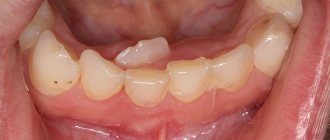
If we proceed from the generally accepted canons of the formation of the dental row in a child, then by six months, maximum by 8 months, teeth should appear. However, in reality this does not always happen. Despite reaching the age of eight months, the baby does not experience teething.
Parents should not panic in such a situation, although the question of why the child has no teeth requires an immediate answer. Sometimes such a development of events is only a slight deviation from the norm, but often indicates a serious pathology.
Facts about teething
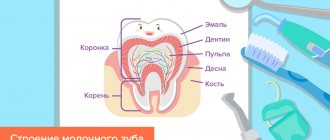
Teething is a complex physiological process that lasts for several years. During this period, the formation of tooth germs and their movement inside the jaw occurs. The process of teething is most often quite painful. There is a gradual change in the bite: a temporary (milk bite) changes to a permanent one. This is due to the development of bones in the child, in particular, with the growth of the skull bones. Also during this period, the formation of bone structures, soft tissues that surround the tooth, and the resorption of the roots of the milk units occurs to free up space for the permanent ones.
The first stage of tooth formation begins in the embryonic period. The complete completion of this process occurs with the eruption of wisdom teeth at approximately 25 years of age.
No teeth at one year of age
Why does a child’s teeth not grow after a year of life?
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Unsuitable climate.
- Poor quality of food and water.
- Diseases and infections.
- Vitamin and calcium deficiency.
To dispel or confirm suspicions, you need to take your baby for examination to a therapist and dentist. To determine the causes of delayed jaw development, blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examinations of organs, and testing of thyroid function may be necessary. To exclude edentia (lack of teeth) from the diagnostic field, fluoroscopy is performed.
When do the first teeth appear?
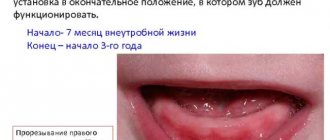
At the time of birth, the baby's teeth are in a state of formation inside the jaw bones. The bone contains a complete set of primary teeth at different stages of growth. The front incisors are the earliest to form and begin to emerge through the gums at six months of age. With the correct development of the child, dental units continue to erupt in pairs, i.e. one on each side. A full set of twenty primary teeth should appear in the first three years of a child's life.
Recommendations for avoiding delay
- After tooth loss, you should not eat or drink hot drinks for several hours.
- The plug that forms in the hole cannot be removed to avoid infection. It will disappear on its own.
- It is not advisable to eat solid food for the first time after the loss.
- If you experience pain, redness, swelling or other signs of exacerbation, you should immediately contact your dentist. Remember, our specialists are always ready to help and answer your questions by phone.
How to determine the delay in teething
If a child is 1.5 years old and still does not have a single tooth, then this is a serious reason to seek advice from a dental clinic.
The normal period for the appearance of the first teeth in the oral cavity is considered to be from 4 to 16 months, subsequent teeth appear gradually after the first.
Permanent teeth begin to grow by the age of 6-7 years.
A slight discrepancy with the established deadlines is not a reason to sound the alarm; you should worry if the child has a complete absence of teeth.
How to help your baby?
Initially, the dentist will take an X-ray of the baby's jaw to make sure that the baby has the rudiments of teeth inside. If there is, then eruption will happen soon. At first, the gums will swell a little and salivation will become very abundant: these are the main symptoms of the rapid appearance of teeth. You can help them a little:
- Teether toys are an excellent device for training gums; they help relieve severe itching and reduce pain.
- Mothers should learn how to gently massage their baby’s gums. It is better to massage with a clean finger lubricated with a special gel for children's gums.
- It is important to add healthy purees and healthy foods to your baby’s diet that will help the child’s body receive the necessary microelements and vitamins.
If the baby generally develops within normal limits, eats well, sleeps, is active and cheerful, then the absence of teeth at 1 year is definitely not a reason to panic. Each child develops at his own pace. In general, boys tend to lag slightly behind girls in some physiological parameters.
From this article it follows that you should not worry unnecessarily! If in any doubt, seek advice from a pediatric dentist at our Babydent
Show more tips
Types of delay in teething
A discrepancy from the average statistical time of more than six months in the eruption of baby teeth is considered a delay.
The delay from the average time in the appearance of permanent teeth should not exceed a year. There are two types of late eruption.
- Late formation of dental follicle. In such a situation, the relationship between the development of the tooth and its appearance in the oral cavity is observed, but both processes proceed more slowly than expected.
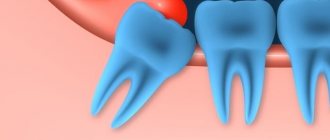
- Late eruption. With this development, the tooth is fully formed, its root grows, but the dental unit cannot erupt. Fully formed teeth remain in the bone – impacted. They may be completely under the gum or partially visible from under it.
Before worrying about delayed eruption, it is necessary to diagnose the presence of a tooth germ in the bone. To do this, a panoramic photograph is taken, which makes it possible to distinguish the complete absence of a rudiment from a delay in formation.
What about the deadlines?
Some parents use a special formula to determine how many teeth a baby should have at nine months. It looks like this:
K=M – 4,
where K will be equal to the number of teeth, and M will be the number of months of the toddler’s life.
But even if teething begins only at one year, parents should not panic. This is also the norm.
Children's teeth may appear one at a time or in pairs. Moreover, in this way not only the first ones erupt, but also those following them. There are cases when a baby has as many as four teeth coming out at the same time. By the way, massive teething will affect the timing.
It is human nature to doubt. Especially for parents of little ones. It often happens that a child is 9 months old and has no teeth. Why? If at this age or even a year the baby does not have a single tooth, you should consult a doctor to make sure that the little one does not have rickets or hypothyroidism.
Typically, the first twenty teeth should appear before two and a half to three years of age. Each baby’s jaw should have four incisors, two canines (also called canines) and four molars. In an adult, it is considered normal to have twenty-eight or thirty-two teeth - on each jaw there are 4 incisors, two canines, four premolars and from four to six molars.
When baby teeth begin to emerge, there are initially no gaps between them. This is normal. A little later, when the child’s jaw grows, by the age of four the teeth begin to diverge and gaps form between them. This process is necessary to accommodate the molars because they are much larger than baby teeth. If such gaps do not appear, then subsequently the molars will not be able to fit in and will grow crookedly.
Reasons for delay in teething
There can be many reasons for delays in teething.
- Hereditary factor. If parents cut teeth later than other children, then this symptom may also be observed in their children.
- Prematurity or low birth weight of the baby.
- Diseases of the expectant mother during pregnancy, injuries during childbirth, as well as illnesses of the child in the first few months after birth.
The factors listed above most influence the timing of eruption, as well as the quality of formation of dental units.
Other reasons include:
- violations in the child’s diet;
- lack of certain vitamins and minerals;
- hypothyroidism;
- rickets and its consequences.
It should also be taken into account that girls are ahead of boys in development, and, therefore, their teeth appear earlier.
What to do to ensure that your child’s teeth develop normally
Before and during pregnancy:
- Maintain dental health.
- Eat well and varied.
- Eat more foods high in calcium.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Walk in the fresh air more often to maintain a healthy level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Treat in strict accordance with medical recommendations.
After childbirth:
- provide the child with a rich and balanced diet;
- monitor the baby’s hygiene;
- walk in the fresh air to harden the child’s body;
- prevent infection and diseases of internal organs;
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner in case of painful syndromes.
What determines the timing?
The timing of the formation of both temporary and permanent dental units in children can be compared with certain phenomena.
- Floor. In girls, all teeth, except the first upper chewing one, erupt earlier than in boys.
- Jaws. Teeth appear faster on the lower jaw than on the upper jaw.
- Position of teeth. Molars and premolars most often erupt with a delay.
- Bite. In primary dentition, delay occurs much less frequently than in permanent dentition.
- Population. Scientists have found that people living in different countries have different timing for the appearance of teeth. For example, among Europeans, delayed eruption is a fairly common occurrence.
- Climatic conditions. In warm climates, teeth erupt faster than in cold climates.
- Level of urbanization. City residents develop teeth faster than those in rural areas.
- Evolution. Recent generations are more likely to encounter anomalies in the eruption of wisdom teeth and canines in the upper jaw. Scientists explain this phenomenon with the evolution of humans as a species, and with the lack of space due to a decrease in the overall size of the jaw.
What complementary foods does a 9 month old baby eat?
The diet of a 9-month-old baby is already quite varied. Your baby can continue to receive breast milk and/or formula and complementary foods. The products will no longer include only cereals, vegetables, meat and dairy products, but also bread, butter and vegetable oil, and fish. And in order not to harm the baby, when switching to a “common table”, mothers adhere to the scheme for introducing complementary foods
— the table contains recommended foods for feeding and portion sizes per day depending on the child’s age. Complementary feeding introduced in a timely manner will become the basis for proper nutrition and good appetite even for small children.
What else should you pay attention to?
If you are no longer breastfeeding or your baby has been bottle-fed since birth, we advise you not to rush into introducing whole cow's milk and the milk of other animals. Let only baby formula remain in the diet for now, since it is adapted to the physiological characteristics of the digestion of babies, which means it is easier to digest.
Among MAMAKO® baby food there are mixtures for children in the second half of life, and complementary feeding products for a baby at nine months (including for nutrition with a tendency to allergies). Buckwheat and corn porridge, 5-grain porridge and cream soups of pumpkin and spinach with goat's milk, fruit puree with goat's curd - all these are complementary feeding options allowed by pediatricians for children under one year old.
From 6 months to 2 years, young children are especially open to new taste sensations. And mother can help her baby develop them. How? Try offering your child multi-ingredient cereals. For example, buckwheat porridge with apple and carrots. Many kids are very curious about new and varied tastes and eat such treats with pleasure.
Edentia of the upper jaw
The upper jaw is more often than the lower jaw and is subject to various types of anomalies. As a rule, patients have symmetrical hypodentia of two teeth. And since the front teeth are involved in sound production and form the purity of pronunciation, this type of deformation is the most noticeable. The patient's speech becomes lisping and slurred, the smile “creeps away”, and saliva splashes.
Edentia of the lower jaw
The lower jaw has a small prosthetic bed, so when edentulous, the tongue begins to take the place of the lower teeth. As a result, the patient’s diction changes significantly and his well-being worsens.
Complications
Adentia leads to a variety of physical and aesthetic complications:
- in the area where a tooth is missing, the unloaded bone gradually atrophies;
- the face may become asymmetrical, lip closure is disrupted, and the chin and nasolabial folds deepen. Often the position of the corners of the mouth changes, they begin to sink;
- underdevelopment of the jaws occurs. It is expressed more strongly the more teeth are missing, various dentofacial deformations appear;
- with multiple edentia of the lower jaw, its strong protrusion and deep bite are observed;
- with anomalies of the upper jaw, the lower dentition begins to overlap the upper one;
Underdevelopment of the jaws is not observed in all cases, and not all children and adults express it in the same way. However, in all cases, edentia leads to negative changes in appearance.
With complete or multiple edentia, the bite is formed incorrectly and the function of oral digestion is disrupted. The food is poorly crushed, and the patient is forced to give up many tasty dishes. We should not forget that with this pathology a person’s self-esteem decreases, he begins to worry about the fact that he looks unattractive, withdraws into himself and is less likely to make contact with people.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose the disease, the dentist needs a detailed examination of the patient’s oral cavity. The doctor asks the patient a number of things:
- causes and timing of tooth loss;
- information about previous diseases;
- data on dental prostheses previously used by the patient.
During the examination, the dentist notes the asymmetry of the face, the severity of the chin and nasolabial folds, the degree of reduction in the height of the lower part of the face, the presence of a jam, the nature of the closure of the lips, the topography of the transitional fold, the degree of mouth opening, the nature of the jaw relationship. The specialist also determines the presence of crunching in the joints, pain when moving the lower jaw and diagnoses the degree of atrophy of the alveolar processes.
The examination necessarily includes palpation of the oral cavity and radiography of the TMJ. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines further treatment tactics (prosthetics), selects the appropriate type of prosthesis and impression material for the patient.