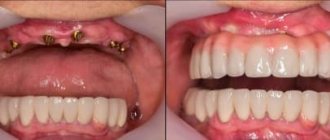
Not everyone manages to keep their teeth intact throughout their lives. When teeth are lost, the patient loses the ability to smile beautifully, and he experiences disturbances in speech and chewing functions. Orthopedic dentistry is designed to solve these problems. Restoration of the structure and functions of the masticatory apparatus occurs through the installation of orthopedic structures. Modern designs for prosthetics completely replace lost teeth. They are adaptive, hypoallergenic, and have a long service life.
What is fixed prosthetics?
Fixed prosthetics involves implanting an artificial root into the bone tissue where teeth are missing. Subsequently, a prosthesis is installed on the root. The patient will not be able to remove the structure on his own. There is another method of restoring the dentition - using removable structures. But it has disadvantages, so it is mainly used only if the patient is not suitable for fixed dentures.
Differences in dentures
Indications for installation of a prosthesis
The general indication for prosthetics is damage or absence of a certain number of dental units. Dental defects lead to ineffective chewing of food. The bite is disturbed, the aesthetics of the smile suffers. The most common indications for prosthetics are the following disorders:
- Adentia (complete or partial loss of teeth). Restoration of the dentition is carried out by removable prosthetics or implantation of dental units.
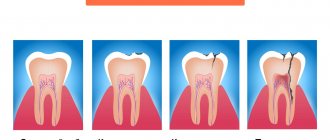
- Complete or partial destruction of the coronal part of the tooth, in which filling is impractical. When preserving the root, a pin structure or stump tab is used.
- Pathological abrasion of enamel, which is a systematic violation of the enamel layer of dental units. The loss of hard dental tissues leads to malocclusion.
- Traumatic damage to teeth. The patient may be offered various options for restoring the dentition, depending on the severity of the situation.
- Pathology of the alveolar process leading to serious malocclusion. A frequent consequence of partial edentia, leading to the restructuring of the alveoli and a decrease in the functionality of the dentition.
- Single and multiple dental defects. The patient can be offered various design options depending on the existing problems.
When is fixed prosthetics prescribed?
Main indications for fixed dental prosthetics:
- the absence of one or more teeth – both nearby and in different parts of the dentition;
- congenital or acquired defects of tooth enamel (tetracycline teeth, fluorosis, discoloration due to injury or root canal treatment with outdated methods);
- large chips and cracks;
- the presence of spaces between teeth (diastema, trema);
- as a support for a bridge prosthesis.
Consequences of missing teeth
If you are missing 1 or more teeth, consider this dental restoration option. By delaying the process of prosthetics, patients waste time. In the future, the procedure will be more extensive, expensive, and painful.
Due to the increased load on the remaining teeth, they begin to decay faster. The bite is disturbed, pain appears in the temporomandibular joint.
Expert advice
There is no clear answer to the question of which prosthesis to choose in a given case. The structural features of the patient’s jaw apparatus, his age, and the severity of the problem are of great importance. Approximate recommendations are given in the table:
| Situation | Type of prosthetics |
| Clinical picture | Recommended type of prosthetics |
| Availability of dental units suitable for fastening the structure | Conditionally removable prosthesis |
| The dentition lacks a large number of dental units, and the installation of bridge-like structures or implantation is impossible | Removable prosthetics |
| Molars or incisors are completely absent from the dentition | Removable prosthetics. It is recommended to choose acrylic dentures |
| Molars and premolars are missing | Partially removable prosthetics |
| Requires installation of temporary prostheses | Partially removable prosthetics |
Contraindications
Not all patients can get fixed dentures, because there are strong contraindications:
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint;
- tooth mobility;
- chronic periodontal disease;
- pregnancy;
- severe bruxism;
- oncological diseases, blood diseases, mental disorders.
There are few absolute restrictions on installation. You can always choose the option of fixed prosthetics for each patient, taking into account his individual characteristics.
Advantages of bar dentures
A denture with a bar fixation is the best solution of all the options for removable prosthetics on implants
- Convenience Smaller and lighter than traditional ones, more comfortable to use. They do not rest on the gums and do not injure them, and do not move while eating. Easy care.
- Simplicity Implants are placed in points with sufficient jawbone size. There is no need for expensive and complex bone grafting.
- Functionality The load is distributed evenly, the beam transmits pressure not only to the point around the implant, but also to the entire bone. Atrophy is excluded.
- Reliability The structure is strong, the fastenings do not become loose, high stability and chewing efficiency. With proper care it lasts a lifetime.
A prosthesis on a beam is the best of all removable prosthetic options on implants.
The design is reliable due to the beam fixation system. Holds securely and is not subject to overload or breakage.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
Types of fixed dentures
There are many different ways to restore teeth using fixed dentures, each of which has its own installation features, advantages and disadvantages.
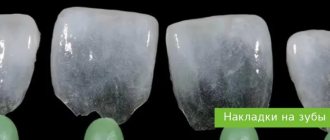
Veneers
Veneers are distinguished by their features from all other types of dentures. These are just thin shells that are glued to the tooth surface. Indications for installation are dark enamel color that cannot be bleached, chips, cracks in the smile line, darkened filling. You can close a tooth gap with veneers.
Veneers on teeth
It is not advisable to carry out the procedure in the following cases:
- inflammation – caries, pulpitis, periodontal disease;
- interfering fillings;
- bruxism;
- malocclusion.
Ceramic (porcelain) onlays are fixed with dental cement. They last up to 10 years and are not painted. They are quite thick, you have to remove part of the enamel for normal fixation.
Lumineers, nanoveneers, glass veneers are ultra-thin and practically do not require removal of enamel. Installed instantly using special glue. They have an excellent aesthetic effect, do not damage teeth, and do not stain. You cannot chew with your front teeth or bite hard food.
Stump inlays
Stump inlays are used when the outer, chewing surface of the teeth is damaged. They are distinguished by reliable fastening and are not painted. They look natural and can last a long time. Inlays are preferable to fillings. The main indication is tooth decay of more than 30%. The inlays are made from durable materials and can last for a long time.
Installation of the stump tab
Dental bridges
This is a system that consists of several artificial teeth and crowns for attachment to healthy dental units. Fixed bridges are indicated when there is a deficiency of several units in one row. A structure is made that can withstand long-term loads. Strong fixation with dental cement is required. The solution prevents the structure from moving when chewing.
An adhesive dental bridge is gentle on teeth. No grinding of healthy teeth is required, but can only be used on one tooth. This is a one-piece crown with attachments to adjacent teeth on the lingual side. Dental glue is used for fixation.
A composite dental fixed prosthesis is used when the anchoring teeth cannot be properly processed due to their inclination in the mesial or distal position. For such situations, composite structures are provided that are secured using hooks (clasps), tabs, rings, various types of locks, and telescopic crowns.
Types of bridges
Indications:
- incorrect position of supporting elements;
- the presence of several support units;
- increase in supporting units with an existing prosthesis.
Cantilever is a non-removable denture, which is suitable in the absence of one unit, with a single fulcrum, instead of two, like a standard bridge. A cantilever is an artificial tooth in a denture. The supporting part on the adjacent healthy tooth in the form of a crown. Installed if for some reason it is impossible to install an implant. Placed in cases of loss of incisors and premolars.
Combined fixed denture . The main part is firmly fixed to the supports with a cementitious composition. Connected with locking fasteners. This could be a clasp design. It is attached using clasps and attachments.
Clasps are hooks that firmly hold the structure in the oral cavity. Disadvantage: noticeable, aesthetically unattractive. Attachments are means of fixation. Invisible in the oral cavity. The designs are distinguished by precision manufacturing, as 3D modeling is used. The physiological characteristics of the patient are taken into account. This makes them comfortable. There are no side effects. A person quickly gets used to the structure, chewing and speech functions are restored. The materials do not cause allergies. Serve for more than 10 years.
Crowns
Prosthetics using a crown is used to restore one tooth, even after complete destruction, but with the root preserved. Fixed crowns replicate the anatomical features of the teeth and completely restore chewing function. In dental practice, various types of dental crowns are used.
Types of crowns
Metal-plastic – conditionally temporary, which involves installation with a metal base in combination with a plastic coating. Metal structures are made of nickel, chromium or cobalt. The disadvantages include the rapid loss of appearance due to staining of the plastic when drinking coffee, strong tea and other coloring products. The crowns are not strong enough; an allergic reaction may develop to the metal.
Metal-ceramic - their base is made of cobalt, chromium, titanium, gold and other metals. For an aesthetic appearance, a ceramic layer is applied to it at high temperature. The advantages of metal-ceramic crowns include:
- High mechanical strength due to a cast metal frame. Ceramics are also durable.
- Aesthetics. They do not become colored when eaten with coloring foods (such as coffee). Chips of ceramics are rarely observed. Dentures are always tailored to the shape of the patient’s teeth and the color of the patient’s enamel; ceramics completely recreate the anatomical features of the enamel.
- Long service life. Metal-ceramic dentures last up to 20 years. With preventive measures I can last up to 35 years.
Metal - such crowns were previously used everywhere. Now they are most often installed only on chewing teeth due to aesthetics. They are made in the laboratory, stamped or cast with spraying. Metal crowns are very durable and reliable. They fit tightly to the tooth, preventing further destruction. Disadvantages include allergic reactions to metal. It must be taken into account that only one type of metal is used to prevent galvanic syndrome. This is a burning sensation in the mouth and a “metallic” taste. Gold crowns are made from an alloy of gold and palladium or platinum, since gold is a soft metal. They have excellent biocompatibility and do not cause allergies. But they do not look very good, so it is not recommended to place them on the front teeth.
Ceramic or metal-free crowns are the most aesthetic and beautiful crowns. They are practically indistinguishable from real teeth. All-ceramic or porcelain are made according to a personal impression from pressed material without other components. There are also mixed materials:
- ceramics with zirconium dioxide. It is a more durable material than pure ceramics. Due to the light transmittance, an almost complete imitation of real teeth is achieved. Zirconium crowns do not cause allergies.
- aluminum oxide and ceramics. This is a translucent hypoallergenic material that is comfortable and resistant to temperature fluctuations.
Positive aspects include low weight, good biological compatibility, and hypoallergenicity. They can be placed even on weakened teeth with minimal grinding. The main disadvantage is the high cost and fragility of ceramics. They are not designed for intense chewing loads; they are often installed on the upper incisors. Service life with proper care is up to 10–15 years.
Zirconium dioxide crowns are a modern material that is manufactured in a laboratory using computer equipment. Laser scanning is used to accurately analyze the dentition. A computer program simulates an accurate crown for the tooth. The data is transferred to a milling machine, which grinds the prosthesis from the workpiece. The main advantages include:
- high levels of mechanical strength.
- excellent aesthetic properties. Crowns are practically indistinguishable from the patient’s natural teeth.
- environmental friendliness and biological compatibility. Zirconium dioxide is safe for human health.
Acrylic and plastic crowns are a temporary option; they are used until permanent dentures are installed. They are placed to protect prepared teeth from destruction and to hide defects in the dentition on abutment teeth or implants. They provide a uniform load, reducing the risk of jaw bone resorption. A person gets used to a permanent prosthesis faster.
Fixed denture on implants
Implantation is the installation of an orthopedic structure that replaces teeth supported by artificial titanium implants, which are implanted into the patient’s jaw. Fixed dentures on implants allow:
- completely restore the full function of chewing, the aesthetic component;
- improve the quality of human life.
Advantages:
- aesthetics – the prosthesis cannot be distinguished from the patient’s own teeth;
- physiological – no discomfort when chewing. Does not feel like a foreign body;
- maintaining the integrity of your teeth;
- full chewing load allows you to preserve bone tissue;
- absence of the problem of an “senile” face - timely prosthetics will allow you to maintain a youthful appearance for a long time even in adulthood;
- simplicity, ease of maintenance - do not require additional equipment. It is enough to brush your mouth 2 times a day.
The following indications for implantation exist:
- single defect, especially in the smile area;
- absence of a significant number of teeth in a row;
- there is no last tooth where the structure can be secured;
- complete edentia is the only possibility that allows the structure to be securely fixed.
In the first days after installation of a fixed denture on implants, discomfort in the form of pain and swelling is possible. But as healing progresses, all discomfort goes away.
If previously prosthetics were performed only on implants that had taken root, modern materials and technologies make it possible to speed up the process. Exists:
- immediate installation (after implantation or in the first 3 days, this is called one-step implantation, such an operation is possible even immediately after tooth extraction);
- early exercise (from 2 to 6 weeks);
- late prosthetics (from 3 to 6 months).
In case of partial tooth defect, a one- or two-stage technique is performed with late installation of dentures on the implant. Fixation of crowns for 3 or 6 months after implantation. Engraftment of implants on the lower jaw takes 3 months, on the upper jaw from 5 to 6 months. Engraftment depends on bone density. When building bone tissue, the time period increases. Sometimes complete prosthetics are performed only after 1.5 years.
The indication for early loading is usually a missing front tooth, when the patient needs to eliminate an aesthetic problem. First, a temporary plastic crown is made. Then it is replaced with a permanent one made of zirconium.
Basal technique: with edentulous bone tissue often atrophies, the volume is not enough for implantation. Basal implants are used, which are installed in a deeper layer. This eliminates the need for bone grafting. The specialist must be fluent in the basal technique to avoid complications.
All-on-4, All-on-6: The technology was developed by implant manufacturer Nobel-Biocare from Switzerland. Its peculiarity is that the fixation of the entire fixed bridge prosthesis is carried out only on 4 or 6 implants.
Dentures on implants
In case of complete absence of front teeth, it is optimal to use 4 implants for prosthetics. The technique is safe for the patient and the installation takes place in a single visit, which allows you to get all your teeth back in one day. 6 implants are used in more complex cases (absence of all teeth, for example), as they allow the prosthesis to be secured in the mouth even more reliably. This type of prosthetics has been used for more than 20 years and has successfully proven itself among patients: dental units look great, chewing function is restored in full, and no special care is required.
Bar denture
As is easy to understand from the name, the basis of this prosthesis is a beam - a structural element that takes on a vertical load. In implantology, this is the chewing load that is transferred from the jaw to the prosthesis and to the installed dental implants. In order for the pressure on the implants to be distributed evenly, they are all connected by a horizontal beam, on which there are places for attaching the orthopedic structure. For this purpose, special recesses are made in the prosthesis itself, through which the prosthesis is attached to the implants with special screws. Thus, the beam-fixed prosthesis becomes repairable, since if necessary, it can be removed (by unscrewing the screws), repaired and put back in place. Such a prosthesis allows you to restore several missing teeth or the entire dentition on one of the jaws.
Note!!!
It is believed that the bar prosthesis is conditionally removable, but it is necessary to remove the structure from the oral cavity quite rarely: this is usually done when it is necessary to clean the prosthesis, replace it, or repair it.
Which fixed dentures to choose
Microprosthetics with veneers are recommended for restoration of the smile area. These are modern techniques that allow you to achieve aesthetics. In addition, they are not colored with food coloring.
In case of partial absence of teeth, implants or bridge types of prostheses are used. The best option is implantation of All on 4 or All on 6. They are characterized by a long service life and a good aesthetic effect. Bridge structures are suitable for installation directly on the upper and lower jaw.
Popular questions about prosthetics
Here are collected popular questions from patients about prosthetics asked on the site forum. Experienced dentists answer.
Which prosthesis to choose: plastic or silicone?
Silicone has a short period of adaptation, is comfortable to wear, and does not rub the gums. Disadvantage of silicone: caring for them is more difficult.
Which type of prosthesis is better: a bridge structure or a suction cup prosthesis?
If there is a problem of missing several dental units in a row, the optimal choice would be a bridge. It will ensure uniform distribution of the load on the jaw, will serve for a long time, and is comfortable to use.
Which prosthesis to choose: plastic or nylon?
It all depends on which dental units need dentures. For chewing teeth, acrylic plastic is more suitable as the most durable and comfortable material to wear. Nylon dentures are suitable for premolars and incisors.
Which prosthesis design should I choose from plate-type prostheses?
If a temporary prosthesis is needed, then a removable plate structure is chosen. A fixed prosthesis is chosen in the absence of at least three dental units in a row in the dentition.
Which denture should a person prone to allergies choose: acrylic or nylon?
Nylon has more hypoallergenic properties. In addition, a nylon prosthesis is more flexible and less likely to rub the oral mucosa.
How does adaptation proceed after fixed prosthetics?
Adaptation to fixed species occurs individually. After installation, you may experience the following inconveniences:
- excessive salivation;
- gagging;
- discomfort during chewing;
- speech distortion;
- loss of taste.
The sensations last for several days. Many people complain of pain, scratches and abrasions. Pain when chewing at first may be normal. You need to limit solid foods. If you are salivating, you need to drink more, if you have a gag reflex, breathe through your nose, rinse your mouth with saline solution.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor if there is severe pain, structural mobility, swelling in the area of the pins, or increased temperature. Timely assistance will help quickly resolve the problem. Independent actions lead to damage or breakage of the structure and rejection of the implant.
Pros and cons of bar prosthetics
The beam prosthetics technique has its advantages and disadvantages, which should definitely be taken into account before making the final choice in favor of this technique for restoring lost teeth. The advantages of beam prosthetics include:
The most correct distribution of the load, which ensures the durability of the results of prosthetics, extends the service life of the installed prosthesis, and eliminates the processes of bone tissue atrophy;
Bar prosthetics are applicable for complete edentia;
Bar dentures are fixed in the oral cavity as reliably as possible: the product cannot fall out when eating or actively talking;
Bar prostheses do not require specific complex care and allow
eat solid foods. Bar prosthetics has a lower cost compared to classical methods of dental implantation;
If necessary, the prosthesis will be easy to restore: only the product itself is removed.
There are also disadvantages to beam prosthetics. First of all, the treatment period is quite long; a permanent prosthesis can be installed in place only after the implants have completely healed. Installation of a bar prosthesis also requires a sufficient amount of bone tissue in the area of prosthetics, and services for bar prosthetics are more expensive compared to removable prosthetics.
Care of fixed dentures
Doctors recommend following the rules of care after installation. This is necessary to speed up the survival rate and increase the service life of the structure.
Required:
- carry out dental hygiene at least 2 times a day;
- use a medium-hard brush;
- exclude viscous confectionery products, chewing gum, nuts, seeds, hot or too cold drinks;
- use the irrigator 2 times a day - morning and evening;
- brush your teeth with dental floss;
- eliminate smoking;
- Visit the dentist twice a year for hygienic cleaning.
Beam prosthetic systems: design features
Beam fixation of dentures makes it possible to achieve strong fixation of the orthodontic structure in the oral cavity, and in addition, it contributes to the correct distribution of the load from the installed prosthesis on the bone tissue. A metal beam is used as a fastening element, connecting the implanted implants to each other, and having specialized recesses for installing the prosthesis.
The prosthesis and the beam are connected to each other using locks. Bar prosthetics are conditionally removable, which means that you cannot remove the prosthesis yourself. Only a doctor can remove the structure from the oral cavity, and this is usually done for high-quality professional hygienic cleaning of the prosthetic product, which needs to be done from time to time.
How much does fixed prosthetics cost?
The dental clinic in St. Petersburg “Yulistom” has a powerful diagnostic base and its own dental laboratory. Doctors were trained in the largest clinics in Europe and the USA. This allows for treatment and prosthetics in the most difficult cases. You can make an appointment on the website at a time convenient for the patient.
Approximate cost of prosthetics in our clinic:
| View | Price in rubles per unit |
| Veneers | from 18000 |
| Implants | |
| Hi-Tec | 27850 |
| Straumann | 44000 |
| Crowns | |
| Metal-ceramic | from 9500 to 15500 |
| Metal (cast) | 6500 |
| Temporary | 2000 |
| From zirconium dioxide | 25000 |
| Stump inlays | |
| Cast | 4000-5000 |
| From zirconium dioxide | 10500-13000 |
| Ceramic lined | 6000 |
Preparation for beam prosthetics and main stages of treatment
Preparation for beam prosthetics involves carrying out a number of diagnostic measures. The beam prosthesis is placed on implants, and therefore general tests are required, a panoramic photograph of the jaws is taken, which allows a qualitative assessment of the condition of the tissues of the oral cavity. Detailed diagnostics are required to exclude possible contraindications to beam prosthetics and eliminate the risks of possible complications after implantation. Next, the treatment is divided into several successive stages.
Implantation
Before implantation, the type of implants that will be used as a support for the beam prosthesis is selected, and the area of their implantation is also determined. An operation is performed to install titanium screws - artificial roots are implanted and then plugs are placed on them. The number of implants will depend on the characteristics of the clinical case. Typically, from 4 to 8 implants are used.
A bar prosthesis cannot be installed with less than three screws - otherwise it will not be possible to achieve a stable position of the structure in the oral cavity. With immediate implantation, a temporary prosthesis can be immediately installed on implanted implants. A permanent bar prosthesis is placed only after osseointegration of the implanted titanium screws.
Fixation of permanent prosthesis
A permanent beam prosthesis is made using impressions of the patient's jaw. The structure will be fixed to the implants using a beam that fastens titanium screws together and has recesses for installing the prosthesis. After the permanent beam prosthesis is made in the laboratory, the patient comes to try it on. If the fitting reveals inaccuracies in the design, the patient will feel severe discomfort - the product is corrected. If everything is fine, the doctor will install the prosthesis in place and fasten it to the beam by snapping specialized miniature locks.
The treatment ends with a detailed consultation on the rules for caring for the beam prosthesis. Compliance with the doctor’s recommendations will ensure a long useful life of the beam prosthesis, and will also eliminate the risks of negative side reactions and complications.
Survival and service life of implants
The healing time of implants is: on the upper jaw - from 6 months, on the lower jaw - from 3 months. Much here depends on the age of the patient, the quality of his bone tissue and the experience of the doctor installing the implants. But, if the implant is successfully implanted, it is almost impossible to remove it from the jaw.
A well-established implant will serve you for at least thirty years. If you follow your doctor's recommendations, the implant will last a lifetime. This refers to the part of the implant that is placed into the gum, the plate and abutment. The crown placed on the implant will have to be replaced, but it will last 10-15, or even 20 years.
What are conditionally removable prosthetic models?
Partially removable structures are prostheses that the patient cannot remove on his own, but a specialist is able to remove or replace them. They are used for complete or partially edentulous teeth and have two main types of fastening:
- With the help of implants. The implants themselves can be normal standard root-shaped with a lifetime guarantee or thin basal or other mini-implants that are used for atrophic phenomena of the bone for undemanding patients. In general, root-shaped implants and similar designs make it possible to firmly fix the prosthesis on the jaw and achieve its complete immobility and functionality. and attached to the thickness of the alveolar process of the jaw. This will not happen with basal implants or mini-implants, since this is a temporary implantation.
- If the edentia is incomplete or the patient has age-related contraindications to implantation, then the dentures are attached to their own remaining teeth. The structure is glued to adjacent teeth using special materials, for example, a cementitious composition. The reliability of fixation in such situations is much less, and the service life is shorter.
Deciding which prosthesis is better in case of complete absence of teeth is quite simple: using a digital diagnostic model. Since implants allow you to adequately distribute the load across the jaw evenly and without errors, and with their help it is possible to include absolutely any geometry of the new dentition into the treatment plan, such digital prototyping of the treatment result will allow you to immediately understand at what points and how many implants are needed. With implantation, the prognosis for the future is much more honest, since bone resorption stops forever, chewing function is fully restored, and the dentition can never be distinguished from the present.