Content:
- What will happen if left untreated?
- Why does it occur
- Classification 3.1. Root 3.2. Residual 3.3. Follicular 3.4. Teething 3.5. Primordial 3.6. Lateral periodontal 3.7. Calcifying odontogenic
- Symptoms
- How to treat 5.1. Surgical treatment 5.3. Conservative therapy 5.3.1. Depophoresis - an innovative method of conservative treatment
A pathological neoplasm formed in the gum as a result of a protective reaction to infection or injury is called a cyst.
Its appearance is caused by penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through the root canals. As a result, severe inflammation develops. Tissues that are involved in the inflammatory process slowly die. A cavity is formed. Liquid exudate accumulates in it. A cyst in the gum is a way to protect against further spread of the infectious process. A dense capsule appears around the lesion, holding necrotic cells inside. Its dimensions can range from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters.
If the diameter of a cyst on the gum does not exceed 5 mm, it is called a granuloma. In total, dentists distinguish three stages of inflammation:
- granuloma;
- cystogranuloma;
- cyst.
The sooner the patient seeks medical help, the better. If you postpone treatment until later, you may lose your tooth.
The difficulty is that in the first stages inflammation most often does not manifest itself. But the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the tumor is rapidly increasing. To stop the abnormal process, the body sends immune cells to its source. This negatively affects the functioning of the immune system and leads to its weakening.
What will happen if left untreated?
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease leads to dangerous consequences for health. Thus, the patient may encounter:
- destruction of roots, their strong loosening;
- jaw fracture;
- tumor formation;
- purulent abscess;
- periostat;
- osteomyelitis.
The disease can cause the development of sepsis. This is a very serious condition in which the infection enters the blood and quickly spreads throughout the body.
Why does it occur
Among the main causes of pathology:
- advanced caries;
- jaw injuries;
- illiterate root canal treatment;
- overload of individual units as a result of poorly performed prosthetics;
- congenital anomalies of the upper/lower jaw;
- infections of the nasopharynx and oral cavity.
Regardless of the characteristics of the provoking factor, a gum cyst should be treated under the supervision of a dentist. Self-medication for this diagnosis is unacceptable.
Why does a dental cyst form?
The cause of cyst formation is an untreated root canal infection.
The reasons for infection in the root of a tooth can be different:
- As a complication of insufficiently treated or completely neglected
- caries/pulpitis,
- periodontitis,
- periodontal diseases,
- inflammation under the dental crown,
- Error and infection during endodontic treatment (root canal treatment).
- Tooth injury.
- Immune disorders in the body.
- Chronic diseases of the ENT organs: runny nose, sinusitis, tonsillitis.
Children in primary and mixed dentition can also suffer from dental cysts. Even newborns may experience teething with a purulent cyst - the so-called. Bona knots.
Classification
All cysts that occur in the human oral cavity can be divided into the following types:
- root;
- residual;
- follicular;
- teething;
- primordial;
- lateral periodontal;
- calcifying odontogenic.
Let's talk about each of them in more detail.
Root
It is a consequence of granuloma that appears due to periapical inflammation and necrosis. Located in the area of the apical part of the root. The boundaries of such a structure are easily determined. Its size can be from 2 mm to 3 cm. But even with a large diameter, root formation does not lead to a change in bone volume or displacement of the incisor. Only if a secondary inflammatory process is involved, the disease makes itself known through pain and swelling.
When identifying a disease, you need to understand what led to its appearance and take measures to eliminate the provoking factors. Usually the problem can be resolved with endodontic therapy.
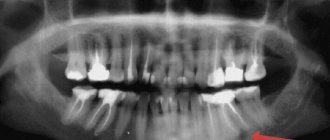
Residual
It is also called residual. Appears after removal right in the place where the roots of the torn out unit were previously located. X-ray diagnostics helps determine the presence of a residual structure.
Follicular
It is formed from the tissues of the follicular sac that covers the rudiments. Easily visible in the photo. Often leads to serious damage to premolars and molars.
