Discoloration of gums is a fairly common problem with which patients often seek help from a dentist. The seriousness of this disease lies in the fact that the blue color of the gums can indicate not only some dental disease, but also the presence of severe somatic pathologies. Diagnosing the disease at an early stage and promptly starting treatment is the key to quickly getting rid of the disease without developing any complications.
Important information about diseases and factors that cause blue gums in adults
When blue gums near a tooth are discovered, or generalized (along the entire row) changes in the shade of the oral mucosa become noticeable, then there is no time for jokes. Many are beginning to wonder what this might be connected with. And we will tell you about the most common – dangerous and not very compelling reasons for this phenomenon.
The reasons for blue gums can be different.
Diagnosis of gum cancer
Oncopathology of the oral cavity is visual, that is, diagnosed during a routine examination without the use of any equipment.
During the initial examination, cells are scraped from the wound for cytological analysis, or, in the absence of an ulcer, the tumor is punctured with a thin needle. If possible, a part of the tumor is “bitten off” with a special instrument - this is a biopsy for histological analysis. The diagnosis of cancer is established solely by the result of a biopsy; cytology allows only to suspect the disease.
After morphological confirmation, an ultrasound of the oral cavity is performed, which explains the relationship of the neoplasm with the surrounding tissues, primarily with the bone and blood vessels, and the CT scan clarifies the condition of the entire anatomical region.
Next is the search for metastases: ultrasound of the neck, CT scan of the lungs or MRI.
Possible dental causes
Some dental patients notice that they have blue gums after tooth extraction. Indeed, this is not uncommon. Often the phenomenon is caused by traumatic effects on tissues, vessels and capillaries during surgical procedures. And such a symptom may not necessarily occur only after root removal, but also after procedures such as anesthesia, incisions, suturing, and gum retraction. Changes in mucosal swelling can often be seen after the following operations: gingivectomy, vestibuloplasty, osteoplastic procedures, implant installation.
Important! After surgery, blue gums in an adult are most often discovered due to too large-scale intervention or traumatic actions of the doctor. And also if the patient has a history of various chronic diseases, for example, hypertension, diabetes, or poor blood clotting. In this case, there is a high risk of hemorrhages in the tissue and the formation of various hematomas.
If there is blue gum near a tooth, this may be due to other dental factors:
- poor-quality prosthetics: after installing structures that do not correspond to the anatomical characteristics of the patient, or are too “driven” under the gums, hematomas may form, since the tissues are compressed too much and cease to be properly supplied with blood,
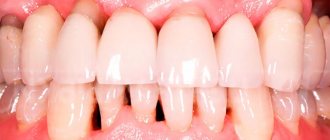
- the presence of crowns with a metal component in the mouth: materials based on alloys of base metals can, over time, interact with saliva and oxidize, leaving blue gum above or below the tooth. Blue gums can even appear from a metal-ceramic crown,
Gums may remain blue after whitening
- teeth whitening carried out by an inexperienced dentist, cosmetologist, or, more often, by the patient himself (for example, at home, using inappropriate means and folk recipes). In the process, a doctor or home “experimenter” may leave soft tissues without proper protection, apply too much product and not remove the excess, overexpose the composition and thereby provoke a burn,
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease,
- purulent processes in the affected teeth, mucous membrane, bone tissue: for example, gumboil, enlarged cyst or granuloma, abscess, osteomyelitis,
- the presence of removable dentures in the mouth: at the initial stage, they can put pressure on the mucous membranes, injure and irritate them, and impair blood circulation in the tissues. During operation, such problems arise in the absence of timely corrections and against the background of inevitable atrophy of the jaw bone,
- complications after surgical interventions: for example, alveolitis after tooth extraction. This may also be inflammation of the tissue around the implant, indicating mucositis or peri-implantitis,
- cervical caries.
“5 years after wearing a metal-ceramic bridge, my gums became blue, and they become exposed when I smile. It was very ugly. After that, she stopped opening her mouth wide at all. She hardly smiled. Complexed. And when the bridge cracked a few years later, the dentist suggested replacing it with zirconium dioxide so that there would be no blue discoloration. It cost me a lot more, but now everything looks very natural and doesn’t interfere with my smile.”
