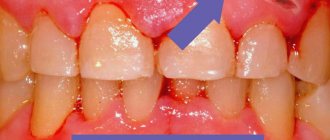
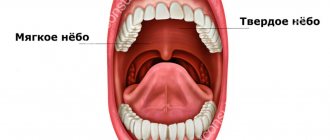
The gum has a pale pink color; normally it is not felt at all. The gums in the area of the tooth can be fixed or mobile. Between the teeth, the gum grows into the interdental spaces, filling them, thereby preventing food from getting stuck between the teeth.
For what reasons can gums hurt:
- due to the eruption of wisdom teeth
- due to food getting between teeth
- due to gum mobility
- due to gum injury
- due to gum suppuration
- due to tooth extraction
When a wisdom tooth erupts, the gum covering this tooth begins to thin out, often food gets between the gum, tooth and cheek and this also causes pain in the gum. In the oral cavity, the gum becomes red, swollen, and when touched it hurts terribly.
Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Causes of scratches on the gums
Gums play a big role in the development and condition of the dentition. Gum tissue, surrounding the surface of the teeth, protects them from infection. Therefore, any damage to the mucous membrane of the gums can lead to destructive processes in the periosteum and infect the periodontium.
Very often, the causes of scratches on the gums are quite banal; they appear due to carelessness:
- When using a hard toothbrush, damage to the mucous membrane occurs, leading to microtrauma.
- The habit of chewing and gnawing foreign objects (pens, pencils, matches, toothpicks). Careless movement can injure your gums.
- Eating solid foods (lollipops, grilled candies, crackers, seeds).
- Damage to the gums by a medical instrument during treatment, tooth extraction, or when installing a prosthesis.
You can scratch your gums with the edges of teeth that are broken or poorly polished. Poor-quality dentures also injure your gums.
However, children are much more likely to injure their gums. Many babies often have the habit of sucking their fingers, pulling toys into their mouths, while damaging the mucous membrane with a nail or a sharp edge. As a result, a painful wound remains on the gum.
A child can get a scratch if:
- eruption of the first tooth, the sharp edge of which can injure delicate tissue;
- accidental bite with the primary incisors located in the front;
- independent attempts to eat with a spoon or fork;
- unexpected falls during the game.
Typically, a scratch on the gum does not cause much discomfort and heals quite quickly. But if pathogenic bacteria get into the wound, the cut can become inflamed and lead to complications that will require long-term treatment.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
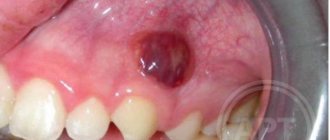
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Mucosal injury
For any person, the cause of pain in the mouth can be ordinary injuries.
Trauma is often the cause of mouth pain.
For example:
- eating something too hot/cold. This injures the mucous membrane, and pain quickly appears in it. Inflammation indicates the presence of injury to the mucosa, caused by temperature exposure, and at the same time incompatible with its integrity. Eating something very hot can cause injury to both the palate and the tongue, as well as the throat;
- rough food, which can leave scratches on the roof of your mouth and on the inside of your cheeks. This causes pain and burning to appear after a day or two;
- A child has more ways to damage his or her mucous membrane than an adult. The baby can scratch it with his thin nail or put something in his mouth, for example, a toy. And if the child is somewhat older, his mucous membrane can be damaged by lollipops and chips.
When choosing a remedy for pain, it is very important to pay attention to the nature of the injury:
- in case of a burn, it is useful to rinse your mouth with warm water and then use Metrogil Denta dental ointment;
"Metrogil Denta"
- In case of mechanical damage, it is recommended to immediately use antiseptics by rinsing your mouth with them. For an adult, it is useful to rinse your mouth with a mixture: 10-15 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide per glass of water. Decoctions of calendula and chamomile are also good. Also good are the drugs “Rotokan” and “Miramistin”, which fight infection as well as inflammation.
