We talk about a cold that has popped up on our lips and immediately remember Acyclovir. This is an immunomodulator belonging to the group of antiviral drugs used to treat herpes types 1 and 2, genital herpes and chickenpox. It contains no toxic elements, it acts selectively - only on the cells of the virus itself, suppressing their reproduction.
Acyclovir-Acri ointment
So, let's start with the fact that herpes does not only occur on the lip; viral diseases affect various parts of the human body. Therefore, Acyclovir is sold in the following forms, each of which has its own indications for use: cream and ointment for topical use 5%, tablets (200 mg, 400 mg, 500 mg), solution for intravenous injection Lyophilisate 250 mg, ophthalmic ointment 3%.
Indications for use
Acyclovir is indicated for the following diseases:
- infectious lesions of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the herpes simplex virus (primary and recurrent genital);
- chicken pox;
- shingles;
- herpetic lesions in children in the first month of life (including intrauterine infection);
- prevention of cytomegalovirus infection in patients who have undergone bone marrow transplantation;
- herpetic lesions of the cornea of the eyes (for eye ointment);
- Epstein-Barr virus infection.
Doses and method of administration
Dosage of the drug Acyclovir
Dosage
The dosage depends on the disease and the severity of its course.
- Hepatic infection of the skin and mucous membranes involves prescribing 200 mg of medication to children and adults 5 times a day at an interval of 4 hours, interrupted by sleep (8 hours). Duration of therapy – 5 days.
- When preventing influenza or ARVI, Acyclovir is prescribed 4 times a day, 200 mg every 6 hours.
- As a complex therapy for severe immunodeficiency, the drug is taken at a dose of 400 mg 5 times a day.
- Chickenpox in children and adults whose body weight exceeds 40 kg requires taking the medicine 800 mg 5 times a day. Children over 2 years of age with a body weight below 40 kg take the drug at a rate of 20 mg per kilogram of weight 4 times a day for 5 days.
- Treatment of herpes zoster involves taking Acyclovir for children over 6 years of age and adults, 800 mg every 6 hours for 5 days. Children from 2 to 6 years old take the medicine 400 mg 4 times a day, and children under 2 years old receive it 4 times a day 200 mg.
How to use Acyclovir
The method of use of Acyclovir depends on the form of release. The tablets are swallowed without chewing, regardless of food intake, with plenty of water. Apply the ointment and cream using a cotton swab to the affected areas in a thin layer 5 times a day (every 4 hours plus a night break). The lyophilisate (intravenously) must first be diluted to the desired concentration. Eye ointment is applied in a 1 cm strip behind the lower eyelid 5 times a day after 4 hours.
Acyclovir ointment
Acyclovir ointment and cream are intended for external use, and application to the surface of the mucous membranes (nasal and oral cavities) is not recommended, but not contraindicated. It is necessary to remember some rules for applying medications to the mucous membrane and consult a doctor!
Herpetic rashes in the oral cavity are localized on the palate, inner sides of the cheeks and lips. As for the nasal cavity, herpes sores appear both in the vestibule of the nose - the thin skin inside the nose - and on the mucous membrane, which is located 1.5-2 cm from the edge of the nostril. If herpes appears on the lip or on the eve of the nose, then the application technique is the same as for the rest of the face and body - on cleansed skin 5 times a day, every 4 hours, with a break at night.
As for the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, due to the fact that drool and mucus interfere with the penetration of the drug and, at the same time, contribute to the spreading of the ointment over the mucous membrane, which reduces the effectiveness of the drug, the most correct decision would be to switch to the tablet form of Acyclovir. Also, do not forget that the mucous membrane is a very thin tissue, which means that the development of allergic reactions is stronger and more pronounced.
Acyclovir cream
If the ointment still needs to be applied, then clean the oral or nasal cavities before using Acyclovir. It is advisable to rinse them with saline solution or other rinsing or rinsing agent, and then blot the surface with a gauze pad or cotton ball. Then apply a small amount of cream or ointment pointwise. There may be a burning sensation and pain. If they pass, then apply the remaining cream or ointment. If the pain intensifies, then this is an allergic reaction, and the use of the product must be stopped. Remember that the cream and ointment will enter the esophagus through the oral cavity; in small quantities this is not dangerous, but it is better to use another form of Acyclovir.
Types of stomatitis
Everyone is more accustomed to saying “stomatitis”, but it would be more correct to say “stomatitis”, since this is a generalizing concept for a whole group of diseases. Depending on the causes of stomatitis, it can be divided into several types, each of which has a number of characteristics.
Viral or herpetic stomatitis in children
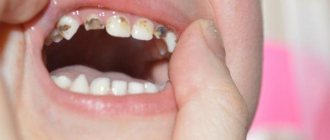
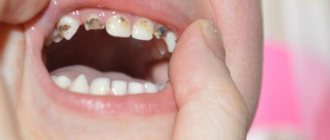
One of the most common types of stomatitis in children is caused by the herpes simplex virus. Typically, a child becomes infected through airborne droplets. In addition, the virus is transmitted through dishes, toys, and household items. Most often, herpetic stomatitis appears in a child between the ages of one and four years. The disease begins with a cold, accompanied by lethargy and increased body temperature. Sometimes there is a runny nose and cough. Around the second day, small round or oval erosions of a light yellow color with a bright red border appear on the lips, tongue and inside of the cheeks. Swelling appears, the gums begin to bleed, and the child refuses to eat.
Traumatic stomatitis in a child
The disease is caused by mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. For example, burns from hot food, a too hard nipple, the habit of chewing a pencil. In addition, traumatic stomatitis often occurs in children with malocclusion due to frequent biting of the cheeks and tongue.
Candidal stomatitis
Appears in children under one year of age. The cause is Candida fungi. The main symptom is the appearance of a white coating in the baby’s mouth. It should be noted that this should not be confused with regular flowering after feeding. A cause for concern is if plaque persists and the baby refuses to eat.
Drug or allergic stomatitis in children
Caused by certain allergies or reactions to medications. If this type of disease is suspected, it is necessary to identify and remove the allergen, otherwise there is a risk of unpleasant consequences, including anaphylactic shock.
Each type of stomatitis is characterized by a certain childhood age. Young children often have candidiasis or fungus (thrush). At the age of “I want to know everything” in a child of 3-4 years, stomatitis is usually infectious in nature, when the infection is transmitted through dirty hands or objects. From one to four years, an acute herpetic form of the disease is often observed.
Can chickenpox be treated with Acyclovir?
Acyclovir can help fight chickenpox
In the instructions for use of Acyclovir, chicken pox (varicella zoster), or simply chickenpox, appears among the indications for use. Acyclovir actively fights it, but it all depends on the immunity of the individual person and the nature of the disease. For moderate and severe forms of chickenpox, Acyclovir is prescribed both in the form of tablets and as a cream or ointment. For adults, the drug is prescribed at an early stage of the disease, and for children under 12 years of age - only in case of intolerance to the painful condition or in severe cases of the disease. The dosage regimen is as follows: adults are recommended to take 1-2 tablets of 400 mg each. every 4 hours 3-5 times a day. The pediatric dose is half the adult dose, and the time interval between doses is increased by 1 hour, but not more than 4 times a day. Cream or ointment is applied pointwise to affected areas up to 5 times a day. If the mucous membranes of the eyes are affected by chickenpox, in this case an eye ointment is used, placed behind the lower eyelid up to 5 times a day. Acyclovir is used for 5 days, but the attending physician may make adjustments to the therapy.
Is it possible to use Acyclovir for a cold?
Acyclovir can be prescribed for ARVI
Acyclovir successfully fights herpes viruses, but sometimes a therapist prescribes Acyclovir for ARVI. Why? It is no secret that with ARVI and colds in general, the immune system is weakened, and this is fertile ground for the manifestation of herpes, which, against the background of the same ARVI, does not alleviate the situation. Although Acyclovir is ineffective in the fight against viruses that cause respiratory diseases, it is used as a prophylactic agent to prevent the development of herpes.
Acyclovir during pregnancy
A pregnant woman's immune system is weakened and may be susceptible to viral infections. Therefore, expectant mothers and those undergoing lactation are asking the question, “Is it possible to use Acyclovir during pregnancy?” According to the instructions, the use of acyclovir during pregnancy is permissible, but with caution. Moreover, this formulation means that use is possible, firstly, only as prescribed by a doctor, and secondly, only when the therapeutic effect is greater than the risk. This applies to all dosage forms. As for the lactation period, the drug passes into breast milk. Therefore, first consult a doctor, and then take the drug. In case of negative reactions, it is necessary to change therapy or stop breastfeeding for a while.
What are the side effects of acyclovir?
Common side effects after taking acyclovir may include:
- headaches and dizziness;
- pain in the gastrointestinal tract, feeling of nausea;
- hives (itchy skin with large red rashes);
- fast fatiguability.
If you observe the following symptoms, you should contact an ambulance as soon as possible:
- skin hemorrhages on the body;
- vomit;
- problems with urination;
- behavioral changes;
- pain in the mouth when using the buccal form of acyclovir.
Interaction with other drugs and alcohol
Acyclovir and alcohol
When a doctor prescribes a particular drug, the question arises about compatibility not only with other drugs (more on this below), but also with alcohol. After all, a cold often appears at the wrong time, but plans are made to attend an event where there will be strong drinks. What to do in such a situation? Despite the absence of direct contraindications, alcohol and medicine are incompatible.
It is not recommended to take Acyclovir with alcohol
Firstly, alcohol, by suppressing the activity of leukocytes and the production of antibodies, reduces the body's defenses. Secondly, any drug puts a strain on the liver and kidneys, and alcohol has a similar effect. And when the liver cannot cope with processing, enzymes are released that suppress the action of Acyclovir. That is, the effect of the immunomodulator will be zero. Also, this can provoke intoxication of the body and increase the risk of side effects such as nausea and vomiting; convulsions, disturbances of consciousness; tremors and hallucinations; allergies (itching, skin rashes, urticaria, angioedema); loose stools; anemia; shortness of breath, pain in the sternum, increased heart rate; disorders of swallowing and respiratory functions; cephalalgia, dizziness, drowsiness.
If you suffer from a hangover after drinking, this is not the right time to take Acyclovir. When a hangover occurs, the body is already under stress. Taking the drug may cause a deterioration in your general condition.
Acyclovir and antibiotics
It may happen that Acyclovir is taken at the same time as antibiotics. When treating viral diseases, simultaneous use of antibiotics is not recommended, as they will simply interfere with each other. That is, treatment will be ineffective either from Acyclovir or from another drug. The one-time use of medications will not speed up the patient’s recovery, and the liver will not say “thank you” to you, since it creates an additional load, which can lead to negative consequences. In exceptional cases, as prescribed by a doctor, a one-time dose is possible, but it is associated with risks. Be sure to consult with your doctor.
Symptoms of acyclovir overdose
You should stop taking acyclovir if you experience these symptoms:
- easy bruising or bleeding, purple or red dotted spots under the skin;
- changes in behavior (motor restlessness and emotional agitation, confusion, hallucinations);
- disorders of the urinary system (anuria (lack of urination), painful or difficult urination), swelling of the lower extremities;
- feeling tired, shortness of breath.
Uncomplicated side effects of acyclovir include:
- skin allergic manifestations (itching, soreness of the skin when touched, rashes);
- nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting, stomach upset (diarrhea);
- headaches and/or dizziness;
- pain in the mouth when taking acyclovir tablets buccally (by the cheek).
Typically, cases of acyclovir overdose have been recorded extremely rarely, but common manifestations are allergic reactions, which entail a number of symptoms:
- hives, blisters, itching;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or legs;
- hoarseness;
- cardiopalmus;
- general weakness;
- pale skin;
- confusion and/or loss of consciousness;
- the appearance of unusual bruises on the body;
- blood in urine and stool;
- numbness, burning or tingling in the upper and lower extremities;
- temporary inability to move parts of the body.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Analogs
Acyclovir analogs
Along with Acyclovir, patients with viral diseases are prescribed Remantadine. Is it possible to take Acyclovir and Remantadine at the same time? What's better? Remantadine prevents the proliferation of viral cells, strengthens the immune system, and is also used as a prophylactic during influenza epidemics.
Indications for taking Remantadine are:
- tick-borne viral encephalitis;
- flu;
- herpes type 1 and 2.
The drug can be used by children aged 7 years and older.
The main purpose of Acyclovir is the treatment of herpes, chickenpox and antiviral therapy. By integrating into the DNA structure of viruses, Acyclovir prevents them from multiplying and developing. If necessary, the medicine can be prescribed to children.
You should not take Rimantadine and Acyclovir at the same time, since both of these drugs are similar. Only the attending physician can accurately determine the required drug and calculate the dosage.
What you need to know about acyclovir
Do not forget that acyclovir, like all other medications, must be stored out of the reach of children. Never share your medications with other people, so as not to harm their health. Remember that acyclovir should be used only for its intended purpose.
Always consult your doctor to make sure the information on this page applies to your individual situation.
Sources
Acyclovir / Drugs.com (English)
Acyclovir / State register of medicinal products (ukr.)
apteka24.ua provides comprehensive and reliable information on issues of medicine, health and well-being, however, diagnosis and choice of treatment methods can only be made by your attending physician! Self-medication may be unsafe for your health. apteka24.ua is not responsible for possible negative consequences arising from the use by users of apteka24.ua of the information posted on the site.
Preventative treatment
The question often arises of how to prevent such an unpleasant situation as the manifestation of herpes. What should be the prevention? The recommendations are simple:
- Get vaccinated every three years to avoid infection or recurrence of the disease;
- Take acyclovir as a preventive measure when the disease may be triggered. Consult your doctor to determine your risk factors;
- Don't forget about hygiene;
- Strengthen your immune system: lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and move more.
Acyclovir against herpes
Prevention of stomatitis in children
Irritative stomatitis can be prevented with good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups and proper nutrition. Because many adults and children carry the herpes virus and can transmit it even without symptoms, there is no practical way to prevent herpetic stomatitis. However, parents may discourage their child from kissing, eating, or playing in close contact with people who have an active herpes infection.
Ulcers can be minimized by teaching children to avoid injury, even minor trauma to the mouth. If our doctor determines that a child has a nutritional deficiency, parents can make sure the child is taking appropriate supplements and eating recommended foods. It won’t hurt to visit the dentist once every six months if we have previously discovered stomatitis in the child. Regular visits to our clinic will help prevent serious complications and detect the disease in time.