- Physiological causes of gum swelling
- Pathological causes
- The gums are swollen and painful
- The gum is swollen and bleeding
- Flux with pus
- When you need to see a doctor urgently
- How to relieve pain
- How to treat swollen gums
- Rinse recipes
Bad teeth are not always the reason for going to the dentist; often patients come with gum pathologies. The reason for treatment is serious tissue damage with inflammation and suppuration. You should not try to treat them yourself - in order to avoid the development of disease due to gum tumors, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible to prescribe adequate therapy.
Causes of gum swelling
Physiological
Normal gums are pink, painless and of normal size. But sometimes they swell for natural reasons:
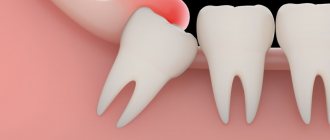
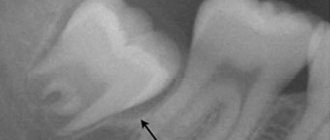
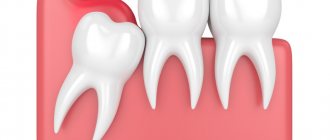
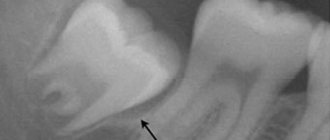
- during teething - in children and adults (wisdom teeth);
- after tooth extraction—slight swelling and redness of the gums is observed for up to 3 days;
- after injury - damage to the soft tissues of the gums leads to their swelling for some time while integrity is restored;
- during pregnancy - under the influence of hormones and due to the redistribution of blood in the body, gums may swell in women carrying a child;
- injury from dental structures - veneers, braces and fillings, if installed incorrectly, come into contact with gum tissue, causing damage to them.
There is no need to panic if the gums of a child aged 1 to 7 years are swollen. At this time, baby or permanent teeth erupt, which may cause swelling and redness in this area. Sometimes small balls appear - cysts. They are safe and in most cases go away on their own over time. If the cyst interferes with tooth eruption, it is surgically removed in dentistry in 1 session. The procedure is performed under anesthesia and does not cause any discomfort.
Pathological
In most cases, gum swelling occurs due to inflammation. Pathological reasons:
- periodontitis - local inflammation above or below the tooth;
- periodontitis - inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
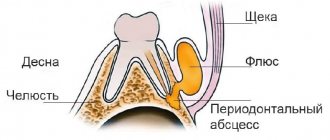
- periodontal abscess - suppuration localized at the edge of the tooth;
- stomatitis - ulcers that appear on the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- secondary infection against the background of immunodeficiency - with HIV or hepatitis, even opportunistic microorganisms can cause oral diseases;
- atypical sore throat - spreads to the gums, the main symptom is that it is painful for a person to swallow;
- Vitamin deficiency C - a lack of vitamin affects the gum tissues, causing them to swell.
Swelling of the gums due to an allergic reaction is also considered pathological. It can develop from an injection of an analgesic during dental treatment or from any irritant to which a person is sensitive.
Causes of edema
Swelling of the gums is a consequence of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the soft tissues, causing infection.
Provoking factors:
- tartar formed due to poor oral hygiene;
- advanced form of caries;
- untreated stomatitis;
- infectious diseases of the throat;
- mechanical damage to soft tissues;
- difficult teething;
- immunodeficiency;
- vitamin deficiency (mostly severe lack of vitamin C);
- herpes virus activity;
- allergies to dental drugs or materials;
- development of purulent processes inside the tooth;
- the presence of tumors on the tooth root;
- gum diseases.
Before making a diagnosis, the dentist will definitely prescribe diagnostics to determine the internal state of the tissues, which will more clearly define the clinical picture and identify the main cause of the pathology.
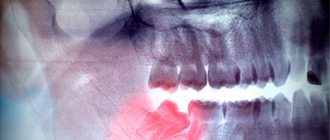
Swelling of the gums with acute pain
When the gums are not only swollen, but also very painful, this may be a symptom of a serious pathology of the oral cavity. Most often, such complaints are accompanied by periodontitis. This is an inflammation of the soft tissues that support the tooth. Other symptoms of periodontitis include:
- increased body temperature;
- suppuration in the area of swelling;
- lack of temperature sensitivity of the tooth, as well as a reaction to sweets.
If swelling in the gums is accompanied by fever, it may be periodontitis. This is due to the fact that the factors in the development of pathology are most often related to infection.
Causes of periodontitis:
- transition of the inflammatory process from the throat or sinuses to the gums;
- penetration of microbes through the dental canal into the periodontium;
- advanced caries;
- poor-quality dental treatment, due to which irritating substances entered the periodontium;
- trauma to the periodontium or the tooth located next to it.
In rare cases, periodontitis develops as a consequence of an immunological reaction, that is, an allergy.