"Miramistin"
The main rule: no self-medication! Therapy must be prescribed by a specialist. Otherwise, you can make the situation even worse. So if symptoms appear, it is recommended to visit a doctor. He will prescribe the best treatment for a particular situation.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
How does pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms depend on how far the gum has receded from the tooth. Most often patients complain of:
- increased bleeding and soreness of the gums;
- bad breath that cannot be eliminated with standard hygiene products;
- taste of pus;
- separation of purulent masses from the inflammatory focus;
- the appearance of deep periodontal pockets;
- loosening of individual units.
In the first days of the disease, patients may not experience any significant discomfort. They are just beginning to notice that in certain areas of the jaw the tissue seems to have sagged and become less voluminous. Because of this, the crown part of the tooth, on the contrary, looks elongated.
If the gums have peeled off, there is no need to try to do anything on your own. Without qualified help, it will still not be possible to cope with the recession. Postponing competent therapy until later is fraught with even more serious violations.
Acute and chronic injuries
Acute gum injuries include injuries resulting from soft tissue injury:
- Too hard bristles of a toothbrush
- Fish bone
- toothpick
Bruised gums are possible from falls and fights. Thermal burns are also possible if you consume too hot food or drink.
Chronic injuries include those that a person receives as a result of prolonged exposure to irritating agents on soft tissue:
- Food constantly stuck between teeth
- Poor quality filling that extends beyond the tooth
- Orthodontic devices (braces, plates)
- Poorly fitted clasp on a prosthesis
- Edges of a crown on a tooth
Mechanical injuries may be accompanied by slight bleeding. And with chemical and thermal injuries, erosion forms at the site of damage. With chronic injuries, purulent discharge may form on the gums. In advanced cases, surgery may be required. But more often local treatment is enough. Minor injuries can be treated with special healing balms prescribed by the dentist.
Dental pathologies
The infection can be acquired by not following the rules of personal hygiene, as well as by contact with an already sick person. The most common pathologies are listed below.
Stomatitis
There are several types of stomatitis that can cause pain in the oral mucosa.
There are several types of stomatitis
| Type | Description |
| Catarrhal | Mild inflammation of the oral mucosa. Appears due to lack of oral hygiene and the formation of tartar. It also occurs as an allergic reaction to certain medications. With it, the oral mucosa becomes red and swollen, and may be covered with a whitish coating. If you eat anything hot/spicy, pain, itching, and burning occur in the mucous membrane. |
| Acute herpetic | Occurs due to the herpes virus. The younger and younger generations are at risk. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. Sores covered with a yellowish coating form on it. Pain is felt in the mouth, saliva begins to be produced more abundantly. The patient feels unwell, does not want to eat, and feels worse. If the pathology takes a severe form, the temperature rises to 40 degrees. Then the patient begins to feel sick, vomit, and have a headache. The mucous membranes in the mouth become covered with ulcers. |
| Ulcerative-necrotic | Appears due to microorganisms - spindle-shaped rods, as well as spirochetes. They are found in periodontal pockets and under the gum near wisdom teeth that have not fully erupted. If the immune system does not work at full strength, the pathology becomes active, resulting in stomatitis. It first touches the gums, after which it is possible that it will spread to the entire oral mucosa. Large ulcers appear, diseased areas of the mucous membrane die off. A gray-green coating appears on the gums and ulcers. In this case, the patient feels pain in the mouth, which becomes stronger during eating. The gums begin to bleed, an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, salivation becomes more abundant, the patient feels worse, and the temperature rises to 38-40 degrees. |
| Aphthous | It develops due to allergies to certain foods, stressful situations, hormonal imbalance, insufficient intake of certain substances by the body (iron, vitamin B12, folic acid), systemic pathologies, injuries, for example, damage to the mucous membrane by one or another “chemical”, failures in the functioning of the immune system. The slightest trauma to the mucous membrane is enough for stomatitis to begin to develop. In this case, single/multiple ulcers appear on the tongue, floor of the mouth, soft part of the palate, as well as on the inner surface of the lips and cheeks. Before the formation of visible signs of aphthous stomatitis, the patient feels pain. Ulcers also create discomfort. Moreover, it is so strong that a person cannot eat or swallow normally, even speaking causes pain. |
| Traumatic | The cause is mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa. This usually affects the gums and tongue. Redness and swelling appear in the injured area. Among the forms of this type of disease are Bednar's aphthae, also known as aphthae (ulcers) of newborns: in a baby up to one year of age, small round ulcers appear on the mucous membrane approximately in the center of the palate. The reason for their occurrence lies in the careless actions of adults: lack of caution when wiping the mouth or causing injury with a rough nipple while bottle-feeding. If the case is severe, some of the ulcers may merge, creating a large wound surface resembling a butterfly. A yellow coating often appears on it. Now medicine knows methods to prevent complications. |
- Allergic stomatitis
Gingivitis
This disease is inflammation of the gums. They hurt while eating, talking, and the pain is felt even when at rest. The likelihood of contracting this pathology does not depend on age category.
