What is tooth flux?
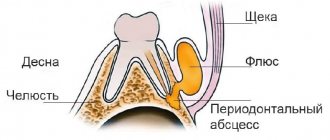
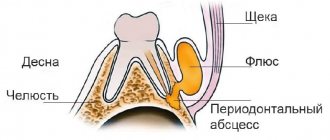
Flux, or, in dentist's language, periostitis, is a very unpleasant pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the periosteum and soft tissues. The causes of flux on the gums can be different: trauma, gum disease, poor-quality dental treatment - all this can lead to a complication in the form of periostitis. The localization of the disease does not depend on the area of the jaw: flux of the upper and lower teeth occurs equally often.
Flux under a tooth (or above a tooth, if we are talking about the upper jaw) visually resembles an inflamed sac. However, this is far from the only possible manifestation of periostitis. There is also a serous form, when the periosteum becomes inflamed as a result of trauma and damage, as well as one of the most unpleasant types - diffuse, when the infection is localized in different parts of the jaw, which requires extensive surgical intervention with the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
Treatment of gum inflammation at the Eurodent clinic
Self-medication in case of gum disease is only permissible as a temporary measure to relieve pain. To ensure that the disease does not become chronic, you should definitely contact a dental clinic. When you see a doctor, you will be given an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment will be prescribed.
The Eurodent clinic operates 24/7, so you can contact us for qualified help at any time. We remind you that the initial consultation is free.
We are waiting for you at the following addresses: Zheltoksan, 83, ug.
st. Aiteke bi and Zhandosova, 42, corner. st. Aimanov. Based on: 6 votes
Symptoms of gumboil
Flux on the gums in adults occurs much more often than in children (approximately 80-90 percent of all cases). A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it does not go unnoticed. This is one of the most unpleasant diseases, causing severe discomfort. The most striking symptoms are the classic purulent flux.
Symptoms
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues. At the advanced stage, the side of the face on which the flux is diagnosed swells.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Discomfort and pain when eating and talking.
- Flux of the lower tooth (in the molar area) can lead to numbness of the lip and part of the chin.
- Weakness, headache, fever.
How to remove swelling of the cheeks and gums
If the tumor does not cause particular concern, then it is a natural phenomenon after tooth extraction.
There are ways to relieve pain and reduce swelling, as long as it is not harmful to health.
- It is necessary to apply cooling compresses to the inflamed cheek several times during the day, this can be a bottle of cold water, ice in a cloth, a damp towel, which should be kept for twenty minutes, periodically cooling it in cold water. You will immediately feel relief and notice how the tumor decreases in size.
- People with high blood pressure are more susceptible to post-operative swelling. They are recommended to take sedatives and blood pressure-normalizing medications after tooth extraction.
- Conventional anti-edema products can relieve swelling well - gels, creams, ointments that can be applied to the outside of the cheek.
- To relieve pain, which is inevitable after complex removals, you can take a painkiller (except aspirin) or an anti-inflammatory drug and lie down to rest.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
When to see a doctor
If you have followed all the rules, carried out all the procedures aimed at reducing swelling, and your condition continues to worsen, then this is a sure sign that you need to urgently consult a dentist. Immediate medical attention is required if:
- the next day the swelling increased, and the pain did not decrease;
- the temperature has risen, general health has worsened;
- opening the mouth is accompanied by painful sensations, and the smell of rotting from the hole is felt.
All these symptoms should prompt an immediate visit to the dentist to avoid serious consequences.
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
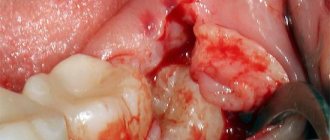
Surgical procedures
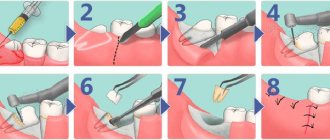
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Causes of periostitis
In addition to advanced caries, swelling of the cheek due to a tooth can be caused by other factors.
