Features of treatment
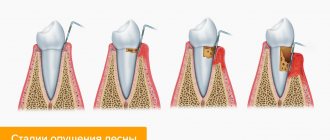
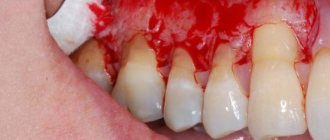
Gum recession is a consequence of impaired circulation of periodontal tissues that nourish bone tissue, resulting in bone atrophy and a decrease in gum level towards the root. The difficulty of treatment is that the loss of soft tissues has an extensive etiology and occurs under the influence of a number of factors:
- inflammatory process and accumulation of plaque and granulation tissue in periodontal pockets;
- improper brushing technique;
- errors in prosthetics;
- mechanical damage, chemical and thermal burns;
- malocclusions, poor-quality orthodontic treatment;
- elderly.
Only in the latter case does recession develop independently, that is, as a consequence of the aging of the body and the mucous membrane in particular. In other situations, the disease is provoked by very specific factors, so successful recovery from gum recession is possible only after identifying and stopping the underlying pathology. For example, in case of periodontitis, it is necessary to remove all dental plaque and carry out anti-inflammatory therapy. If the recession is associated with orthodontics, then it is necessary to correct the bite or replace an incorrectly installed brace system. The same applies to prosthetics: often it is low-quality or incorrectly manufactured dentures that contribute to injury and death of soft tissues.
Gum augmentation and plastic surgery
The gums play a very important role. The gum protects the neck of the teeth from harmful or traumatic factors, fixes the tooth itself, and gives the smile a beautiful shape.
Gum augmentation is a procedure during which its shape is changed in order to cover an exposed area of a tooth or correct it around an implant.
The shape of the gums can change after dental interventions, injuries, inflammatory processes (gingivitis, periodontitis) or due to congenital structural features of the jaw, its developmental anomalies, which can be corrected using gingivoplasty. Gum plastic can prevent or eliminate an aesthetic defect and give the gum the desired appearance.
When is gum surgery necessary: indications
- Gum plastic surgery when the root is exposed (recession). One of the most important and common indications for this intervention. Closing gum recession is necessary to prevent tooth decay, reduce its sensitivity, and reduce the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory complications;
- Correction of a gummy smile. Exposing mostly the gums, rather than the teeth, while smiling can be embarrassing for both those around you and the person himself. In such cases, gum plastic will do an excellent job of eliminating the defect, and additional production of veneers will be able to correct any non-standard situation;
- Gum augmentation with implantation or bone grafting. It is produced to cover the bone tissue being built up, fix the implant, and eliminate aesthetic defects.
All types of gingival margin reconstruction directly depend on the gum biotype. The thicker the gingival contour, the cheaper and simpler the treatment. If the gums are of the ultra-thin biotype, any surgical treatment will be a challenge for the patient and the doctor.
Methods for gum extension
There are two ways to perform gingivoplasty: using your own flap of the oral mucosa or using a special collagen matrix or barrier membranes.
Flap plastic flap of the mucous membrane. This technique uses only the patient's own tissue:
- An incorrectly located area of the gum is excised, unable to return to its original position;
- If there is a lack of tissue available at the excision site, a tissue flap is formed from adjacent areas of the mucosa (adjacent gum, palate, inner surface of the cheek);
- The flap or gum edges are sutured under tension in close contact with the tooth surface using surgical knots.
The use of a collagen matrix is somewhat different. The material is simply tightly sewn to the existing defect, which ensures the subsequent formation of its own tissues on the existing collagen mesh.
Gingivoplasty for a gummy smile
With this type of smile, several millimeters of gum, most often the upper one, are exposed. This gives the face an unusual expression when smiling.
Correction of a gummy smile is carried out by excision and modification of excess soft tissue. Thanks to this, the smile and gum contour are given an aesthetically correct shape.
Gingivectomy is also used for the eruption of wisdom teeth or after their removal, for excess gum tissue after installation of a dental implant, for bite correction, and tooth extraction.
Progress of the operation
Gingivoplasty is conventionally divided into several stages:
- Preparing for the intervention. The oral cavity is disinfected using antiseptics or other disinfection methods. If necessary, the surgical field is delimited from other areas of the mucous membrane;
- Anesthesia. Most often, local infiltration anesthesia is used using any modern painkillers or other anesthetics approved by an allergist;
- Tissue dissection. Necessary incisions and excision of excess soft tissue are made;
- Directly plastic. It is possible to directly stitch the incision after removing excess gum, form a flap, or use a collagen matrix with their fixation to the surrounding tissues;
- End of operation. The surgical wound is sutured with surgical sutures.
Postoperative recovery
After gum surgery, it is important to follow certain rules to prevent complications and promote the healing process. This process can take from 5 to 20 days, depending on the extent of the operation performed and the individual speed of regeneration.
- Until healing is complete, you must strictly adhere to the rules of oral hygiene: brush your teeth at least twice a day (do not touch the surgical site with a brush), use special solutions with antiseptics;
- In the first 7-10 days, you may need to constantly wear a special protective mouthguard;
- For the first 5-10 hours after surgery, smoking and eating are prohibited. You can drink after 2 - 3 hours; you can only drink soft boiled or mineral water without gas at room temperature or slightly warm;
- During the entire healing period, it is forbidden to eat hard, spicy, sweet foods. The ban also applies to hot and cold dishes;
- During the entire rehabilitation period, physical activity, flying, diving, off-road driving, sauna, bathhouse are prohibited.
The swelling should completely disappear within 3-5 days after gingivoplasty. If this does not happen or any complications develop (bleeding, enlargement of the operated gum, pain, fever), then you should immediately contact your doctor.
The article used materials from the site: https://doctorlevin.ru/
Indications for closing gum recession
Elimination of gum recession is necessary when the first visual signs appear, that is, when its free edge drops. In this situation, the only effective way is surgery. Conservative treatment of recession is carried out at the stage when the patient has not yet observed changes in the shape and position of the gingival margin. Analysis of symptoms and diagnostic procedures help identify predisposition to the disease. Increased sensitivity of teeth, inflammation, bleeding, an abundance of plaque and tartar - all these symptoms clearly hint at a pathological process, which sooner or later will lead to more serious complications. Another warning sign is the individual structure of the gums. A narrow and thin layer of attached gum (in simple terms, its base) and a wide root part of the tooth clearly indicate a high predisposition to the development of recession.
Gum augmentation: what is it?
There are many oral diseases: some of them are widespread, and some are much less common. The second example includes cases of gum recession (decay), which requires attention from the dentist. It is this problem that we will talk about in this article, and we will also get acquainted with methods for increasing and closing gum recession.
What is gum recession (loss)?
Sooner or later, a person may face the problem of exposed teeth, which occurs due to a decrease in the volume of gum tissue. It is this process that is called a recession, which is fraught with a potential threat, and quite a serious one. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that the person himself does not feel the development of the problem at all: recession is diagnosed through a visual examination by an experienced dentist.
Gum loss is a sluggish phenomenon that is not felt at all by the patient (except for a slight reaction to changes in food temperature and brushing teeth).
Among other things, some patients consider recession a natural phenomenon associated with age-related changes in the body, leaving this problem without due attention. This can be called a serious mistake fraught with a potential threat. So why does recession occur, and what are the reasons for gum loss? Let's name the main ones:
- Anatomy of the jaw structure;
- Periodontal diseases of various nature;
- Removal and loss of tooth(s);
- Untimely and poor-quality oral hygiene;
- Genetic characteristics (susceptibility to gum recession);
- The presence of bad habits in a person (for example, smoking and love of seeds).
The nature of the development of recession is atrophy of the gum tissue, as a result of which its volume begins to decrease.
Another possible option is the presence of inflammatory processes (mechanical and bacterial origin): the result is similar - the gum tissue decreases in volume, resulting in gum loss.
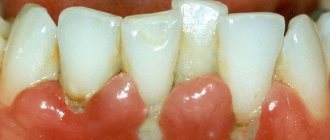
Symptoms of gum recession
And yet, there are certain symptoms of the development of the disease, knowing which, you can promptly identify the development of a recession. These signs include the following phenomena:
- General symptoms: exposure of tooth roots, reduction in the volume of soft tissues, manifestation of basal caries, increased sensitivity to cold and hot drinks (food);
- Symptoms of traumatic recession: reaction to temperature changes, tooth trauma, tissue reduction by no more than 3 millimeters;
- Symptomatic signs: the appearance of plaque, increased bleeding of the mucous membrane, loose teeth, discoloration of the gums.
If you have noticed the presence of one or more symptoms from the above list, you should immediately contact your dentist.
It is likely that this is not gum recession at all, but another disease, however, the need for treatment remains in any case, since any of these symptoms indicate the presence of a serious problem with the teeth and gums.
Gum extension in Kirov
Gum recession today is treatable, which consists of a augmentation procedure. In Kirov, a similar operation is performed in Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry, whose specialists have extensive experience in solving similar problems.
To fully understand the essence of the procedure, you should consider all possible techniques that are related to closing gum recessions.
First of all, it is necessary to consider the materials used for gum augmentation:
- Xenograft – using materials of animal origin. As a rule, this technique is practically not used today due to the long survival time of tissues;
- Allograft - in this case we are talking about donor tissue that is taken from another person. The difficulty of carrying out an extension operation lies in the need to find a donor;
- Autograft is the patient’s own gum tissue, which is taken from the outgrowths of the chin and lower jaw;
- Alloplast is the most common method based on the use of synthetic materials and compositions. A completely safe and, one might say, gentle method of gum augmentation in Kirov, which is chosen by most dentists, as well as the use of a lateral flap. The material retains the advantages of the methods described above, however, its use is not associated with the use of donor tissue or human tissue.
Surgical treatment of gum recession
So what treatments for gum recession exist today (given the variety of augmentation materials described above)? Let's look at five options related to surgical methods:
- Use of a lateral flap. We are talking about donor areas adjacent to the defect site (applicable only if there is a sufficient amount of materials). This flap is placed over the affected area, allowing the tissue to heal and closing the gum recession;
- Moving the gum flap to the recession site (also in case of sufficient tissue volume). Unlike the first method, the donor tissue is stretched while maintaining natural fixation to the source. That is, this is not an independent flap taken from another area, but an increased length of a fragment of the patient’s gum;
- Use of tissues from the hard palate. This is some kind of alternative to the first method, only in this case it is not the gum tissue that is used, but the palatal tissue;
- Combined techniques that combine the first three methodologies;
- Guided tissue regeneration. For this purpose, special membranes are used that are introduced into the affected area and promote the growth of natural tissue.
Any type of operation described above is performed using anesthesia, therefore, the patient does not experience pain during manipulation.
Disease prevention
To ensure that gum growth is not required (or is diagnosed at an early stage), we advise you to follow simple preventive recommendations:
- You should sign up for Prof. dental examinations every six months. This will prevent the presence of recession, as well as predict the occurrence of other diseases of the teeth and oral cavity;
- Caries should be treated in a timely manner, since the presence of root disease is one of the key reasons for the development of gum recession;
- Careful oral hygiene using suitable toothbrushes and toothpastes;
- You should avoid trauma to the gums, including the use of excessively hard brushes, which causes bleeding gums;
- The appearance of recession, which you noticed, will certainly lead to the scaling of the problem, since the loss of gum tissue itself does not stop. On the contrary, over time the volume of affected tissue will only increase.
Today, operations to increase and close gum recession in Kirov are carried out at Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry.
This is a very common problem that has effective and painless treatment. Sign up for a consultation at Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry and get answers to all your questions regarding gum tissue extension in Kirov! Information by phone: 8 (8332) 255-717 . Be healthy and take care of the beauty of your smile!
How to stop gum recession?
Therapeutic treatment of gum recession is aimed primarily at eliminating the inflammatory process, normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity, increasing immunity and the body's protective properties.
Therapeutic techniques
- Professional cleaning and sanitation of the oral cavity.
It is used as a preventive measure, and is also the first step in the treatment of the inflammatory process. - Closed curettage of periodontal pockets.
A therapeutic procedure for removing dental plaque in periodontal pockets. - Treatment of gum recession with laser.
Photodynamic laser therapy or laser curettage is performed. - Anti-inflammatory therapy.
The doctor prescribes gels, ointments and rinses (usually topical use), which have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. - Antibiotic therapy.
- Taking vitamins and supplements.
During recession, vitamins C, D, B9 are prescribed, as well as preparations containing the protein amelogenin, which helps restore soft and hard tissues.
Surgery
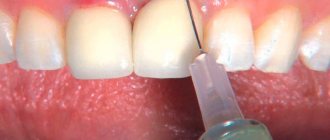
- Treatment of damaged tissues and suturing.
The simplest manipulation that is performed during recession, when the gums are damaged as a result of mechanical stress. - Flap surgery.
