Nosological classification (ICD-10)
- A41.9 Septicemia, unspecified
- A49.3 Mycoplasma infection, unspecified
- A59.0 Urogenital trichomoniasis
- A74.9 Chlamydial infection, unspecified
- B00.0 Herpetic eczema
- B00.1 Herpetic vesicular dermatitis
- B18 Chronic viral hepatitis
- B25.9 Cytomegalovirus disease, unspecified
- B34 Viral infection of unspecified localization
- B37.3 Candidiasis of the vulva and vagina (N77.1*)
- G03.9 Meningitis, unspecified
- J06 Acute upper respiratory tract infections of multiple and unspecified localization
- J11 Influenza, virus not identified
- J18 Pneumonia without specifying the pathogen
- N39.0 Urinary tract infection without established location
- N76 Other inflammatory diseases of the vagina and vulva
- O35.3 Fetal injury (suspected) due to maternal viral disease requiring maternal medical attention
- O35.8 Other fetal anomalies and lesions (suspected) requiring maternal medical attention
Compound
| Ointment for local and external use | 1 g |
| active substance: | |
| interferon human recombinant alpha-2 | 40000 IU |
| excipients: tocopherol acetate - 0.02 g; anhydrous lanolin - 0.34 g; medical petroleum jelly - 0.45 g; peach oil - 0.12 g; purified water - up to 1 g |
| Gel for local and external use | 1 g |
| active substance: | |
| interferon human recombinant alpha-2b | 36000 IU |
| excipients: alpha-tocopherol acetate - 0.055 g; methionine - 0.0012 g; benzoic acid - 0.00128 mg; citric acid monohydrate - 0.001 g; sodium tetraborate decahydrate - 0.0018 mg; sodium chloride - 0.004 g; human serum albumin solution 10% - 0.02 g; distilled glycerin (glycerol) - 0.02 g; carmellose sodium - 0.02 g; ethanol 95% - 0.055 g; purified water - up to 1 g |
| Suppositories for rectal use | 1 sup. |
| active substance: | |
| interferon human recombinant alpha-2b | 150000 IU |
| 500000 IU | |
| 1000000 IU | |
| 3000000 IU | |
| excipients: alpha-tocopherol acetate - 0.055/0.055/0.055/0.055 g; ascorbic acid - 0.0054/0.0081/0.0081/0.0081 g; sodium ascorbate - 0.0108/0.0162/0.0162/0.0162 g; disodium edetate dihydrate - 0.0001/0.0001/0.0001/0.0001 g; polysorbate 80 - 0.0001/0.0001/0.0001/0.0001 g | |
| base: cocoa butter and confectionery fat - up to 1 g |
Release form and composition
The gel is a gel-like opaque mass with a uniform consistency of medium viscosity. The composition has a white-gray tint. Available in 12 ml aluminum tubes and polystyrene jars of the same volume. The pharmaceutical product is supplied in cardboard boxes and includes instructions for use.
Composition of the drug, 1 g:
- Alpha-tocopherol acetate
interferon Alpha-2b (recombinant type) – 36,000 IU – main active ingredient; - methionine – 1.2 mg;
- sodium chloride – 4 mg;
- alpha-tocopherol acetate – 55 mg;
- ethanol – 55 mg;
- carmellose sodium – 20 mg;
- glycerol – 20 mg.
Due to the targeted effect, the gel helps to increase the concentration of secretory antibodies (IgA), thereby ensuring a prolonged therapeutic effect.
Pharmacodynamics
Human recombinant interferon alpha-2b has pronounced immunomodulatory, antiviral, antiproliferative properties, suppresses the replication of RNA and DNA viruses.