Inflammation of the gums
Periodontal disease can serve as a starting point for infection to penetrate the periodontal tissue. This diagnosis requires a thorough examination and often long-term treatment.Reaction to poor-quality canal filling
If depulpation is carried out without modern diagnostic equipment, the doctor may not completely clean the root canals. As a result, the remaining nerve tissue becomes inflamed and leads to such unpleasant complications as periostitis.
Inflammatory reaction to tooth extraction
Any tooth extraction is considered a minor surgical operation. It leaves an open wound that can become infected. In this case, the inflammatory process in the tissues occurs quickly and with complications in the periodontal tissue and periosteum.
Cyst formation in periodontal tissues
A tooth cyst can develop in a person over several years, and then at one point this process can spread to the periosteum tissue. If the spread of infection has gone so far, then the most likely option is to remove the diseased tooth, cleanse the affected tissues, and thoroughly treat all tissues with antiseptic drugs.
Infection due to injury
As a result of an open fracture of the jaw, pathogens can penetrate the tissues near the tooth, both soft and bone.
Infection through lymph nodes
In rare cases, the infection enters the periosteum through blood vessels or through inflamed tissue in the lymph nodes, such as with tonsillitis.
An indirect factor in the occurrence of periostitis may be concomitant diseases, decreased immunity, sore throat, acute respiratory infections, stress, etc. By the time a tooth hurts and a cheek swells, there is probably an accumulation of pus in the periodontal tissues. This process is quite dangerous for the body, as it can be accompanied by symptoms of acute inflammation:
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, body fatigue;
- headaches, local pain in the area of inflamed tissue;
- formation of a purulent fistula with access to the oral cavity or through the soft tissue of the cheek;
- increased pain symptoms at night or when trying to chew.
If caries can be ignored, then with periostitis, patients simply “fly” to the dentist for help. The course of the disease can be so acute that there is no way to tolerate it. The specialists of the LeaderStom network of clinics have extensive experience in treating periostitis. With such a diagnosis, therapy is required not only for the tooth itself, but also for the entire body. Therefore, be prepared to follow all doctor’s orders, take antibacterial medications and regularly rinse your mouth every half hour.
If you have a toothache or a swollen cheek, it is recommended to immediately seek help from a dentist, but if this is temporarily unavailable, the following recommendations will help you cope with the pain.
- If your cheek is swollen and your tooth hurts, you should not apply warm compresses or bandages to your face, as heat promotes even greater inflammation of the dental tissues and can cause complications.
- A cold compress should be applied to the affected side of the face.
- Be sure to take a pain reliever.
- Rinse your mouth several times with infusion of chamomile, sage, and St. John's wort.
- It is strictly prohibited to take anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics without a diagnosis of “periostitis” and a doctor’s prescription.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Why is tooth flux dangerous?
An inflammatory process of this type tends to develop and, as it spreads, affects deeper layers of tissue. If left untreated, flux often develops into phlegmon - a serious purulent inflammation that has no definite boundaries. The most severe forms of flux provoke the development of sepsis, which can lead to infection of the entire body and even death. It is important not only to know how to cure gumboil and visit the dentist on time, but also to follow a number of preventive measures so that the likelihood of complications developing is minimal.
- Regular and high-quality hygiene.
- Treatment of caries at the initial stage. Flux, dental cysts and other complications often arise due to untreated pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Preventative visits to the clinic to assess the condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning.
Inflamed gums: causes of the disease
The causes of inflammatory processes in the gums are external and internal. External ones include:
- Damage to the gums when brushing your teeth with a hard brush;
- Trauma from solid food;
- Accidental injury with a toothpick;
- Various dental diseases;
- Receiving microtrauma when installing braces or dentures;
- Insufficient or incorrect oral hygiene.
The internal reasons for which the gums become swollen and painful are “systemic failures” in the body:
- Diseases of internal organs or entire systems - gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, endocrine, etc.
- Immunodeficiency, hereditary diseases;
- Chronic vitamin deficiency;
- Reaction to medications;
- Pregnancy.
Any of these reasons can cause gum diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease.