Over time, minor gum problems can develop into much more serious problems if left untreated. If you experience persistent, prolonged pain or your gums are bleeding, you should immediately consult a doctor. In this case, you should inform him about your situation if it is not visually noticeable yet, because during pregnancy you cannot do x-rays, as well as some types of anesthesia.
You will also need to consult a doctor if your gums are swollen and red, or if plaque quickly appears when brushing your teeth regularly. If the doctor considers treatment necessary, then it would be more advisable to resort to it in the second trimester of pregnancy, when such measures will already be safer for the pregnant child.