As a rule, follicular formations quickly increase in size and can spread to adjacent teeth, changing their location and angle of inclination. Traditionally, their treatment involves surgical curettage.
Teething
Appears during the period of eruption of permanent units. Covers the emerging rudiment. May contain blood. Visually resembles edema, swelling. Has a bluish tint.
Sometimes it ruptures spontaneously, spontaneously. Then the person simply notices that the “ball” has disappeared, the liquid has flowed out of it. In rare cases, surgery may have to be performed. During this procedure, the blood sac is opened, and the structures that interfere with further eruption of the molar are excised.
Primordial
Formed on the basis of the tooth germ. Most often diagnosed in the area of the posterior units. This type of formation is prone to recurrence. To cure the primordial structure, it is necessary to curettage the altered tissues.
Lateral periodontal
Rarely encountered in dental practice. It has modest dimensions. Clearly visible on X-ray images. This cavity is called a lateral cavity, since it is fixed to the side of the tooth root.
The tumor can only be removed by curettage. The material obtained during the operation is necessarily sent for histological analysis to ensure that the disease present in the person is benign.
Calcifying odontogenic
Another rare type of cyst. Observed in the lower part of the supporting surface of the jaw. Well visualized on x-rays. There is cloudy contents inside. Its color depends on the degree of calcification.
Immediately after diagnosis, surgical curettage is performed.
What is the difference between a cyst and a granuloma?
A dental cyst is often confused with a granuloma, another dangerous disease in which a round-shaped formation forms in the root area. It is important to distinguish between them, since the diagnosis directly affects the treatment plan and its prognosis. For granuloma, in most cases therapeutic treatment is sufficient. But a cyst requires more radical measures.
Here are the main parameters by which a dental cyst and a dental granuloma differ:
| Difference options | Cyst | Granuloma |
| Size | 0.9 - 3 cm | 0.5 - 0.8 cm |
| Structure | Cavity with fluid or pus | Solid formation covered with connective tissue |
| Clinical picture | The tooth becomes mobile | No mobility observed |
| X-ray result | The image shows a round capsule with clear boundaries | There are no strict outlines of education |
| Condition of periodontal tissues | The mucous membrane is usually not inflamed. In this case, bone loss occurs. | There is severe swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. But bone tissue does not decrease so much that it can be detected clinically. |
Symptoms
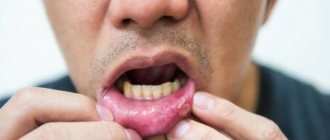
The disease manifests itself as a dull pain when eating solid food. A fistula may form on the gum. Patients also complain of:
- swelling of the face;
- swelling;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- high sensitivity to temperature changes;
- increased volume and tenderness of the lymph nodes;
- toothache.
If a tooth looks healthy, but pain occurs when pressing on it, you should definitely make an appointment with a dentist. The same must be done if the gum is swollen, swollen, or a fistula has formed on its surface.
Prevention of dental cysts
Taking standard care of your dental and general health will help prevent the development of cysts.
To prevent dental cysts from bothering you, you must:
- Undergo regular preventive examinations with your dentist every 6 months and a professional hygiene procedure. Do not refuse if the doctor offers you an X-ray examination - he has reasons for this.
- Treat caries and pulpitis in a timely manner.
- To identify hidden caries at an early stage of the disease, for this in our clinic we use digital (not x-ray) diagnostics using the Diagnocam apparatus. We recommend undergoing such diagnostics at least once every six months.
- Brush your teeth well yourself using dental floss, irrigator, and mouthwash. Pay attention to cleaning your tongue.
- Strengthen immunity.
How to treat
Today, doctors are trying to eliminate the disease without resorting to tooth extraction. The unit is pulled out only if it is completely contained in the inflammatory capsule and its tissue is significantly destroyed.
In other situations, therapy may be:
- surgical;
- conservative.
Surgery
Cystectomy is a procedure aimed at removing the cyst and the changed part of the root apex. The technique is considered highly effective. Its only drawback is its difficulty.