Treatment of gum swelling
The choice of treatment for gum swelling depends on the root cause of the problem. For example, if the gums are swollen due to caries, the disease should be treated as soon as possible. For gingivitis, the main measures are aimed at reducing the number of pathogenic microorganisms. For this purpose, tartar and plaque are removed, and then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
It is important to note that whatever the cause of the swelling, the first thing you should do is visit a dentist. Self-medication only aggravates the problem and complicates subsequent treatment. In addition, by postponing a visit to the clinic “for later,” the patient risks getting a serious complication.
If your gums bleed due to inflammation
Bleeding gums, associated with their swelling, is characteristic of periodontitis and gingivitis. In this case, the tooth does not hurt and does not cause discomfort. The difference between these diseases is that gingivitis occurs primarily. And if this condition is repeated more than once, it is already periodontitis - a pathology with a chronic course. Other symptoms of the disease include:
- bright red gum color with a bluish tint;
- pain at the site of swelling or throughout the jaw;
- swelling of the gums partially covers the tooth.
But the main distinguishing feature of periodontitis is bleeding gums. There are several reasons for this condition:
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- the presence of systemic inflammatory pathologies;
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- Tartar deposits;
- injuries of soft tissues of the oral cavity, occurring with complications;
- long-term treatment with glucocorticoids;
An x-ray is taken to confirm the diagnosis. It shows a noticeable reduction in the interdental septa, and less often, exposure of the tooth root.
Diagnostics
Determining the causes of a symptom is the responsibility of the dentist. Patients may need to be seen by an ENT doctor and an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. Consultations with a neurologist, traumatologist or rheumatologist are less often indicated. The doctor collects complaints, examines the dynamics of the development of the disease, finds out possible provoking factors, establishes the nature of pain, their relationship with the time of day, food intake, and other circumstances.
Based on the survey data, general and dental examination, a diagnostic action plan is drawn up, which may include the following procedures:
- Radiography.
X-ray examination of the upper jaw is used to detect tumors, purulent bone lesions, traumatic injuries, and dental diseases. For sinusitis, X-rays of the paranasal sinuses are performed, and for mastoiditis, images of the temporal bone are taken. - Other imaging techniques
. and MRI are used at the final stage of the examination when radiographic data are ambiguous, to detail the changes identified on the X-rays. They allow you to accurately determine the location and extent of lesions in neoplasms, injuries, purulent inflammation, and other pathological processes. - Otolaryngological techniques
. Along with radiography and CT, anterior rhinoscopy, probing of the maxillary sinus, and diagnostic puncture of the sinus are used in the diagnosis of odontogenic sinusitis. If mastoiditis is suspected, otoscopy, hearing testing with tuning forks, and audiometry are performed. - Punctures, biopsies
. For deep perimaxillary phlegmon, a non-palpable area of fluctuation, puncture of the pathological focus is recommended. Enlarged lymph nodes against the background of space-occupying formations are an indication for a biopsy to exclude lymphatic metastases. - Lab tests
. During inflammatory processes, a general blood test reveals an increase in ESR, leukocytosis, and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. Examination of purulent discharge allows us to identify the causative agent of the process and determine antibiotic sensitivity. Histological or cytological analysis makes it possible to establish the type of neoplasm and differentiate between malignant and benign tumors.
Treatment planning
When gums are inflamed and even your cheeks hurt
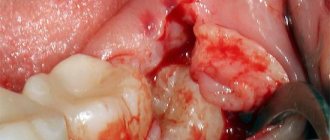
Sometimes the gums not only swell, but a new growth becomes noticeable on it. It is often pale in color due to the presence of pus inside. This is what a periodontal abscess looks like:
- the surface of the neoplasm is elastic and tense;
- swollen tissue around the abscess;
- the palate and cheek swell;
- sometimes the general body temperature rises, more often local;
- swollen tissues of bright red color;
- fluid movement is felt inside the abscess.
This disease is often called "flux". It has a rather characteristic picture. An abscess develops due to lack of treatment for periodontitis: suppuration appears that cannot come out. “Flux” is accompanied by very severe pain and swelling.
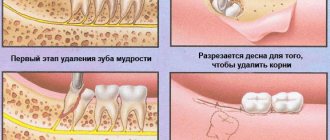
Treatment of an abscess is carried out only surgically and in a hospital setting. Attempts to cure flux at home with lotions or self-opening can result in phlegmon, sepsis and, in rare cases, even death. In the best case scenario, the patient will receive major surgery with pus removed through large incisions in the face instead of a small hole in the gum. Therefore, you should not delay visiting the dentist.
Reason to see a doctor
If you were able to independently determine the cause of the gum swelling (an erupting tooth is visible, an injury is obvious, a tooth was recently removed, etc.) and it does not require the intervention of a doctor, you do not need to go to the clinic. But if the inflamed gum hurts for more than 3 days and there is no improvement in the condition, you should still consult a doctor.
If you have gum inflammation, you need to urgently go to the hospital in several cases:
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth and pus was found;
- not only the gums are swollen, but also the cheek;
- when you tilt your head to the painful side, you feel heaviness;
- there is a high temperature;
- swollen tissues are very different in color from healthy ones (white and yellow tumors indicate suppuration, and bluish and burgundy shades indicate blood stagnation);
- the pain seems to pulsate and is not relieved by analgesics.
