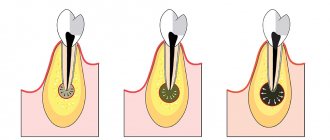
Many dental diseases develop latently for quite a long time and, like many other diseases, in the first stages of development they are easily and simply controlled, for example cysts, which can be easily treated with conservative and non-surgical methods, the main thing is not to let the problem take its course.
The main problem of diagnosis and timely dental treatment is that patients, who remember what dentistry was like in the USSR, prefer to endure and ignore the initial symptoms “until the last” and turn to the dentist after the development of complications or already in advanced situations, when without surgical intervention not enough.
In addition, there are a number of diseases that appear and develop without pain or discomfort, asymptomatically, and therefore are discovered completely by chance on an x-ray or already at the stage when there are visible signs of inflammation and the preservation of the tooth becomes doubtful. Such dangerous and hidden pathological processes include a dental cyst, which does not manifest itself in any way, is detected by chance and so surprises patients with completely unexpected worries and expenses.
What is a dental cyst?
A cyst is any cavity formation that forms inside the jaw bone or in the gum and limits the penetration of infection from the source of inflammation into healthy tissue.
A dental cyst develops very slowly and its development begins with the penetration of infectious agents, microbes and inflammatory products into the tissue around the tooth root, which the body cannot cope with. The human defense system tries to autonomously fight inflammatory and necrotic processes but, unfortunately, is defeated. To prevent further spread of the infection, a capsule is formed filled with decay products of dead and infected bone cells; the body tries to prevent the infection from spreading to surrounding tissues.
!Important: The main inconvenience and problem is that such hidden cystic processes, regardless of location (no matter in the jaw, in the abdominal cavity or in the ovary), always develop asymptomatically and unnoticeably. And the most annoying thing is that these formations are found only during an exacerbation, when a surgeon is already needed.
Now in our clinic there is a special diagnostic case “CT scan for searching for hidden cysts.”
All dental cysts will have to be treated, even if nothing bothers you. In order not to waste time, it is better to delay, as they gradually increase and involve the surrounding tissues in the pathological process. The result of this progression of the disease is periostitis, known to ordinary people as “flux”. A pronounced clinical picture of inflammation develops with pain, swelling and hyperemia, the main treatment for which, unfortunately, will only be tooth extraction followed by extraction of the cyst.
!Important: Currently, there is a lot of information about the treatment of cysts with laser. However, the confusion of information makes it impossible to understand the problem of using medical lasers to treat cysts.
Currently there is:
- Laser sterilization of canals using a SIRONA laser or other devices.
Plus : Modern, fashionable, there is an illusion of expensive quality. Disadvantage : the price is inadequate, there is no medical evidence of the advantages of this type of treatment over other methods of canal sterilization. Very questionable marketing.
- Laser surgery of the cyst shell itself, laser disinfection of the cavity in the bone.
Plus: Super speed of the operation, burning out the cyst occurs literally in seconds. Minus : unforgettable smell, heals worse, the result of healing of the wound surface after a laser burn is worse and longer than after surgical removal of the cyst. We haven't used it for two years now.
!Important: Please understand that laser canal treatment is a marketing term that duplicates the classic treatment of root canals with a contact antiseptic. Despite the modernity of this method of dealing with the problem, such as “laser cyst treatment”, its effectiveness remains in doubt, and therefore you should not rely too much on it.
Types of neoplasms under the roots
In the dental classification, there are 3 types of cysts under the crown; let’s look at them in more detail:
- root or radicular: located in the apical part of the root. Appears due to infection during preparation before prosthetics or due to injury,
- primary or keratocyst: most often located near the lower molars - large chewing teeth. It does not appear in any way for a very long time; it is discovered by chance on an x-ray - in the corner of the jaw, on its body or branch. The bone tissue is greatly sparse,
- follicular or tooth-containing: develops from the tooth germ of a canine or wisdom tooth on the upper or lower jaw. Can cause ameloblastoma, a benign tumor
- residual: we can say that this is a secondary cyst, since it develops on the site of a previously poorly removed one,
- paradental or retromolar: most often located between the dystopic wisdom tooth and the roots of the adjacent one, on which the “figure eight” presses.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS ON 4 IMPLANTS - from RUR 170,000.