The complex composition of the drugs (ointment, suppositories, gel) causes a number of new additional effects: in the presence of antioxidants (tocopherol acetate and/or ascorbic acid), the specific antiviral activity of human recombinant alpha-2b interferon increases, its immunomodulatory effect on T- and B-lymphocytes increases , the level of secretory immunoglobulins of class A increases, the level of immunoglobulin E normalizes, and the functioning of the endogenous interferon alpha-2b system is restored. Ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol acetate, being highly active antioxidants, have anti-inflammatory, membrane stabilizing, and regenerating properties. The use of the drug VIFERON® as part of complex therapy makes it possible to reduce therapeutic doses of antibacterial and hormonal drugs, as well as reduce the toxic effects of this therapy.
It has been established that when using the drug VIFERON® there are no side effects that occur with parenteral administration of interferon alfa-2b preparations, and no antibodies are formed that neutralize the antiviral activity of interferon alfa-2b.
Description of the drug
Viferon gel has all the advantages characteristic of liniment, but provides much better results due to rapid absorption by the problem area (it has a “lighter” glycerin base). The ointment is made on a Vaseline basis, it is denser and thicker in consistency.
Viferon gel is actively used for the treatment of stomatitis in both adults and children.
Gel Viferon can be used for preventive purposes. It is prescribed during pregnancy, breastfeeding and infants under 1 year of age. For the form in question there are no age criteria or restrictions on use.
Clinical and pharmacological group
Viferon is an interferon and belongs to the therapeutic group of MIBP-cytokines. The drug is characterized by a pronounced antiviral and immunomodulatory effect. The components of the medication suppress the activity of herpes viruses (Herpes Simplex) and stimulate the phagocytic function of neutrophils in problem areas.
pharmachologic effect
The high effectiveness of the pharmaceutical agent in the fight against herpetic diseases of the oral cavity is due to the activity and interaction of several active substances at once.
- Interferon type alpha-2b is characterized by immunomodulatory properties: it forms increased cytotoxicity of lymphocytes to pathogenic cells, enhances the phagocytic activity of macrophages. Prevents the replication of DNA that contains viral agents.
- Alpha tocopherol acetate – increases the resistance of healthy cells to viral microorganisms by stabilizing their membrane structure. The antioxidant in question quickly eliminates swelling and triggers regenerative biochemical processes.
- Ascorbic acid increases the efficiency of the patient’s immune system and accelerates the body’s response to viral agents. The effect is achieved by increasing the secretion of class A immunoglobulins.
The drug helps reduce therapeutic doses of hormonal and antibacterial medications during complex therapy. The gel form allows you to prolong the action of the components.
Indications for the drug Viferon®
Ointment
viral (including herpetic) lesions of the skin and mucous membranes of various localizations;
treatment of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections in children over 1 year of age.
Gel
in complex therapy of ARVI, incl. influenza, frequent and prolonged acute respiratory viral infections, incl. complicated by bacterial infection;
prevention of acute respiratory viral infections, including influenza;
in complex therapy of recurrent stenotic laryngotracheobronchitis;
prevention of recurrent stenosing laryngotracheobronchitis;
in complex therapy of acute and exacerbations of chronic recurrent herpetic infections of the skin and mucous membranes, incl. urogenital form of herpetic infection;
in complex therapy of herpetic cervicitis.
Suppositories
In complex therapy:
ARVI, including influenza, incl. complicated by bacterial infection, pneumonia (bacterial, viral, chlamydial) in children and adults;
infectious and inflammatory diseases of newborns, incl. premature babies: meningitis (bacterial, viral), sepsis, intrauterine infection (chlamydia, herpes, CMV infection, enterovirus infection, candidiasis, including visceral, mycoplasmosis);
chronic viral hepatitis B, C, D in children and adults, incl. in combination with the use of plasmapheresis and hemosorption for chronic viral hepatitis of pronounced activity, complicated by cirrhosis of the liver;
infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (chlamydia, CMV infection, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, papillomavirus infection, bacterial vaginosis, recurrent vaginal candidiasis, mycoplasmosis) in adults;
primary or recurrent herpetic infection of the skin and mucous membranes, localized form, mild to moderate course, incl. urogenital form in adults.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults
It is important to start etiotropic treatment in a timely manner to prevent chronicization of the pathology. Therapy for stomatitis includes a set of measures:
- the symptomatic part of therapy consists of taking antipyretic drugs;
- in case of severe pain, painkillers are prescribed;
- the key stage of treatment is to find and eliminate the root cause of stomatitis: the causative agent or the underlying disease; which helps prevent relapses of the painful condition;
- local treatment involves the use of local agents with a healing and antibacterial effect;
- An important component of the treatment plan is the selection of a diet and the exclusion of products containing aggressive and irritating substances (menthol, sodium lauryl sulfate) from the regimen of regular hygienic treatment of the oral cavity.