Even in the absence of these symptoms, but if the cause of gum swelling is unknown, it is worth visiting a specialist. This will help avoid dangerous complications, as well as quickly alleviate the condition, relieve or reduce pain.
First aid for swollen gums
Under no circumstances should a heating pad be applied to an inflamed gum! This is dangerous due to the rapid spread of infection and the development of complications.
To “live until the morning” when you can go to the doctor, you can take several actions that can alleviate the condition:
- apply cold to the sore side - this will constrict the blood vessels and temporarily relieve the fever;
- take an analgesic - but only while you sleep at night; in the morning you need to come to the doctor without pain relief, so as not to erase the picture of the disease;
- drink an antipyretic - if a high temperature prevents you from falling asleep, you can bring it down, but don’t forget to mention it in the morning at the doctor’s office;
- rinse your mouth with an antiseptic - this will slightly slow down the spread of inflammation;
- use a spray with lidocaine on the painful area - this will temporarily relieve the pain.
All of the above measures can only be used as temporary measures. Only a doctor can prescribe adequate treatment after an in-person examination.
How to treat swollen gums
Treatment of inflamed gums begins with identifying the cause of the disease. To do this, an X-ray of the jaw and an examination of the oral cavity are performed.
Further tactics depend on the established diagnosis. If surgical intervention is necessary (opening an abscess, removing a cyst), it is performed immediately. The patient is anesthetized in the dentist's chair, and then all necessary manipulations are performed.
After surgical treatment, maintenance drug therapy is prescribed. It allows you to avoid the development of complications. Most often, the patient is prescribed rinsing with an antiseptic solution and taking anti-inflammatory drugs. Antibiotics are sometimes recommended to prevent bacterial complications. They should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor, and exactly the drug that is indicated in the prescription. This is important to achieve a guaranteed positive effect.
Some drugs do not combine with each other. Therefore, uncontrolled use of medications can harm the patient himself. If you choose the wrong antibiotic, the bacteria will not only not die, but will also develop resistance to the drug. Then it will take a long time to select a suitable remedy, which will complicate the patient’s life - it will no longer be possible to quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Rinse recipes
The patient's attending physician should prescribe rinses. They are not allowed for all diseases. After surgical treatment, rinsing too hard can cause the suture to come apart. An infection or food particles will get into an open wound, which will cause new inflammation and suppuration.
It is impossible to completely cure swollen gums with rinses. But they are advised to be combined with drug treatments to alleviate the condition and enhance the effect of the drugs.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula, lemon balm, sage, St. John's wort. Some components can cause allergies, so you need to be careful with them. However, they have a mild anti-inflammatory effect and can help relieve swelling and reduce inflammation.
- Propolis tincture - dilute it with warm water and rinse your mouth 2 times a day. The product helps against ENT diseases (sore throat and sinusitis), which often develop into inflammation of the gums.
- Soda and salt - add 1 teaspoon of each powder to a glass of warm water and stir. The product has a wound healing effect and helps stop bleeding gums.
In addition to rinsing, lubricating the area of inflammation with tea tree or fir oil is also effective. They have an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect. However, they should not be applied to the site of suppuration. It is also worth considering the risk of plant allergies.
There are many reasons for gum swelling, not all of them are obvious. Only a doctor after diagnosis can figure out what caused the inflammation. Independent attempts to cure the disease often lead to serious complications, so you should not expect that the swelling on the gums will go away on its own. It is better to visit a doctor and make sure there are no risks or get competent and timely treatment.
What to do?
First of all, you need to make an appointment with a dentist and conduct an X-ray examination, as a result of which you can determine the true cause of the tumor, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an individual treatment plan. Most patients are prescribed antibiotics or antiseptic drugs. Do not forget that treatment with traditional methods, which promise a quick recovery and supposedly relieve symptoms in a couple of hours, is not acceptable, since it can cause even more harm and lead to irreversible consequences. As a last resort, to relieve pain and reduce swelling, you can rinse your mouth with warm and clean water, but under no circumstances drink hot drinks or massage the sore spot.
In especially severe and advanced cases, surgical intervention will be required: a dental surgeon in Minsk makes an incision in the gum, removes pus, and, if necessary, removes the diseased tooth. All operations are performed under anesthesia, but sedation will be more effective in this case, allowing treatment to be carried out while you sleep. While the patient sleeps peacefully, without feeling discomfort or pain, all procedures are carried out as accurately and quickly as possible. It is safe for the body and is often used even in pediatric dentistry.
undergo dental treatment under anesthesia using drug sedation at the Minsk Family Dentistry Center. High-level specialists, modern equipment that meets European quality standards, affordable prices and an individual approach to each patient - we guarantee high-quality treatment without pain and complications. But you can only maintain the beauty and health of your teeth through joint efforts, so don’t forget about prevention: regular teeth cleaning, dental checkups at least once every six months, as well as timely treatment of oral diseases - together we can create the perfect smile!