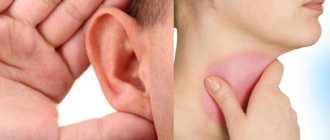
Ear pain is a fairly common symptom. Painful sensations in this case give the patient a lot of unpleasant moments, and it is very difficult to simply “endure” such pain. It is noteworthy that pain in the ear is not always associated with diseases of the hearing organ. Such painful sensations can also be caused by other organs that radiate, that is, “giving off,” to the ear. A condition in which the ear hurts, but there is no inflammation in it, is called otalgia.
Otalgia can be caused by many reasons:
Temporal arteritis
The disease is an inflammation of the vessels of the temporal artery.
If the inflammatory process spreads to the ear artery, the patient will also experience pain in the ears. This disease is typical for older women. It causes blurred vision, headaches, pain in the temples, and increased fatigue. Make an appointment right now! Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Along the branches of the vagus nerve, pain can radiate to the ear from the esophagus, thyroid gland, and organs of the cardiovascular system.
If you have ear pain, you should definitely consult with an otolaryngologist, since this condition may signal the presence of serious diseases in the body. If the ear is healthy, no abnormalities have been identified, and the pain does not go away, it is necessary to diagnose the nose, larynx, pharynx and, if necessary, other organs to identify the cause of otalgia. Further treatment will depend on the diagnosis.
Ear pain: causes
Ear diseases are a common problem that many people experience, regardless of age. Such pathologies can be caused by a large number of reasons. Each disease requires a different approach to treat. For this reason, there is a danger in self-diagnosis of the disease and treatment. If you experience ear pain, the first thing to do is consult a doctor.
Pain in the outer ear
Practice shows that the main cause of diseases in this department is infections. The outer ear is not protected, so the risk of microorganisms entering is high. But even taking into account this fact, the immune system copes with its functions and neutralizes the threat.
Another reason could be injury. Improper cleaning of the ears, blows and injuries provoke the occurrence and spread of the inflammatory process.
Among the symptoms of damage to the external part are:
- Itching in the ear;
- Acute pain in the ear;
- Movement of the jaws is accompanied by increased pain;
- Impact on the sink leads to increased discomfort.
Also, pain in the outer ear can be caused by the following diseases:
- Otitis externa. The cause is bacteria;
- Furuncle (ulcer);
- Injuries. The result of various injuries. Very often, pain in a child’s ear can be caused by foreign objects that children manage to insert into their ears.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that pain in the outer ear may indicate the presence of cerumen, a tumor, or a foreign object. In some cases, such symptoms are characteristic of eczema.
Middle ear pain
This department directly interacts with the outer ear and nasopharynx. For this reason, the disease can be transmitted to the middle ear. Pathological processes developing in the middle ear have a negative impact on the condition and functioning of other organs and tissues.
Among the symptoms indicating the presence of pathology in the middle ear are:
- Shooting pain in ear;
- Sensation of pulsating in the ear;
- Hearing problems in the affected ear;
- Distortion of the perception of one's own voice.
Pain in the ear in this area may indicate that the following pathologies are highly likely to develop:
- Acute inflammatory processes in the middle ear;
- Tumors in the area of the tympanic cavity;
- Trauma and disruption of the integrity of the eardrum;
- Problems with the functioning of the auditory tube.
In some cases, severe ear pain may occur after going to the pool. The pain spreads both to the outer ear, where the infection could have entered, and to the middle ear, where the pain is caused by strong water pressure when diving to depth.
Problems in the inner ear
In most cases, damage to the inner ear is not accompanied by pain. This significantly complicates the detection of pathologies.
Symptoms of internal disease include:
- Problems with coordination arise;
- Difficulty maintaining balance;
- Nausea;
- Extraneous or uncharacteristic sounds in the ears;
- Headaches on a regular basis;
- Progressive hearing loss;
- Dizziness.
The list of common inner ear diseases includes:
- Labyrinthitis (infectious and inflammatory process);
- Hearing loss (impaired functioning of the apparatus responsible for the perception of sound waves);
- Meniere's disease (increased pressure in the labyrinth caused by an increase in labyrinthine fluid);
- Otosclerosis (pathological bone growth).
It is important to note that all of the above reasons are relevant for all ages.