Marina Olegovna, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
Blue gums after installation of metal-ceramic crowns
Gingivitis: my gums hurt
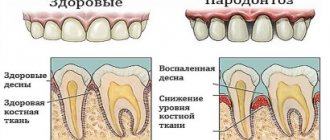
The process, which is characterized by gum inflammation, swelling, redness and bleeding, is called gingivitis and is one of the most common periodontal diseases in both children and adults. Only 3% of people can boast of absolutely healthy gums. How to get into such a small percentage of lucky ones? The answer is simple - follow the necessary measures to prevent gum inflammation, regularly visit the doctor and not let even seemingly harmless signs of an incipient disease take their course.
Gingivitis is the last of all diseases in periodontology in which the inflammatory process can still be stopped. Next comes periodontitis, a disease in which inflammation spreads to other periodontal tissues. From this point on, treatment is based only on bringing the disease into remission and attempts to relieve symptoms as much as possible at the time of relapses, as well as in the future when it is necessary to resort to tooth extraction. Therefore, gingivitis in children and adults requires increased attention in order to avoid serious periodontal problems.
What internal diseases may the symptom indicate?
If you have blue gums, then the reason for this phenomenon is pathological changes occurring in the body against the background of various systemic diseases. Thus, due to diseases of the blood, heart, and metabolic disorders, blood vessels become thinner and capillaries become fragile, and internal local bleeding occurs.
Doctors say that a similar symptom sometimes occurs against the background of iron deficiency conditions, that is, with anemia. For kidney disease and thyroid problems. And in diabetes mellitus, when the processes of nutrition and tissue regeneration are disrupted, even minor traumatic injury can lead to the formation of long-term non-healing hematomas.
Forecast
An individual prognosis for the course of the disease is based on the size of the neoplasm and the depth of its penetration deep into the jaw, involvement of vessels and nerves in the conglomerate.
The degree of damage to the lymph nodes affects life expectancy; metastases almost halve the likelihood of cure. Much determines the aggressiveness of cancer cells; low differentiation is not in favor of the patient.
Specific percentages by years of survival are unknown because the incidence is low and statistically gum cancer is not distinguished from the group of oral carcinomas.
Other factors leading to the problem
Another reason why an adult’s gums may turn blue is a burn. It is not difficult to get it if you eat too spicy foods, hot soups and sour drinks. A bad habit such as smoking can also contribute to this.
The symptom may indicate chemical burns, when delicate tissues are damaged due to the use of aggressive compounds unsuitable for the oral cavity. For example, alcohol, manganese, iodine, peroxide.
Very often, pathology occurs due to bruises and injuries received in the area of the maxillofacial apparatus. And the safest reason that can explain the blueness of mucous membranes is the consumption of drinks and dishes with food or natural dyes that give pigment to the teeth, gums and tongue. For example, blueberries, blackberries, soda pop, plum wine and plums. Fortunately, you can easily get rid of this problem by thoroughly cleaning your mouth with a brush and paste.
Possible associated symptoms
Typically, blue gum above or below a tooth is not the only symptom that something is wrong. Typically, people with a similar problem note other warning signs:
- mucous membranes swell and begin to bleed, may move away from the necks of the teeth,
- itching and soreness in the gums occurs: the discomfort intensifies with pressure, any mechanical impact, while eating food,
- a nearby tooth hurts, it can also become mobile,
- body temperature rises,
- there is a strong foul odor coming from under the gums, pus may be released,
- Plaque intensively accumulates on the necks of teeth.
Symptoms
Changes in gum color are usually accompanied by the following complaints:
- pain when brushing teeth and chewing food;
- itching;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- periodontal bleeding;
- accumulation of abundant plaque on the teeth;
- formation of tartar.
Symptoms depend on the cause of the disease and on the individual characteristics of the body. Eliminating the cause of gum discoloration is the first thing to start treatment with.
When does it make sense to go to the doctor?
Of course, in any unclear situation this will be the best solution. However, many people prefer to wait a few days, observe the condition of their blue gums and evaluate their overall health. And this is not prohibited if you do not have a rapid increase in body temperature and positive dynamics are observed.
In what cases should you urgently consult a doctor?
In cases where blue gums persist for longer than 3-5 days, with severe pain, high fever, loss of appetite, a change from a local process (when the gums turn blue in the area of 1 tooth) to a generalized one (the pathology spreads to neighboring elements of the row, increases in size, grows ) you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Risk group
Knowledge of risk factors allows you to calculate a likely “candidate” for the development of oral cancer and timely modify behavior towards a healthy lifestyle, eliminating actions that are hazardous to health.