A gentle diet includes adding soft fermented milk products, neutral vegetables and fruits, cereal porridges, lean boiled meat and low-fat broths to the diet. Tea and coffee should be avoided; it is recommended to replace them with decoctions, fruit drinks and water. Spicy, sour, hot dishes or food, parts of which can physically injure tissues affected by stomatitis, are excluded. After eating, you should rinse your mouth with water or a medicinal solution.
In cases of recontamination of ulcerated areas of the mucosa, drugs containing chlorhexidine bigluconate are used. Long-term use of these drugs has an unpleasant side effect: dark spots appear on tooth enamel and fillings, which disappear after the end of treatment.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Ointment: since when applied externally and locally, the systemic absorption of interferon is low and the drug has an effect only in the lesion, it is possible to use the drug VIFERON® during pregnancy and lactation.
Gel: since the systemic absorption of interferon when applied topically is low and the drug has an effect only in the lesion, it is possible to use the drug VIFERON® during pregnancy and breastfeeding. During lactation, do not use the drug on the area of the nipples and areola.
Suppositories: the drug is approved for use from the 14th week of pregnancy. There are no restrictions for use during lactation.
The difference between VIFERON suppositories and Ointment and Gel: local and systemic action
The main difference between rectal suppositories and external forms of the drug (ointment and gel) is their systemic effect. This means that the incoming active substances (interferon and vitamins E and C) exert their therapeutic effect on the entire body, providing a generalized approach to the treatment of a particular disease. VIFERON Ointment and Gel act locally, that is, only at the site of application. They do not have a systemic effect. That is why experts often recommend both forms: local and systemic, in order to enhance the clinical effectiveness of therapy.
Side effects
Ointment: in most cases, VIFERON® is well tolerated. When applied to the nasal mucosa, side effects are weak and transient and disappear on their own after discontinuation of the drug.
Gel: in extremely rare cases, a local allergic reaction may occur in some highly sensitive individuals. In such cases, stop using the drug.
Suppositories: in rare cases - allergic reactions (skin rashes, itching). These phenomena are reversible and disappear 72 hours after stopping the drug.
Symptoms of stomatitis in adults
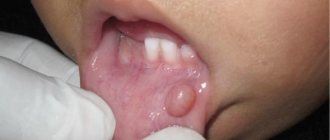
Aphthous stomatitis. At the beginning, signs of general intoxication of the body and malaise, hyperthermia, soreness of the mucous membrane, which soon becomes covered with aphthous ulcers, are recorded. During the healing process, canker sores become scarred and leave scars.
Herpetic stomatitis. When the oral cavity is infected with herpetic virus type 1-2, there is a high risk of developing acute herpetic stomatitis. Typically, the rapid beginning of the formation of the clinical picture: hyperthermia, pronounced signs of general intoxication of the body. During examination of the oral cavity, hyperemic, edematous mucosa with areas of bleeding gums is visible. Increased saliva secretion and bad breath may occur. A few days after the manifestation of the pathology, the mucous membrane becomes abundantly covered with small pustules and vesicles, and necrotic changes in the epithelium occur.