The price includes all procedures for installing Osstem implants (South Korea), including anesthesia and diagnostics.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and fix your prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Why does a dental cyst develop?
There are several main reasons for the development of dental cysts. The main factors that provoke the formation of cysts:
- Mechanical damage to the gums (injuries can be very minor, for example, wounds from nut shell fragments). Infections of the oral cavity (small scratches on the gum are enough for pathological microorganisms to penetrate into its tissues and form a cavity inside that is invisible to the patient and even dentists for a long time); A periodontal cyst appears .
- Complications after unprofessional dental procedures (incorrect installation of fillings, insufficient cleaning of the canals, inadequate treatment of caries and other procedures); Pulpitis develops, then periodontitis, and a radicular cyst .
- Problematic and difficult to erupt wisdom teeth. follicular appears .
- Soft tissue cysts and cysts in the lymph nodes. Infectious pathologies of the upper respiratory tract (these structures are closely related to the oral cavity, therefore the mechanism of cyst development is the same as in the previous version, and the spread of bacteria through the blood and lymph cannot be ruled out).
Cysts, according to their origin, are of the following types:
- follicular (its contents include an unerupted tooth, the germ of which has become infected);
- radicular (develops in the area of the tooth root, most often caused by prolonged periodontitis);
- primary (appears when the development of a tooth or surrounding tissues is disrupted);
- paradental (forms in the area of baby teeth during severe eruption and infection);
- residual (capsule that forms after tooth extraction).
Treatment after removal
After removal of a dental cyst, you must carefully follow the doctor’s instructions and come for follow-up examinations on time. A responsible attitude to this issue will reduce the risk of complications and speed up the patient’s recovery process. After a few days, you need to visit your dentist to monitor the condition of the hole, as well as change the dressings. If there are no complications, after five days the stitches can be removed, but adhere to the recommendations in diet and hygiene.
After tooth extraction, it is possible to prescribe oral baths, rather than rinsing, with chamomile solution or other anti-inflammatory drugs. It is necessary to temporarily exclude solid foods in the form of crackers, nuts, and candies from the diet.
It is necessary to take antibiotics prescribed by a doctor for five days. And if pain occurs, taking painkillers or NSAIDs is allowed.
What are the clinical manifestations of a dental cyst?
In the first stages of the disease, the patient does not feel the problem at all. The only sign of pathology may be slight discomfort when pressing or a feeling reminiscent of crepitus (crunching). As the cyst grows, the following symptoms appear:
- a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, a feeling of fullness, twitching, or fullness in the affected area;
- aching pain in the tooth or even in the entire jaw when biting, which makes differentiation difficult (typically worse at night);
- problems with the chewing process (discomfort and increased pain);
- an increase in the size of the gums on the affected side (its swelling, and with an exacerbation of infection - severe hyperemia);
- swelling of the face, in particular the cheeks on the affected side due to impaired functionality of the lymphatic system.
During the period of an acute infectious process in the area of the cyst, that is, during the development of flux, general signs of inflammation are observed: increased body temperature, headache, enlargement and soreness of the nearest lymph nodes. At such moments, the pain becomes sharp and throbbing.
Symptoms
At an early stage, the disease is practically asymptomatic, which is why it is so difficult to diagnose when the cyst is small and still amenable to therapeutic treatment. When the cyst begins to grow, aching and nagging pain appears, intensifying while eating (with pressure on the sore tooth). At a later stage, the pain becomes almost constant and is difficult to get rid of with conventional analgesics.
Another symptom of a cyst is redness and swelling of the gums. Body temperature may increase as the body undergoes an inflammatory process.
An x-ray can reveal a cyst, so at the first symptoms it is important to consult a doctor and check the disturbing tooth for the presence of a cyst.
Treatment of dental cysts - basic techniques
Therapy for a dental cyst is rarely carried out in the initial stages of the development of the disease, but its accidental discovery cannot be ruled out either. All techniques can be divided into two large groups: therapeutic and surgical, with the latter being the most popular and effective. In recent years, the development of dentistry has also highlighted the treatment of dental cysts with a laser, but the effectiveness of the method is still highly doubtful. Dentists recommend not to take unnecessary risks and treat with classical methods that give guaranteed results.