Less commonly, for cystic changes, hemisection is performed. The operation is indicated for complete destruction of the tooth root. During treatment, the dental surgeon removes the capsule with its contents, the altered root and part of the crown. This leaves a serious hollow defect. It is closed by laying special composite materials and installing a crown (if necessary).
Conservative therapy
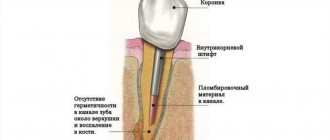
Does not involve surgery. The doctor does not make an incision to access the capsule. Instead, he drills out the roots and treats them. The fact is that the tip of the tooth root connects to the cyst, so after drilling, the contents of the cavity immediately flow out.
When this happens, a medicinal composition and a special anti-inflammatory paste are placed into the canals. Afterwards the filling is carried out. The disease is considered to have resolved if after six months the treated area is not visible on the image.
Conservative treatment helps most patients, so the main emphasis is placed on it when fighting the described disease.
Depophoresis - an innovative method of conservative treatment
The most modern conservative treatment method is depophoresis. It does not require drilling of channels. The doctor exposes only the mouth of the canal, after which he inserts a thin electrode into it. The second electrode is pressed into the patient's cheek. Then it delivers a weak current discharge, along with which copper/calcium hydroxide passes through the channel. It penetrates even the most inaccessible areas, instantly kills pathogenic microorganisms, and destroys necrotic cells. Depophoresis is repeated three times. This is enough to clean the fabrics. Afterwards the tooth is filled. This technique is very effective. It allows you to get rid of the problem forever in 99% of cases.
Cyst on the gum: treatment in different ways
If the pus pressure becomes too high, the mucous membrane bursts and the pus sac opens. Its contents enter the mouth, and a hole appears at the site of the cyst, through which pus will continue to flow into the oral cavity, since the source of inflammation has not been eliminated. Naturally, this situation is not normal, so it is necessary to regularly visit the dentist, who will definitely be able to prevent such complications.
How to treat a cyst? There are two ways:
- Opening the cyst through an incision in the mucous membrane, which will create a strong outflow of pus and significantly reduce inflammation.
- Dental treatment.
In the latter case, several options are possible:
- If the inflammatory process has formed as a result of periodontitis of an untreated tooth, then it is necessary to remove the pulp and seal the canals.
- If the cause of inflammation lies in poorly sealed canals, then the tooth must be retreated.
Treatment may be as follows:
- therapeutic, in which the crown is first removed, then the filling is performed, then the canals are filled again, and a new crown is put on;
- surgical. If the canal was not sealed well enough at the upper part of the root, resection is necessary (through a small hole in the gum, the doctor will use a drill to remove the root tip). This procedure saves the patient money, since there is no need to make a crown and re-fill the canals;
- a complex of therapeutic and surgical measures.
It is worth saying in a little more detail about resection - the name scares many patients, but there is nothing complicated, much less painful, about the procedure.
Resection consists of several successive stages:
- Preparatory procedures. When it comes to a tooth cyst with unfilled canals, a filling is performed several days before the main operation. It's worth noting that this needs to be done in a couple of days, not several weeks or more.
- Local anesthesia. This is a virtually painless procedure. Some patients report slight pain only when the injection no longer works.
- Providing access to the upper region of the root. The surgeon cuts the gum, exposing the bone. Next, the bone tissue is cut out using a drill, which is also not painful, given the previous anesthesia.
- Cutting off the upper part of the root with the cyst and removing tissue from the wound using tweezers.
- When the cyst is eliminated, an empty space remains in its place, i.e. cavity. The size of the cyst can be quite large: then synthetic tissue is placed there, which will speed up the filling of the cavity with normal bone.
- Suturing the wound using special material. A drainage can be installed for a couple of days to ensure the outflow of the resulting ichor.
A number of patients, upon hearing about the resection prescribed for them, worry that the tooth will not last long, but this is not at all the case. In addition, if the procedure is carried out in compliance with all standards, there will be no complications. It is necessary for the doctor to completely remove pieces of the cyst from the wound, otherwise it may form again (according to statistics, the incidence of such a complication is no more than 3%).