Catarrhal and ulcerative stomatitis. The symptom complex of these two types of pathology is similar at the beginning of the disease, but after a few days the ulcerative form is identified by specific signs: severe hyperthermia, fatigue, headache and swelling of the lymph nodes closest to the source of inflammation. Ulcerative stomatitis affects the area of ulcer formation throughout the entire depth of the tissue, catarrhal lesions are limited to the upper layer of the mucous membrane. The pain intensifies while eating, sometimes so severe that it forces you to refuse food. Symptoms develop progressively and are most noticeable in people with weakened immune systems.
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis, or Vincent's stomatitis, occurs as a result of the activity of symbiotic microorganisms: spindle-shaped bacteria and a type of spirochete. The main reason for the pathological activity of these microorganisms is weakened immunity. Clinical manifestations of necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis:
- scattering of ulcers and erosions in the mouth;
- low-grade fever;
- pain and bleeding when pressing on the gums;
- bad breath with a hint of rot;
- the pathological process begins from the gingival margin and spreads further.
Angular stomatitis is widely known as “jams”. This form of stomatitis is characterized by painful cracks in the corners of the mouth. A feature of angular stomatitis is that in other forms of the disease the inner surface of the oral mucosa is affected, and when jammed, the integrity of the outer mucous layer is disrupted. In addition to the seasonal decrease in immunity, among the provoking factors recorded:
- gastrointestinal diseases
- metabolic pathologies
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system
- oral health problems
- long-term use of artificial hormones
- pathological growth of the streptococcus population;
- unbalanced diet;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- incorrect bite.
These factors create conditions for permanent irritation of the mucous membrane, which makes it vulnerable to erosion, attachment and the development of infections.
Allergic stomatitis, with all the polymorphism of manifestations, begins with dryness of the mucous membrane, itching sensations in the mouth and along the inner edge of the lips, the process of eating causes discomfort. The oral mucosa swells, becomes hyperemic, and in the absence of timely treatment, atrophy of the lingual papillae occurs.
Directions for use and doses
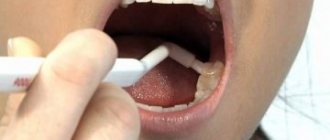
Ointment, externally and locally. For herpes infection, apply a thin layer of ointment to the affected areas 3-4 times a day and rub in gently. Duration of treatment is 5–7 days. It is recommended to begin treatment immediately when the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). When treating recurrent herpes, it is advisable to begin treatment in the prodromal period or at the very beginning of the appearance of signs of relapse.
To treat influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections, the ointment is applied in a thin layer to the mucous membrane of the nasal passages 3-4 times a day throughout the entire period of the disease.
Children from 1 year to 2 years - 2500 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 0.5 cm) 3 times a day; from 2 to 12 years - 2500 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 0.5 cm) 4 times a day; from 12 to 18 years - 5000 IU (1 pea with a diameter of 1 cm) 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
Gel, externally and locally.
In the complex therapy of ARVI, including influenza, long-term and frequent ARVI, incl. complicated by a bacterial infection: a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the previously dried surface of the nasal mucosa and/or to the surface of the tonsils 3-5 times a day using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab (see Note). The course of treatment is 5 days; if necessary, the course can be extended.
Prevention of ARVI, including influenza: during the period of rising incidence, a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the previously dried surface of the nasal mucosa and/or to the surface of the tonsils 2 times a day for 2–4 weeks.
In complex therapy of recurrent stenosing laryngotracheobronchitis: a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the surface of the palatine tonsils using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab in the acute period of the disease 5 times a day, for 5–7 days, then 3 times a day day for the next 3 weeks.
Prevention of recurrent stenosing laryngotracheobronchitis: a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the surface of the tonsils using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab 2 times a day for 3-4 weeks, courses are repeated 2 times a year.
In complex therapy of acute and chronic recurrent herpetic infection (at the first signs of the disease or during the period of warning signs): a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab to a previously dried affected surface 3–5 times per day. day for 5–6 days, if necessary, the duration of the course is increased until clinical manifestations disappear.