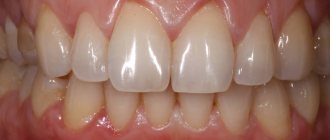
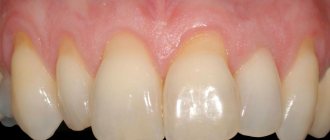
Gum recession plastic surgery, when donor tissue is taken from a healthy area of the mucous membrane to “close” the missing fragment. Allows you to restore 2-3 millimeters of the level of the mobile gum. The advantage of this technique is the relative speed of the operation and a completely acceptable result. Disadvantages: invasiveness, the need to collect donor tissue and the possibility of rejection. In some situations, the color of the donor tissue may be slightly different, which negatively affects the aesthetics. - Tissue regeneration.
It is carried out using a fibrin membrane - a tissue growth stimulator, which resembles a dense clot and is implanted into the site of recession after preparatory surgical procedures. To produce the membrane, blood is required from the patient, but the healthy area of the gum is not harmed (unlike flap surgery). This technique has a number of advantages: minimally invasive, the possibility of treatment in complex cases, rapid tissue restoration and the absence of the risk of repeated recession. The gums after surgery to eliminate recession look healthy and natural. - Treatment of gum recession with collagen.
Implantation of collagen implants of natural origin for tissue restoration. The implants contain fibrillar protein, which is the basis of connective tissue. Previously, collagen was removed after treatment, but modern implants do not require this and dissolve on their own. This method is especially effective for age-related recession.
HOW TO STOP GUM RECESSION?
If you suspect you have gum recession, contact your dentist for an examination and appropriate treatment.
There are various treatment options for gum recession:
Cleaning and polishing the surface of tooth roots
If you have gum recession, your dentist may recommend a procedure to clean and plan the surface of the roots of your teeth. This procedure consists of two stages and is carried out by a dentist. In the first stage, the doctor removes plaque and tartar in the area of the gum line (above and below it). Then the surface of the tooth roots is polished, so that the gums can “attach” to the teeth again. Treatment may be performed under local anesthesia and may require several visits.
The procedure for cleaning and polishing the surface of the roots of teeth is quite effective. After this, you will need to visit your dentist regularly. He will check the condition of your gums and will be able to spot possible problems in time. To protect your gums, be sure to practice good oral hygiene.
Gum operations
For more severe cases of gum recession, your dentist may recommend surgical procedures. These include the following:
- Gum flap surgery: If non-surgical treatments have not been effective, your dentist may suggest flap surgery. During this operation, incisions are made on the damaged gum, then the resulting flap is raised, allowing access to the roots of the tooth. They are cleaned and polished. After this, the gum is reattached to the surface of the tooth.
- Regeneration: This surgical procedure helps regenerate damaged jaw and gum tissue. First, the area above and below the gum line is cleaned to remove bacteria and plaque. A material that stimulates tissue regeneration—a membrane, a tissue-stimulating protein, or a graft—is then attached. This triggers bone and tissue growth in the damaged area. The gum is then securely attached to the root of the tooth.
Gum transplantation
If you have lost gum tissue, your dentist may recommend a gum tissue graft. A section of gum is taken from the upper palate and sewn to the damaged area of the gum so that it covers the roots of the tooth.
Treatment at home
Treatment of gum recession at home is impossible, since in advanced stages of the disease only surgical intervention can correct the situation. It is not possible to get rid of gum recession with ointments, gels and tinctures: at best, they will help cope with inflammation, but they cannot restore the edges of the gums. Anti-inflammatory therapy is used only as an addition to the main treatment. Folk remedies should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor or as a preventive measure. In the absence of pharmaceutical drugs, folk remedies may provide some benefit. A solution based on soda and salt, propolis extract, decoctions of oak bark, juniper and chamomile are just a small part of the folk recipes that can be used for gum diseases.
What to do to prevent the disease?
Preventive measures do not provide a 100% guarantee that you will never experience gum recession, but following them will help minimize the risks:
- regular and high-quality hygiene;
- professional cleaning of dental plaque;
- using a medium-hard toothbrush and proper brushing technique;
- timely diagnosis of caries and inflammatory processes;
- taking vitamins and amelogenin if there are risks of recession;
- giving up bad habits, especially smoking;
- correction of malocclusions, if you have them.