Ear pain causes not related to the ears
In some cases, acute pain in the ear can occur without pathological processes in the auditory organs. Pain can be caused by diseases occurring in neighboring organs.
Among such processes occurring in neighboring organs are:
- Dental problems;
- Trigeminal neuralgia;
- Inflammation of ENT organs;
- Tumors of the larynx, oral cavity, lower pharyngeal region;
- Inflammation in distant organs
- Diseases of the esophagus;
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels (heart attack);
- Degenerative pathologies of the cervical vertebrae.
The most optimal solution when you experience ear pain is if you are seen by a paid therapist (Rostov-on-Don) and excludes those diseases that cannot be treated by an ENT doctor, or, on the contrary, refers you to the right specialist in a timely manner.
We must not forget that only a doctor can correctly diagnose and, based on the anamnesis, as well as test results, make a diagnosis and begin treatment.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce otalgia, ear drops with local anesthetics or oral tablets with analgesics are used before visiting a doctor. Medicines can be used if the pain does not occur due to injury. The pathological process that affects the ear quickly involves the bones of the skull and the brain, so self-medication is unacceptable. A qualified ENT doctor should provide assistance to patients with otalgia.
Conservative therapy
Treatment involves the use of local or systemic medications, or a combination of both. For otitis, ear drops containing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic substances are used, and the ear is toileted. To improve the outflow of exudate from the tympanic cavity, vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose. To reduce pain in the first days (before the eardrum ruptures), heated 96% alcohol is dripped into the ear.
To eliminate the consequences of taking ototoxic drugs, ATP and galantamine are prescribed, which stimulate regeneration processes. Nootropics help improve the nutrition of the auditory analyzer structures. To influence the neurological causes of otalgia, sedatives, anticholinergics, metabolic and vasoactive drugs are recommended. Severe painful paroxysms require the use of anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy methods are effective in practical otolaryngology. To stop the inflammatory process and stimulate local immunity, microwave therapy, laser therapy, and UHF are performed. To prevent hearing disorders during the recovery period, pneumomassage of the eardrum is performed. Reflexology and amplipulse therapy help eliminate paroxysms of neuralgia of the ear node.
Surgery
The tympanic cavity is cleared of pus during myringotomy, followed by washing the ear with antibacterial solutions. In case of chronic otitis and the absence of effect from conservative measures, anthrodrainage is performed in the mastoid area. Indications for surgical treatment are external cholesteatomas, exostoses, and abscesses.
To eliminate the consequences of middle ear trauma, reconstructive surgeries are prescribed: myringoplasty, tympanoplasty, mastoidoplasty. In case of damage to the inner ear, otosurgical interventions are performed to restore the integrity of the anatomical structures. In case of severe illnesses and injuries accompanied by hearing loss, the patient requires selection of a hearing aid or cochlear implantation.
What is “possible” and what is absolutely “not” for ear pain
If a child has ear pain, it is recommended to visit a doctor as an emergency. If you need an ENT doctor, you can make an appointment with him in our clinic.
How to reduce pain?
Folk remedies:
- Ammonia with camphor. The solutions are mixed. Gauze is dipped in the solution and placed in the ear for a few minutes, this allows you to get rid of pain;
- Decoction based on onions. Another way to get rid of pain. A warm decoction is used to wipe the auricle and ear canal. The result is a disinfecting effect and pain reduction.
An alternative option is to take a pain reliever. In some cases, the use of vasoconstrictor drops is allowed.
What not to do?
- Warm up the ear. This action may spread the infection;
- Taking antibiotics. This approach is ineffective and can cause damage to nerve endings;
- Use of medications “as advised.” The use of drops is prescribed only by a doctor based on examination and test data. Only a doctor will help resolve the issue of prescribing the optimal course of treatment for a child and an adult, taking into account the specifics of the clinical picture.
- “Folk” methods of a radical nature.
Our Heratsi Medical Center employs only experienced doctors with high professional training. We have high-precision equipment: an expert-class ultrasound machine, our own laboratory for working with analyses.
The cost of all services of the medical center can be viewed in the “Price” section or by calling the 24-hour hotline.
What is otitis externa?