In complex therapy of herpetic cervicitis: 1 ml of gel is applied with a cotton swab to the surface of the cervix, previously cleared of mucus, 2 times a day for 7 days; if necessary, the duration of the course can be increased to 14 days.
Note. The gel is applied to the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity after cleansing the nasal passages, and to the surface of the palatine tonsils - 30 minutes after eating. When applying the gel to the tonsils, do not touch the tonsils with a cotton swab, but only with the gel; the gel flows down on its own along the surface of the tonsil. When applying the gel to the cervix, you should first remove mucus and discharge from the vaginal vaults and cervix with a cotton or gauze swab.
When applying the gel to the affected areas of the skin and mucous membranes, after 30–40 minutes a thin film is formed, onto which the drug is again applied. If desired, the film can be peeled off or washed off with water before reapplying the drug.
Suppositories, rectally.
1 suppository contains human recombinant interferon alpha-2b as an active substance in the indicated dosages (150,000 IU, 500,000 IU, 1,000,000 IU, 3,000,000 IU).
Acute respiratory viral infections, including influenza, incl. complicated by bacterial infection, pneumonia (bacterial, viral, chlamydial) in children and adults as part of complex therapy. Recommended dose for adults, including pregnant women and children over 7 years old VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Children under 7 years old, incl. For newborns and premature infants with a gestational age of more than 34 weeks, it is recommended to use the drug VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. The break between courses is 5 days.
Premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks are recommended to use the drug VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours every day for 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. The break between courses is 5 days.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of newborns, incl. premature babies: meningitis (bacterial, viral), sepsis, intrauterine infection (chlamydia, herpes, CMV infection, enterovirus infection, candidiasis, including visceral, mycoplasmosis) as part of complex therapy. Recommended dose for newborns, incl. premature babies with a gestational age of more than 34 weeks VIFERON® 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. The course of treatment is 5 days.
Premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks are recommended to use the drug VIFERON® 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours. The course of treatment is 5 days.
Recommended number of courses for various infectious and inflammatory diseases: sepsis - 2-3 courses, meningitis - 1-2 courses, herpes infection - 2 courses, enterovirus infection - 1-2 courses, CMV infection - 2-3 courses, mycoplasmosis, candidiasis , including visceral - 2-3 courses. The break between courses is 5 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Chronic viral hepatitis B, C, D in children and adults as part of complex therapy, incl. in combination with the use of plasmapheresis and hemosorption for chronic viral hepatitis of pronounced activity, complicated by cirrhosis of the liver. The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON® 3,000,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 10 days, then 3 times a week every other day for 6–12 months. The duration of treatment is determined by clinical effectiveness and laboratory parameters.
For children under 6 months of age, 300,000–500,000 IU per day is recommended; at the age of 6 to 12 months - 500,000 IU per day.
For children aged 1 to 7 years, 3,000,000 IU per 1 m2 of body surface area per day is recommended.
For children over 7 years old, 5,000,000 IU per 1 m2 of body surface area per day is recommended.
The drug is used 2 times a day every 12 hours for the first 10 days, then 3 times a week every other day for 6–12 months. The duration of treatment is determined by clinical effectiveness and laboratory parameters.
The daily dose of the drug for each patient is calculated by multiplying the recommended dose for a given age by the body surface area calculated using the nomogram for calculating body surface area by height and weight according to Garford, Terry and Rourke. The calculation of a single dose is carried out by dividing the calculated daily dose into 2 administrations, the resulting value is rounded up to the dosage of the suppository.
In case of chronic viral hepatitis of pronounced activity and liver cirrhosis, before plasmapheresis and/or hemosorption, it is recommended to use VIFERON® 150,000 IU for children under 7 years of age, VIFERON® 500,000 IU for children over 7 years of age, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours. within 14 days.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (chlamydia, CMV infection, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, papillomavirus infection, bacterial vaginosis, recurrent vaginal candidiasis, mycoplasmosis) in adults, including pregnant women as part of complex therapy. The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5–10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued.
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from 14 weeks of gestation) are recommended VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours for 10 days, then 3 times for 9 days with an interval of 3 days (on the 4th day) 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, it is indicated before delivery (from 38 weeks of gestation) VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
Primary or recurrent herpetic infection of the skin and mucous membranes, localized form, mild to moderate course, incl. urogenital form in adults, including pregnant women. The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON® 1,000,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days or more for recurrent infections. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. It is recommended to begin treatment immediately when the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). When treating recurrent herpes, it is advisable to begin treatment in the prodromal period or at the very beginning of signs of relapse.
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from 14 weeks of gestation) are recommended VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours for 10 days, then 3 times for 9 days with an interval of 3 days (on the 4th day) 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, it is indicated before delivery (from 38 weeks of gestation) VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days.
The use of VIFERON suppositories for various diseases
Does VIFERON Candles (suppositories) help children with fever and ARVI?
| The use of the drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) helps reduce the duration of the disease and its manifestations, such as fever, cough, lethargy, etc. |
With a runny nose
| A runny nose is one of the common symptoms of ARVI and influenza. The use of the drug in the complex therapy of ARVI and influenza helps to reduce the manifestations of a runny nose, as well as shorten the period of intoxication and fever. |
For cystitis
| Cystitis is one of the most common diseases of the urogenital tract, which can be caused by various pathogens. The drug is used to treat urogenital infections, including cystitis. The recommended dose for adults is VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5-10 days. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. |
For herpes
| It is recommended to begin treatment of herpes immediately when the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). When treating recurrent herpes, it is advisable to begin treatment in the prodromal period or at the very beginning of signs of relapse. |
VIFERON Candles (suppositories) for stomatitis
| For herpetic stomatitis, external forms of the drug VIFERON are used: Ointment and Gel. They are used to suppress the activation of the herpes virus and strengthen the immune system. VIFERON Ointment is applied in a thin layer to the lesions 3-4 times a day, the duration of treatment is 5-7 days. VIFERON Gel must be applied to the affected areas 3-5 times a day for 5-6 days. It is recommended to begin treatment immediately when the first signs of damage to the mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). |
VIFERON Candles (suppositories) in gynecology
| The drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) as part of complex therapy for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract helps to block the reproduction of the infectious agent. In addition, the use of this drug makes it possible to reduce therapeutic doses of antibacterial and hormonal drugs, as well as reduce the toxic effects of this therapy. The use of the drug is possible from the 14th week of pregnancy. |
For the flu
| Human recombinant interferon alpha-2b, which is part of the drug, helps fight influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections at any stage of the disease. A wide spectrum of antiviral activity allows the drug to be used in the complex therapy of any ARVI. There is experience in using VIFERON for H1N1 influenza. Studies have shown that the drug has a pronounced therapeutic effect against influenza, consisting in a significant reduction in the time it takes for the temperature to normalize and the disappearance of symptoms of intoxication, as well as a shortening of the period of manifestation of catarrhal symptoms. More about this |
VIFERON for the prevention of viral diseases
| Influenza and ARVI viruses most often enter the body through the respiratory tract, through the nose. Therefore, it is important to block the path of viruses precisely at this point of infection penetration. To prevent influenza and ARVI, use VIFERON Gel. Thanks to the gel base, the drug has a prolonged effect - for prevention it needs to be applied only 2 times a day. It is convenient for children and adults. Currently, extensive clinical experience has been gained in the use of the drug VIFERON Suppositories for the treatment of frequently ill children, aimed at reducing the incidence of diseases due to the immunomodulatory effect of the drug. Data from these clinical studies were published in the country's leading medical publications. |