About the reasons
The main reasons for the transformation of granuloma into a neoplasm:
- the prosthesis is incorrectly fixed;
- physician errors in preparing canals for dental prosthetics;
- poor quality treatment and lack of oral hygiene;
- allergies to composite materials and dental glue;
- periodontitis in chronic form.
Note: incorrectly installed dentures and crowns are one of the main reasons for the appearance of cysts. It is important to remember that the first signs of the disease often appear after 2-3 years.
Conservative treatment methods
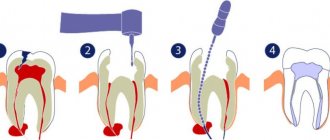
The therapeutic option for treating dental cysts is lengthy and complex, but it is still practiced in dentistry. The conservative treatment algorithm is as follows: ALL WORK IS CARRIED OUT UNDER A MICROSCOPE!
- The first stage is to work with root canals, their immediate sterilization. There may be two therapeutic solutions here. If the canals have been sealed, then they are unsealed and re-treated.
- Repeated flushing of the canals with an antiseptic is mandatory, since the cyst has purulent contents.
- Specific dental techniques are performed to remove the medication beyond the root apex.
- The doctor performs a temporary filling of the canals with a special paste that contains an antiseptic. This and the previous stages of treatment are repeated several times.
- The patient takes an x-ray, which is used to evaluate the dynamics of treatment. If its signs are positive, therapy continues. Otherwise, they proceed to surgical procedures.
- Treatment is carried out over several months with periodic radiological assessment of the reduction in cyst size. Only when it is significantly reabsorbed is the final filling of the canals performed.
- The final stage is filling the tooth.
Therapeutic treatment is advisable only if the size of the cyst does not exceed 10 mm.
X-ray diagnostics –
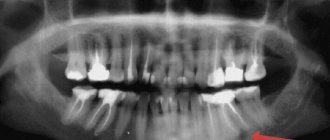
As we said above, the final diagnosis can only be made using an x-ray, on which a cavity formation in bone tissue will always look like a rounded darkening.
In the x-ray images below we have presented you with 3 options for localizing root cysts. The most common location is root cysts at the apex of the tooth root, but cysts on the lateral surface of the root or located between the roots of multi-rooted teeth are much less common. Radiographs of root cysts of different locations –
Operational methods
Surgical therapy for dental cysts is performed when the cavity is large, there is frequent pain and swelling, and there is a crown on the tooth. There are three methods for removing formation:
- Cystectomy. The essence of the procedure is to remove the cyst along with its contents and surrounding affected tissue. It is difficult to carry out such an operation without surgical specialization, and therefore there are strict indications for it: the absence of acute inflammation in the cyst cavity, the absence of teeth in the contents of the cyst, its location on the upper jaw with penetration into the maxillary sinus, or within two teeth.
- Hemisection. Such a surgical intervention involves removing not only the cyst, but also the root of the affected tooth along with part of the crown. After this, the enamel is cleaned and a new crown is placed to hide the defect.
- Cystotomy. The essence of the operation is to remove the anterior wall of the cyst. The main disadvantage is the long recovery period. Indications for its implementation: localization of a cavity in the lower jaw with significant thinning of its wall, destruction of the palatal plate or the bone floor of the nose, a large size of the cyst, occupying more than three adjacent teeth.
The first type of surgical intervention is the most preferable, but it is not always possible to perform it. In the most advanced situations, the doctor has to remove the entire tooth, followed by implantation, and sometimes bone grafting. Recently, dentists are increasingly trying to get rid of cysts using a laser. The technique has not yet reached its perfection, so patients are advised not to take unnecessary risks.
When is laser cyst removal not recommended?
Today, in all areas of medicine, laser treatment is considered the safest method. However, despite all its advantages, the action of laser beams can be dangerous for the body if the patient has contraindications.
The use of another method of removing a dental cyst is recommended for diseases or pathological conditions:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- poor blood clotting rate;
- varicose veins of any form;
- immunodeficiency diseases (including diabetes mellitus);
- cancerous formations;
- postoperative period (in the treatment of any disease);
- individual negative reaction to the action of the laser.
During the procedure, only local anesthesia is used, so such operations are also contraindicated for patients with mental disorders. The doctor can consider each case separately, but to avoid complications, the dentist must be warned about all existing pathologies.
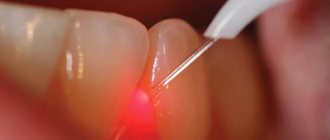
Treatment of dental cysts with laser - an alternative to surgery?
Despite the huge number of positive comments on the Internet about this method of solving the problem, the honesty of such “advertising” is questionable; clinicians and practice show that in 70% of cases, laser cyst removal is ineffective and there are many relapses. Moreover, it is not so easy to find a complex clinic that will have suitable alternative modern equipment if something goes wrong with the laser. Clinics selling laser treatment usually do not use other technologies, only tooth extraction.
Before therapy, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination for the following reasons:
- to identify contraindications;
- to clearly determine the characteristics of the cyst (location, size);
- to assess the individual characteristics of the anatomy and structure of the dentofacial apparatus.
The essence of treating dental cysts with a laser is to open the canals and then insert a special laser light guide there. It looks like a tube or needle and has a drying effect on the inner walls of the canals. Thus, there is hope that the channels and cavity are “cleansed” of necrotic tissue and pathological microorganisms. This treatment has some novelty and a modern name. However, some patients report some discomfort while using the laser device, as well as an unpleasant odor after the procedure. Dentists emphasize that the likelihood of relapse after such therapy is much higher than after classical cyst excision, but they use it to collect statistics on the new technology.
[slide-anything id=”3470"]
How to protect yourself from pathology
To eliminate the possibility of dangerous consequences of prosthetics, incl. the appearance of a cyst under the crown, you need to very carefully choose an orthopedic dentist and a dental therapist. The first one selects the prosthesis, prepares the tooth for its installation and, in fact, ensures the fixation of the crown or bridge. But before that, you need to visit a dentist-therapist who will treat the root canals and carefully seal them. An indicator of the responsibility of doctors is the number of x-rays during the treatment process - at least 5 of them are taken in the process of preparation and prosthetics. They show the smallest voids in the canals and the loose fit of the parts of the prosthesis - if the doctor is not satisfied with the result, he will bring the work to perfection. And the patient will wear dentures without pain and negative consequences.
Advantages and disadvantages of laser treatment
Laser cyst removal has a number of advantages, which are the reason for the growing popularity of the technique. These include:
- Beautiful name.
- Novelty of technology.
- There is no need to use additional antiseptics, since the laser sterilizes well the points it hits and copes with sanitation (although the number of relapses casts doubt on this advantage).
- There is no risk of complications common to surgical interventions, including bleeding.
- The hope is to preserve the natural tooth (however, if the cyst recurs, there is a high probability of losing it).
We must not forget about the disadvantages of the technique, which, at first glance, are fewer than the advantages, but they are quite significant. First of all, the cost of the procedure will be an unpleasant surprise for patients. High prices for laser cyst removal are due to significant interest and demand for alternative offers, but you don’t want to remove a tooth, patients are “grasping at straws.” The effectiveness of laser treatment is still in doubt, especially in cases of significant size of the cyst and its close proximity to the tooth tissue. The patient should think several times before agreeing to such treatment for the disease. Moreover, in case of failure, the dentist returns to traditional surgical techniques, and in some situations removes the cyst along with the affected tooth.
!Important: before starting treatment, draw up a full turnkey estimate, carefully read the contract and the clinic’s warranty for such procedures; it is often easier and cheaper to replace a tooth with a cyst with an implant than to prolong its agony and believe in miracles for money without a guarantee.
User Questions
QUESTION My dentist found a cyst in my front tooth under the crown. She says that while she is small, she can be treated with antibiotics. But he said it was better to remove the crown. Why can't you leave her? Alexei
ANSWER Hello, Alexey.
It is likely that your doctor wants to reduce the chewing load on the tooth. To prevent you from accidentally biting something hard or pushing the infection deeper, it is better to remove the tooth from the bite. Another option is to remove the crown. Don't worry, after treatment it will be put back in place. During the treatment process, the tooth will be covered with a temporary filling. 1Epifanov E.A. Medical rehabilitation for diseases and injuries of the maxillofacial area, 2022.