This is an inflammation of the tissues of the external auditory canal, eardrum and auricle. Otitis externa is widespread. It is considered acute if it lasts less than 4 weeks, chronic if it lasts longer and/or occurs more than 4 times a year.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Diagnostics
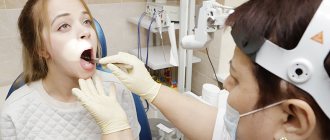
If you have complaints about otalgia, you should consult an otolaryngologist. A preliminary diagnosis is made during a visual examination, when signs of injury to the outer ear, suppuration or liquorrhea, and tumor-like growths in the ear canal are detected. To establish the cause of pain, the examination scheme includes informative instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Otoscopy.
Examination with an otoscope is a simple method for diagnosing otitis media, neoplasms, and boils. The examination reveals skin hyperemia, bulging or retraction of the eardrum, and purulent discharge. If the disease is complicated by destruction of the auditory membrane, during otoscopy the doctor will see the structures of the tympanic cavity. - Audiometry.
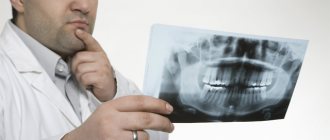
A set of diagnostic methods is prescribed to determine the presence of hearing impairment and its severity. To obtain a complete clinical picture, several types of research are used: speech, tone or computer audiometry. - X-ray of the temporal bone.
X-ray methods allow us to study in detail the structure of the inner and middle ear. X-rays can reveal bone fractures, signs of inflammation or destruction of the mastoid process, and deformation of structures due to the growth of tumors. - Additional methods
. To clarify the localization of the pathological process in case of traumatic injuries to the ear area, a CT scan of the skull and an MRI of the brain are performed. The diagnostic search includes a study of the vestibular apparatus (vestibulometry, stabilography). If there is probable inflammation of the Eustachian tube, it is advisable to perform rhinoscopy and pharyngoscopy. - Laboratory research
. For otitis media, bacterioscopic and bacteriological analysis of discharge from the ear canal is indicated. Children with possible mumps are given serological tests (RSC, ELISA). To verify the diagnosis of a malignant tumor, a histological analysis of biopsy specimens is performed.
Otoscopy for ear pain
Eustachite
Eustachitis is an inflammation of the canal connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx. The degree of pain varies. Characteristic features are:
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- noise and crackling in the ear, the patient hears his voice as too loud with a weakened perception of extraneous sounds;
- sensation of water pouring into the ear.
In the absence of timely treatment, eustachitis becomes chronic, causing chronic exudative otitis media.
Common diseases and symptoms
As medical practice shows, most often painful sensations appear with tonsillitis or sore throat. As such diseases progress, the pain intensifies while swallowing food. In this case, other symptoms also arise, namely:
- weakness;
- sore throat;
- poor appetite.
Painful sensations in the process of opening the mouth are diagnosed with “mumps,” a malignant formation in the larynx or other part of the mouth. With otitis media, pain occurs not only in the ears, but also in the jaw. In this case, it is not recommended to self-medicate, as this will only harm your health.
Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis)
The labyrinth is an organ of hearing and balance, is richly innervated and includes auditory and kinetic receptors, so its inflammation causes:
- severe ear pain and headaches;
- a sharp decrease in hearing, the appearance of noise, crackling, squeaking in the ear;
- dizziness, nausea, loss of orientation in space, horizontal nystagmus.
Labyrinthitis occurs as a result of the penetration of infection in various ways from different parts and cavities of the body:
- from the middle ear with untreated or advanced otitis media;
- with infected meninges during meningitis;
- with blood for diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, herpes;
- damage to the temporal region, the organ of hearing with disruption of the integrity of cells and blood vessels.
The disease requires immediate medical attention.
Possible complications of otitis externa
As a rule, otitis externa does not cause complications and is easily treated. However, if complications do occur, they may include the following:
- temporary hearing loss in the affected ear. Goes away after recovery from otitis media;
- chronic external otitis. It usually occurs when there are difficulties in treating external otitis, for example, in fungal and mixed bacterial-fungal forms;
- spread of infection to deep tissues - cellulitis of the neck, lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis. Similar complications (malignant otitis media) can occur in patients with immunodeficiency conditions, diabetes, and those receiving chemotherapy. Such complications can be life-threatening.