Content:
- Should baby teeth be treated?
- The most common dental diseases in childhood
- Treatment of baby teeth
- Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
- What to do to avoid having to treat baby teeth
Parents often shake their heads negatively when asked whether baby teeth need to be filled. It seems to them that it is not at all necessary to do this, because very soon the temporary bite will be replaced by a permanent one. Dentists categorically disagree with this opinion. Doctors say that you need to take care of the health of your milk units just as thoroughly as your primary ones.
An eternal problem: is it necessary to treat temporary teeth in children?
Some parents do not see the need for such treatment, because they believe that after 6 years, baby teeth will gradually fall out and be replaced by permanent ones. But even one temporary tooth affected by caries and not treated in a timely manner can provoke unpleasant consequences that will create problems in adult life.
However, 5-6 year old children are often brought to see the dentist with “acute pain” and one or even several front teeth that have been destroyed right under the gums. The parents claim that so far they have not caused any problems, and ask the doctor to remove the problematic baby tooth.
Let's figure out why the doctor makes a decision on the need to remove both permanent and temporary teeth, focusing not on the wishes of the grandmother or mother, but solely on the available indications.
Should baby teeth be treated?
There are a number of reasons why it is imperative to take care of your child’s baby teeth. Among them:
- Negative changes in the bite in the case of premature destruction of individual teeth, violation of the location of permanent units. Because of this, in adolescence, a child has to wear braces, which cause him a lot of physical inconvenience and psychological complexes.
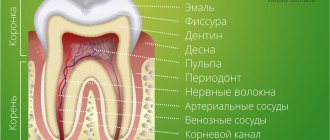
- The risk of infection transferring from a baby tooth to the permanent bud. These complications are possible with pulpitis, cysts, periodontitis. Bacteria can also penetrate bone tissue, and this is very dangerous for the health of a small patient.
- The development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as a result of premature destruction of dental crowns. Then the smile becomes partially toothless and it is difficult for the child to chew food. If large pieces of food enter the stomach, digestive processes worsen and slow down.
- Problems with diction and sound pronunciation. A “toothless” mouth contributes to the development of a lisp. Because of this, the child may be criticized by peers.
Also, when talking about whether it is necessary to treat baby teeth, doctors never tire of reminding them of the pain that a child faces if the dental disease that has arisen progresses. Is it worth exposing your baby to such torture? After all, they can be easily avoided by promptly treating temporary canines, incisors and molars.
The most common dental diseases in childhood
Among the main problems that force children to undergo dental treatment:
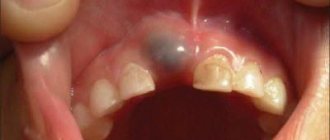
- Caries. Children encounter it most often. The disease is found in more than 60% of children under six years of age. It especially often affects molars. This is due to their relief volumetric surface and the baby’s nutritional conditions. On the crown of molars, plaque is deposited more actively. Pathogenic microorganisms multiply in it. The result of their life activity is progressive caries. The difficulty is that in the first stages, parents are not always able to detect a carious cavity on their own. It looks like a light speck and practically merges with the healthy surrounding enamel. Not knowing about the presence of the disease, mothers and fathers postpone a visit to the pediatric dentist. When the child arrives for an appointment, the carious “hollow” already turns out to be very large.
- Periostitis (flux). A complication of advanced caries, caused by the spread of bacteria, damage to tooth roots and tissues adjacent to them. The cheek is swollen. A voluminous abscess forms on the surface of the gum. When palpated, acute pain occurs. Flux may worsen the baby's general condition.
- Periodontitis. Inflammatory periodontal disease. The latter is formed by: periodontal ligament, gums, root cement and alveolar bone. It hurts your baby to bite into hard food. His temperature rises and headaches appear.
All of these dental diseases are highly treatable. The most important thing is not to put off visiting a dental clinic until later.
Methods for treating childhood caries without drilling
A child has been diagnosed with a carious spot, that is, initial caries - what to do in such a situation. The doctor may offer several options.
- Fluoridation.