High-risk group for malignant processes in the gum area:
- People who smoke have celebrated their fortieth birthday, because the frequency of neoplasms increases with age and the “control point”, after which the incidence doubles with each decade of subsequent life, is precisely 40 years.
- Young people with a full range of risk factors. Before the age of 40, carcinomas of this localization are rare, but early introduction to tobacco simultaneously with chewing betel or nas, with persistence in the mucosal cells of the human papillomavirus type 16, significantly increases the chances of cancer.
An extremely high-risk group when the prospect of becoming a cancer patient over time is very high:
- Suffering from precancerous processes - leukoplakia and erythroplakia;
- Older people who smoke, use dentures, and the older they are, the more likely malignant transformation is;
- Adults with a hereditary predisposition, which is identified by the presence in the family of patients with oral carcinomas.
All patients at risk should visit the dentist at least twice a year and undergo treatment for precancerous processes.
What can dentists offer in the fight against gum pathologies?
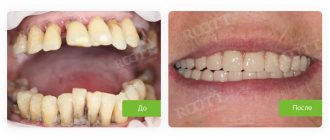
When a person discovers blue gums, he probably asks the question: what to do? The first step is to see a dentist. The doctor will examine your mouth and identify possible problems.
If the cause is poor-quality or incorrectly installed crowns or dentures, they will need to be adjusted or replaced. In case of dental diseases and detection of purulent processes against this background, it may be necessary to open, drainage and antiseptic treatment of tumors, clean the root canals, apply medicated pads and install a sealed filling at the end.
In case of periodontal inflammation, a specialist will definitely prescribe comprehensive treatment[1]. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms, restoring gum tissue and preserving teeth, which, in advanced stages of periodontitis and periodontal disease, can become loose and fall out. What procedures will be required: professional oral hygiene to remove bacterial plaque, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy for gums in the form of rinses, lotions, antibiotic therapy. Some patients are also prescribed plasma lifting and periodontal gels with growth factors.
Expert opinion
Marina Igorevna Tarabanovskaya
Specializations: Dentist-therapist, periodontist
Experience: 10+
“In case of periodontal diseases, it is important not only to undergo treatment, but also to adjust the lifestyle that the patient usually leads. It is necessary to follow a certain diet, stop smoking, and purchase a suitable brush, toothpaste and mouthwash for daily hygiene. And be sure to undergo professional hygiene and examination by a dentist at least twice a year. Otherwise, the pathology will constantly worsen, and the patient risks losing all his natural teeth ahead of time.”
Diagnostic tests
- Schiller-Pisarev test
This test is based on determining the level of glycogen in the gum. Its amount increases significantly during inflammation, while healthy gums do not contain glycogen. Lubricating the inflamed gums with Schiller-Pisarev solution gives a color change reaction from light brown to brown. This research method is used to make diagnoses of both periodontitis and gingivitis.
- Assessment of oral hygiene level
A solution (2 g of potassium iodide, 1 g of crystalline iodine, 40 ml of distilled water) is applied to the outer surface of the six lower front teeth.
The assessment is carried out using a five-point system and each tooth is assessed separately:
- 5 points – complete staining of the entire tooth surface;
- 4 points – staining of ¾ of the tooth surface;
- 3 points – staining of half the tooth surface;
- 2 points - staining of a quarter of the tooth surface;
- 1 point - absence of any staining of the tooth surface.
Then the scores of all examined teeth are summed up and divided by their number (usually the test is carried out on six teeth). This is how the hygiene index is obtained.
As a result, the quality of hygiene is assessed:
- 1.1-1.5 points – good hygiene index;
- 1.6—2.0—satisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.1—2.5—unsatisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.6—3.4—poor hygiene index;
- 3.5-5.0 - very poor hygiene index.
- Vacuum test according to Kulazhenko
Using a Kulazhenko vacuum apparatus, it is possible to determine the time of hematoma formation when a vacuum is applied to the gum area. Typically, the test is carried out in the incisor area by placing a tube of the device on the gum. The formation of a hematoma in 60 seconds indicates the normal condition of the gums, while the appearance of a hematoma in 29-30 seconds signals an inflammatory process.
- Oxygen tension in gum tissue
The sensor of the device is applied to the gum, and the device records the level of tissue hypoxia. Reduced oxygen tension indicates a prolonged inflammatory process.