The formation of teeth is a complex step-by-step process that begins in the first weeks of intrauterine life. Thus, by the time of birth, the baby has the rudiments of 20 primary and 16 permanent teeth inside each jaw. But, like all stages of development, teething in children under one year and older occurs differently. Some endure this period relatively calmly, others are capricious and sleep poorly. Why this happens and how to understand that the baby is cutting teeth, we will tell you further.
Size of modern human teeth
Over more than two million years, the size of teeth gradually decreased due to the transition to eating soft and processed foods. The first transformations affected the fangs - in primates they were larger and more strongly advanced relative to the rest of the row. The interdental spaces have disappeared, the size of the front teeth has become smaller. Refusal of raw meat led to a decrease in the chewing load and a narrowing of the jaw, as a result of which there was no room left for the “eights”. Now wisdom teeth are considered atavism and are often subject to removal.
Signs of teething
How can parents understand that their child is teething? The easiest way to find out about this is by the child’s changed behavior. He sleeps worse and is capricious. He loses his appetite (may completely refuse to eat). But similar symptoms can be caused by other reasons. Therefore, the most obvious sign can be considered swelling of the gums (a small red bump appears on it, which parents can feel rather than see).
The child's changed behavior is associated with the movement of the tooth in the jaw. It seems to tear the gums from the inside, which explains the unpleasant sensations: itching, burning and pain. To remove them, the child can scratch his gums, pull various objects into his mouth, and bite. You cannot stop this behavior; you just need to replace inappropriate objects (for example, toys) with special teethers, the purpose of which is to help relieve the unpleasant consequences of teething.
It is because of the unpleasant sensations that the child may begin to refuse food, especially hot food (increases the pain). A light massage of the gums may help, which should be performed before feeding. It will relieve some of the itching and pain.
During teething, the baby's temperature can rise to 38º, but not higher. Until the teeth appear, parents should pay as much attention to the child as possible, distracting him from unpleasant sensations. This will help the baby get through a difficult time for him.
How are tooth sizes determined?
To determine the size of a person’s permanent teeth, the calculation tables of Wetzel and V.L. Ustimenko with average standards and permissible deviations are used. However, an experienced dentist is able to independently identify the anomaly during a visual examination or by applying the formula for the ratio of the height and width of the natural crown. During diagnosis, the specialist takes into account the patient’s face shape and height. For example, with a wide jaw, the size of teeth exceeding the norm is not a pathology.
To determine the size of the root canal, there are also tables that indicate the average distance from its apex to the cutting edge or cusp of the tooth surface. The longest is the root of the canines - about 26 millimeters, the root canal of the incisors is 21 - 23 millimeters, and the size of the roots of the chewing zone and premolar teeth ranges from 19 to 22 millimeters.
Teeth size for prosthetics
It is especially important to preserve and, if necessary, restore the natural size of teeth during prosthetics, so as not to disrupt the bite and the full functioning of the dental system. The size of the crown is selected by the dental technician, focusing on neighboring or teeth of the same name, monitoring the correct closure of the rows and adjusting the prosthesis during installation.
Determining the size of artificial teeth with complete edentia is carried out by measuring the distance between the corners of the mouth using a special ruler - it corresponds to the width of the six front teeth. And the segment from the edge of the gum to the smile line is equal to the height of the crown. For example, during implantation it is necessary to correctly calculate not only the parameters of the orthopedic design, but also the size of the dental implant. It should be equal in length to the real root, but the choice of titanium rod parameters depends largely on the volume of the jaw bone tissue.
Proportional ratio of teeth sizes
In most cases, specialists determine the proportions of a tooth by correlating its height and width. A result of about 0.75 is considered ideal. The most accurate diagnosis is carried out through the use of formulas.
- Gerlach's formula.
The method is based on the proportional ratio of the sizes of the front teeth and dental units of the chewing zone. The width of the crowns of the upper central incisors should correspond to the width of the four lower incisors. The canine, two premolars and one molar of both jaws are normally equal to each other. The width of the lateral part of the dentition is 10 mm greater than the width of the anterior segment. - Pon's formula.
The distance between the first premolars is equal to the sum of the widths of the four incisors multiplied by 100 and divided by 80, and the distance between the first molars is the sum of the widths of the four incisors multiplied by 100 and divided by 64. - Corkhouse formula.
The length of the segment from the midline to the first molar of the upper jaw should be 2 mm greater than the same distance on the lower jaw.
Caring for baby teeth
You need to take care of your teeth immediately after teething. Moms do it first. For adults, special finger brushes have been created that are convenient for cleaning teeth from plaque, but so far without toothpaste. When the baby learns to rinse his mouth and spit, they move on to brushing with children's toothpaste without fluoride (this can be done earlier if the tube indicates that the toothpaste is from 0 years). So, gradually, the child will form a useful habit of caring for the oral cavity.
Another important reason for caring for teeth from infancy is that it affects the formation of permanent teeth and bite. For example, caries of a temporary tooth can transfer to the germ of a permanent one. And early loss (before 5 years) of a baby tooth will lead to uneven dentition in the future. If the molar does not begin to grow in time, the adjacent baby teeth will move and fill the resulting space.
Normal and deviations in tooth sizes
All dental units of the same name have approximately the same height and width, except for the central (medial) incisors. The size of the front teeth of the upper jaw is normally slightly larger than that of the lower jaw. The height of the crown of the upper central incisors varies from 9 to 12 millimeters, width - from 8 to 9 millimeters. The lower teeth are similar in height, but are about 5 millimeters wide. The size of a person's wisdom teeth does not differ from the parameters of other molars. The table below shows the average width of dental crowns in millimeters.
| Upper jaw | Lower jaw | |
| Medial incisor | 8.5 mm | 5.3 mm |
| Lateral incisor | 6.5 mm | 6 mm |
| Fang | 7.6 mm | 6.7 mm |
| First premolar | 6.7 mm | 6.8 mm |
| Second premolar | 6.4 mm | 7 mm |
| First molar | 9.4 mm | 10 mm |
| Second molar | 9.4 mm | 10.2 mm |
Anomalies in the size of human teeth can be congenital or acquired and are accompanied by malocclusion, impaired chewing functions and an unaesthetic appearance of a smile. The most common deviations are macrodentia and microdentia.
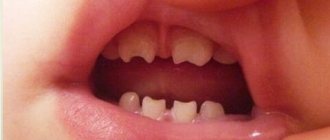
Timing of teething in children
On average, the first teeth in healthy children appear at 5–6 months. But sometimes it happens that someone has a white bump visible at 4 months, and someone smiles with a toothless mouth even at 8-12 months. And this is not a deviation from the norm. According to studies by a number of authors, the timing differs depending on the region of residence, race, and gender of the child. For example, children in the southern regions develop teeth a little earlier than those in the north. The formation of temporary teeth is also influenced by the following factors:
- heredity;
- maternal toxicosis in the second and third trimester of pregnancy;
- prematurity;
- artificial feeding;
- quality of drinking water;
- hypothyroidism and other endocrine pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- weakened immunity;
- rickets.
It is impossible to speed up the timing and influence the sequence of teething in children. The only thing parents can do at this time is to alleviate the baby’s condition if he is restless and in pain (more on this below).
Macrodentia
The tooth size exceeds the norm by more than 2 millimeters. Pathology occurs due to the fusion of two rudiments or the main and supernumerary teeth during the period of formation. The cause of macrodentia can be endocrine diseases, metabolic disorders or heredity. There are five types of pathology:
- localized - one or two teeth are significantly larger than the rest;
- generalized - the entire dentition differs in size from the other;
- isolated - enlargement of one medial incisor;
- absolute - the size of the teeth of both jaws exceeds the norm;
- relative - excessive growth of the upper or lower incisors.
Anatomical features of the upper teeth
- The central incisor (the largest of all eight) has a chisel-shaped crown with a convex surface and one cone-shaped root. The only root canal in 75% of cases is straight.
- The lateral incisor with the same chisel-shaped crown and the same convex surface has a characteristic depression in the enamel - a “blind fossa”. There is one root canal, but more often it is deviated to the side.
- The canines on the upper dentition are often larger than those on the bottom. They are characterized by a crown pointed on all sides and the longest cone-shaped root. Canines have a single root canal, which can be straight (45%), distally deviated (30%) or vestibular deviated (12%).
- The first premolar with a prism-like crown is characterized by a convex lingual surface. On the chewing side there are tubercles, and between them there is a fissure. In the upper dentition, these teeth are always larger than in the lower one. The root has extended longitudinal grooves, which divide it in 60% of cases into two parts - buccal and palatal. There are often also two root canals.
- The second premolar with the same prism-shaped crown has predominantly one straight cone-shaped root with expanded lateral surfaces. Sometimes the root bifurcates closer to the top. There are often two root canals.
- The first molar is the largest tooth in the dentition. The rectangular crown has a diamond-shaped chewing surface with four cusps and an H-shaped fissure between them. There are usually three root canals, but sometimes there are 4 (25%) or 5 (1%).
- The second molar with a classic cube-shaped crown has 4 cusps and an X-like fissure on the chewing side. The tooth has 3 roots and three (87%) or four (13%) canals.
Microdentia
The size of teeth in microdentia is less than anatomical standards. The list of reasons for deviation includes exposure to radiation, premature removal of a baby tooth, narrow jaw, and infectious diseases. There are several types of anomalies:
- isolated - a single violation affecting the lateral incisors;
- relative - the teeth are of normal size, but look smaller due to the enlarged jaw, as a result of which interdental spaces and diastema are formed;
- generalized - the defect covers a group of teeth.