Gingivitis – inflammation of the gums
With gingivitis, the gums turn red and bleed, pain appears in the mouth, and it begins to smell unpleasant. This disease is treated in a dental clinic.
Herpes
This pathology, which occurs in the mouth, is a consequence of the spread of the herpes virus throughout the body. No part of the mucous membrane in the human body is protected from it. But usually this disease manifests itself on the lips.
Small ulcers form on the mucous membrane of the mouth and in the throat, causing pain. At first these are bubbles with yellow liquid. When they burst, they leave behind wounds. They also cause discomfort.
Herpes most often forms on the lips, however, due to this pathology, pain in the oral cavity may occur
The same sensations are felt at any degree of damage. It is very painful to touch the source of the pathology, to eat, or just to drink. Herpes is treated by an infectious disease specialist.
Here it is important to first remove the inflammation, and only then begin the actual treatment. At home, it is useful to rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile and calendula. It would not be superfluous to use Miramistin and chlorhexidine solution.
To defeat the disease, the doctor prescribes specific medications for external or internal use. Self-medication here, as with many other health problems, is harmful.
Important ! Only a specialist has the necessary experience needed to correctly diagnose the disease and determine how far it has gone.
You need to see a doctor who will prescribe appropriate medications
Neuralgia
If inflammation damages nerve endings, the pain spreads widely. With neuralgia of the muscles of the face and jaw, discomfort in the mouth is also possible. Then the pain is felt when the jaw works, which happens while eating, speaking or yawning.
In this case, symptoms include more pain during certain activities. The source of pain is inside the tissue, in the muscle, not on the mucous membrane. A visual inspection will not show anything here.
- Stomatitis medicine for children
With this problem, therapy comes down to restoring damaged nerves and muscles. To make a correct diagnosis, you should undergo an x-ray of the affected area of the face, and also consult with an oral surgeon.
For neuralgia of the muscles of the face and jaw, it is also recommended to consult an oral surgeon
Next, the specialist prescribes therapy, focusing on how severe the case is. Neuralgia is usually treated using antibiotics, as well as some specific remedies.
Worth knowing ! It happens that patients are hospitalized.
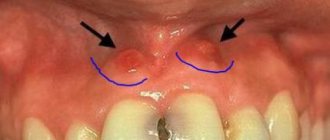
Sialometaplasia
Benign lesion of the palatine salivary glands. At first, you can suspect something is wrong by noticing not too large seals on the hard palate, similar to nodules. The growth of the affected areas occurs quickly, and their dimensions can reach up to 20 mm. With this pathology, the patient feels aching pain and pulsation where the ulcers are localized.
People aged 40-50 years are susceptible to this pathology. Moreover, more than half of the patients are men. The disease occurs due to one of the following reasons:
- damage to the mucosa;
- vasospasm;
- injections for dental procedures.
Sialopetaplasia is a benign lesion of the palatine salivary glands.
Important ! With this pathology, the most important thing is to make a correct diagnosis. This is because its symptoms can easily be confused with other ailments.
Be that as it may, you should always identify the very cause of pain in the oral cavity. Only then can a specialist prescribe the necessary therapy and give certain recommendations on how to keep the mouth clean and prevent relapses.