A special composition with a high concentration of fluoride is applied to the surface of the tooth enamel. The mineral substance helps strengthen the enamel, restore its structure, and helps stop the further process of tissue destruction.
- Remineralizing therapy.
The teeth are coated with compounds containing phosphorus, calcium, magnesium and other minerals. The treatment promotes the remineralization of enamel, restoring its strength and structural characteristics.
- Ozone therapy.
Another modern non-invasive method in which children's teeth are treated with ozone. It destroys different types of cariogenic bacteria, preventing their proliferation in the oral cavity.
- Silvering.
Previously, this method was very popular, today it is used less frequently due to the fact that it affects the aesthetics of the teeth. After silvering, white baby teeth acquire a distinct dark color. The essence of the method is that tooth enamel is coated with compounds containing silver. They have an antiseptic and bactericidal effect, forming a protective film on the surface that prevents the spread of infection. Silvering does not cure caries, but it helps slow down the process of tooth decay.
Treatment of baby teeth
fluoridation
comes to the rescue . The enamel is treated with a fluorine-containing compound. Due to which it becomes stronger, the progression of the carious lesion is inhibited.
Advanced caries, like pulpitis and periodontitis, requires a filling procedure. It is carried out using local anesthetics, so neither the child nor his parents should be afraid of pain or severe discomfort.
When treating the roots of milk units, doctors use a special material, which in the future will be absorbed along with the roots. Thus, the treatment in no way changes the order of tooth replacement.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
What type of anesthesia will be used during treatment depends on the degree of advanced disease. Most often, doctors use a spray that makes the gum tissue insensitive.
If the problem is serious, injectable painkillers are used. But so that the little patient does not feel pain during the injection, the doctor first lubricates the area where the needle is inserted with an anesthetic. This approach to pain relief makes even complex dental procedures not at all scary and as comfortable as possible for the little fidget.
General anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is used only for the most severe illnesses or if it is not possible to persuade the patient to open his mouth and sit quietly in a chair. Parents should not be alarmed if the doctor recommends general anesthesia. It involves the use of a modern, safe drug with a minimum number of side effects.
Why pediatric dentistry offers treatment rather than extraction
If the doctor sees that a tooth that should serve the child for another 4–7 years can be saved, he will definitely treat it. A prematurely removed baby tooth can cause problems with bite and pronunciation and lead to the appearance of very serious dental anomalies. So, if the baby “five” is removed before the permanent molar, the “six,” erupts, the child will have to be observed for a long time by an orthodontist and, most likely, wear a plate.
It is clear what the first experience of visiting a dentist will be like for a child who, at the request of his mother, will have a tooth removed. It is not difficult to assume that a frightened child will most likely become a difficult patient who cannot be lured into the dental clinic by any persuasion. He will certainly have serious dental problems in the future.
What to do to avoid having to treat baby teeth
In order not to have to wonder whether it is necessary to treat baby teeth, it is necessary to pay maximum attention to preventive measures. These include:
- proper and regular brushing of teeth;
- visiting the dentist twice a year (or more often if the child is prone to dental diseases);
- using a high-quality toothbrush and toothpaste;
- balanced diet, avoiding eating a lot of sweets;
- rinse your mouth after every meal.
If you take care of your teeth, the risk of tooth damage will be much lower. This means that a visit to the dentist will mostly be associated with affordable and absolutely painless prevention.
Are baby teeth an important stage in development or a temporary phenomenon?
Teeth, the quality of our life largely depends on them - first milk teeth, then permanent teeth. And then - how does it work out? And if at a conscious age one can safely address the statement to teeth with “you value it when you lose it,” then parents, as a rule, treat their children’s temporary “pearls” quite dismissively: “they will fall out...” Due to this undeniable fact and the constant lack of time among parents, insufficient attention is paid to brushing teeth. Let’s add here store-bought juices with a lot of sugar, cookies from loving grandmothers for their pampered children, sweets from attentive guests and the almost complete absence of solid food in the child’s diet - it turns out that a dental surgeon often helps teeth “fall out.”
Statistics show that already at the age of 4, up to 9% of children have extracted teeth. And, unfortunately, by the age of 6-8 years the number of such children reaches 60%.
But complicated caries is not always the reason for the removal of baby teeth.
The reasons leading to the destruction of the crown parts of teeth or their early loss include:
- ineffective prevention or its absence during the prenatal period, during the embryonic development of the fetus and during breastfeeding;
- insufficient prevention during the period of primary, mixed and permanent dentition (timely treatment of primary teeth is of great importance for the prevention of caries complications and the prevention of early tooth loss);
- retention (non-eruption of a tooth), partial or complete primary adentia (absence of tooth buds).
- injuries;
— enamel hypoplasia (incorrect or incomplete development of tooth enamel, the main causes of which are acute infections during pregnancy, hereditary factors, etc.).
When is it necessary to remove baby teeth?
1. Significant defects in the crown of the tooth, in which restoration of the tooth is not possible.
2. Chronic periodontitis (inflammation of the tissue around the tooth), complicated by purulent processes.
3. The period of physiological tooth change (when the permanent tooth is already visible in the oral cavity, but the milk tooth has not fallen out).
Why is it so important to preserve baby teeth until they are physiologically replaced by permanent teeth?
Milk teeth contribute to the correct formation of a correct permanent bite, and therefore important body functions in which the dentofacial system takes part, such as breathing, chewing, swallowing, speech.
Let's look at some facts that prove the importance of dental function .
A child's usual diet contains a large amount of carbohydrates, the breakdown of which requires thorough chewing of food and wetting it with saliva. In the absence of teeth, especially molars, chewing deteriorates, which leads to a delay in the physiological development of the jaws (the performance of the masticatory muscles decreases, the structure of the bone tissue of the jaw areas with extracted teeth is not fully formed) and the body as a whole.
When teeth are lost, the position of the tongue changes, which is placed in the resulting space, promoting the formation of an open bite (the presence of a pathological vertical gap between the teeth of the upper and lower jaws) and interfering with the correct eruption of permanent teeth.
Early loss of natural teeth in children without timely replacement of defects in the dentition leads to various changes in the dental system.
These include the following.
1. Changing the position of teeth adjacent to the lost one towards the resulting space (up, down, forward, backward, around the axis):
a) the absence of upper primary incisors leads to a noticeable flattening of the upper lip, protrusion of the lower lip, and displacement of the lower incisors forward.
b) in children , when they lose antagonists (teeth of the opposite jaw), unlike adults, the teeth very quickly change their position together with the alveolar process until they come into contact with the alveolar process of the opposite side, which is explained by a tendency to growth, which is not yet completed. The dental arches are bent not only in the vertical, but also in the horizontal direction, either towards the tongue or towards the cheek (dentition becomes asymmetrical).
c) with the loss of primary molars or canines , the overlap in the anterior-posterior direction increases, a so-called distal bite is formed, the first permanent molars shift to the center of the jaw, as a result of which the dental arch is shortened.
2. Reduced bite height.
3. Changing the position of the lower jaw forward, backward, to the side.
4. Changes in the relationships of the elements of the temporomandibular joint, which can be asymptomatic in the first period of development of the deformity. If the elements of the joint are not returned to their previous position with the help of orthopedic devices, such conditions often become pathological, such as arthritis, arthrosis, arthrosis-arthritis.
5. Early removal of baby teeth leads to the fact that the permanent tooth germ lying deep in the jaw is covered with a dense layer of bone, which is an obstacle to the eruption of a permanent tooth.
Particular attention should be paid to the first permanent molars , which are most often affected early by caries. They are of great physiological importance for the proper development of the jaw and the growth of the facial skeleton. They bear the main chewing load for up to 12 years, holding the premolars and seventh teeth in the correct position, and preventing secondary bite deformation.
If the first molars move forward due to early removal of primary molars, there may be a shortage of space for permanent canines and they will erupt outside the dentition.
Krolivets Tatyana Grigorievna,
Orthodontist of the first category,
Candidate of Medical Sciences,
Dental clinic "Implantis".
https://implantis.com.ua/
published 09/07/2012 09:49 updated 03/13/2014 - Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity