Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Inflammation of the gums, or periodontitis, is one of the most common dental diseases. This pathology of the oral cavity can occur due to both chronic diseases and local traumatic injuries.
The main symptom of periodontitis is an acute inflammatory process of gum tissue. Lack of treatment can lead to the development of severe forms of the disease, characterized by tooth loss and displacement.
Prevention and treatment of periodontitis at home
The most effective method of treating almost any disease, including periodontitis, is its prevention. There are simple prevention methods that can be used at home. Their use will prevent the occurrence of periodontitis symptoms and avoid the need for drug and surgical treatment.
The main thing that needs to be done to prevent any pathologies of the oral cavity is to strictly follow the principles of dental hygiene:
- brush your teeth twice a day with therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste using a medium-hard brush;
- After a meal, remove leftover food using dental floss.
- a rinse with an antibacterial effect, for example, Asepta based on lemon balm, calendula or St. John's wort extract, has a soothing effect on the gums;
- it is necessary to regularly consume solid and plant foods, ensuring sufficient chewing load on the teeth;
- one of the reasons for the development of periodontitis is a lack of vitamins A, C and B vitamins in the diet. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to take a vitamin complex containing a sufficient amount of these vitamins;
- You should visit your dentist twice a year for preventive teeth cleaning. Timely removal of plaque and tartar will help avoid gum inflammation and further development of pathology.
Causes of periodontitis
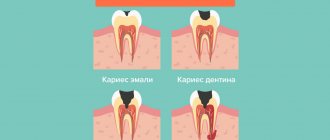
A decisive role in the development of the disease is played by pathogenic microorganisms in dental plaque, which contribute to gum inflammation. The accumulating bacterial plaque hardens. Tartar builds up and penetrates deep into the gums, causing the mucous membrane to begin to peel off from the tooth, creating a free space that is gradually filled with pathogenic bacteria. Gingivitis develops, which without proper treatment quickly transforms into acute periodontitis.
Factors that provoke the development of periodontitis also include:
- regular injury to the gums due to incorrectly installed dentures and orthodontic systems;
- incorrect occlusion;
- accumulation of food particles and plaque under prosthetic and orthodontic structures;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- decreased immunity;
- physical trauma to teeth (impact);
- bruxism.
The development of chronic periodontitis can be influenced by problems with the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, insufficient chewing load (the predominance of soft foods in the diet), autoimmune pathologies, and allergies to certain medications.
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
Orthodontics comes to the fore
Today, a huge mistake is happening both in the search for the causes of periodontal disease and in making a diagnosis, as well as in the method of effective treatment. Instead of putting the tooth into occlusion, removing it from a traumatic bite, patients are offered all these manipulations that I have previously voiced, which are not at all aimed at getting rid of these complaints, but only at the fact that patients are wasting time, the processes are getting worse.
In the treatment of the so-called periodontal disease is a big problem in the loss of time for inadequate treatment, and the loss of time for the patient is a complication of the pathology of dental occlusion, and the transition of the stage of the disease to a more advanced form.
If a patient, for example, three years ago had a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then due to the “treatment of periodontal disease” he has already lost five millimeters, that is, we have lost time.
And if he came to the orthodontist with a loss of bone tissue of two millimeters, then it would be easier to stop the loss of gums, it would be easier to eliminate the development of gum pathology after orthodontic treatment, when the teeth become aligned with the dentition.
We can already talk about the fact that we close all exposed necks of gum recession, thereby treating the neck of the tooth. But when patients waste time on treatments that are inadequate for the disease, sometimes closing the recession is no longer possible. Because there are also strict indications and contraindications for the treatment of gum recession.
Acute and chronic periodontitis: symptoms and treatment
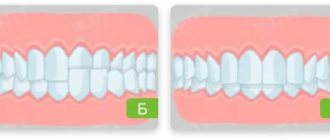
As mentioned, the treatment plan will depend on the severity of the inflammation and how widely it has spread. Periodontitis affecting a few teeth is localized; periodontitis affecting most (or all) teeth is generalized.
Acute periodontitis, which has pronounced symptoms, occurs less frequently than chronic periodontitis and usually affects one or two teeth. It is often caused by trauma to the tooth or periodontal tissue, or improper installation of a crown or filling. This type of disease often occurs aggressively, causing rapid destruction of bone and muscle tissue.
If the pathology is chronic, then phases of exacerbation are replaced by phases of remission. At the same time, chronic periodontitis slowly and steadily progresses from the initial stage to the severe one. This form of pathology can be caused by both local factors (for example, trauma to the oral cavity) and general ones.
How is periodontitis diagnosed?
It is possible to determine whether a patient has periodontitis or not already at the first appointment, focusing on his complaints and the condition of the oral cavity. Moreover, when diagnosing the disease, special tests are used, the most popular of which is the Parma index. It works as follows: a special Schiller solution is applied to the gums, which reacts to unhealthy tissues and colors them in a bright color, revealing the source of inflammation. There is also an index that determines the level of bleeding, and a Russell test that reveals the condition of not only the gums, but also the bone tissue.
X-ray studies, which determine the degree of the disease that has arisen, are the main ones in the diagnosis of periodontitis. For such a study, you can use a radiovisiograph (a device for conventional targeted X-rays), or an orthopantomograph (an extraoral device that can take a picture of both jaws at once). However, the most informative method is considered to be extraoral cone-beam computed tomography, which allows layer-by-layer examination of each piece of the jaw and tooth in three-dimensional format.
Currently, the Florida probe computer diagnostic technique has appeared, which allows you to most accurately determine and record the depth of periodontal pockets - the main pathological manifestation of periodontitis. The examination is easily tolerated by patients and helps the doctor prescribe appropriate treatment.
For periodontitis, a microbiological study is also carried out, with which you can study the microflora of the oral cavity and determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics for a more accurate selection of drug treatment.
Another mandatory test is a blood test. It allows you to identify the cause of the disease, which may be either the initial stage of diabetes or a chronic infectious process in other organs and systems, as well as disorders associated with hormonal levels and metabolism.
In the process of diagnosing periodontitis, consultation with related specialists is often required to identify and treat concomitant diseases.
Professional hygiene for effective treatment of periodontitis
In the vast majority of cases, the development of this disease is associated with insufficient oral hygiene. The periodontal tissues become inflamed due to extensive dental plaque, so the first thing to do to treat periodontitis is a professional cleaning.
This procedure includes the following steps:
- removal of dental plaque
- polishing the tooth surface
- treating the tooth with protective varnish.
Modern cleaning methods are gentle on the enamel and cause minimal discomfort. Also, at the stage of removing tartar and plaque, preparations should begin for the treatment of caries and the removal of hopelessly affected teeth.
Classification of periodontitis
The most effective treatment for periodontitis can be chosen when its form is accurately diagnosed. Classification of types of disease is carried out according to the severity of its symptoms, the presence of complications and consequences of the development of periodontitis.
Based on the form of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished:
1. An acute form of periodontitis, in which the process of inflammation in the periodontium develops at a rapid pace and can cause the appearance of abscesses and fistulas.
2. Chronic periodontitis is asymptomatic and its development is slow. The disease may not show itself in any way, but tissue destruction will still occur, and therefore it is so important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment of chronic periodontitis.
According to the area of manifestation, periodontitis is graded into the following types:
1. Localized periodontitis. This type of disease arises mainly from gum trauma and responds well to treatment.
2. Generalized periodontitis. Treatment of generalized periodontitis is a complex and lengthy process, since the disease spreads to a significant part of the periodontium.
Periodontitis is also classified according to the stages of its development and the appearance of various complications that arise due to improper or late treatment of the disease. It is important to understand that only a qualified doctor can correctly diagnose the type of periodontitis and choose a method of treatment. In our clinic in Moscow, Vanstom, innovative methods and means are used to diagnose and treat periodontitis. Come to us for your dental health! Address of our clinic: Moscow, Baumanskaya metro station, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28.
Drug treatment of periodontitis
The next stage of treatment is to relieve inflammation and eliminate bleeding gums to prevent further development of the disease. This goal is achieved through drug therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of periodontitis are divided into local and general:
- local remedies are used to treat the affected areas. This includes rinses, antiseptic solutions, anti-inflammatory gels and balms. Local treatments also include therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, which can be used as an addition to the main therapy;
- general drugs, which are combinations of antibiotics in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections.
Non-invasive treatment for periodontitis may also include physical therapy. Auxiliary procedures using laser or electrophoresis will help eliminate inflammation faster.
Treatment methods
Treatment includes a complex of local and general measures, prescribed individually, based on the results of the examination, according to the severity of the disease, the characteristics of its course, and general health. Effective comprehensive treatment of periodontitis is aimed at eliminating periodontal pockets, strengthening teeth and gums, and preventing the destruction of soft and hard tissues.
Hygienic cleaning
Regardless of the stage of the disease, the first stage of treatment is the removal of all dental plaque. For this purpose, special ultrasonic equipment is used, which allows you to carefully remove plaque and stone even in the most inaccessible places. After curettage (scraping) or ultrasonic cleaning performed using manual instruments, the gums are treated with an antiseptic, and medicinal dressings with an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent are applied.
Drug therapy
For mild cases of the disease, local medications for periodontitis are prescribed (gels, ointments, rinses) that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and healing effects. In difficult cases, systemic antibiotic therapy, hormonal and antihistamine medications, and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed. Conservative treatment is effective at an early stage of the disease.
Preparations for the treatment of gum periodontitis have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiseptic effects. The therapeutic effect is provided by using the drug as rinsing solutions, applications to the gums, tablets for oral administration, injections into the gums (vitamins, FiBS, aloe preparations, etc.). Course of treatment – from 2 to 4 weeks
at intervals of several days.
Physiotherapy
For the speedy elimination of the infectious focus and active tissue regeneration, additional physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - ultraphonophoresis, darsonvalization, ozone therapy, electrophoresis, gum massage, laser therapy. Localized periodontitis can be completely cured at an early stage without resorting to drastic measures. That’s why it’s so important to see a dentist at the first warning signs of illness.
Orthopedic treatment
During the treatment, orthopedic structures are corrected, parts of the fillings are removed from the interdental spaces, and crowns that have sunk deeply under the gum or are installed incorrectly are replaced. Splinting for periodontitis is indicated for degree II tooth mobility. Temporary splinting is carried out before curettage or immediately after it, permanent splinting is carried out a month after treatment.
Surgical methods
In severe cases of periodontitis, with deep periodontal pockets and defects of the gingival margin, in addition to conservative treatment, surgical treatment is required. Radical intervention involves cleaning the periodontal pockets with and without dissection of the gums, gingivectomy is an operation to remove inflamed, overgrown areas of the gums. The intervention involves reducing the volume of gum pockets and forming an aesthetic gingival margin. After the procedure, the natural process of tissue regeneration begins. When the alveolar septa are completely reabsorbed, excessively mobile, non-viable teeth are removed.
In case of significant destruction of the jawbone, when it cannot firmly hold the tooth in place, osteoplastic surgery is performed - directed bone regeneration. To do this, the area between the tooth and the bone is filled with a biocompatible osteoplastic material, which serves as a platform for the formation of new osteoblasts and restoration of bone volume.
Modern methods of treating periodontitis, such as laser and vector therapy, show impressive results. In just one procedure, gum pockets are reduced, swelling, pain, and bleeding disappear. Non-contact methods have a biostimulating effect and significantly accelerate tissue healing. Regardless of the severity of periodontitis, the correct occlusion is determined for all patients, and selective grinding of the teeth is carried out according to indications.
Surgical methods
Treating periodontitis surgically is the most radical method. But in the later stages of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate periodontal pockets and remove non-viable teeth. This can only be done surgically.
The degree of intervention depends on the severity of the pathology. In some cases, a positive result can be achieved by simply depulping the tooth to remove pathogenic bacteria. The procedure for splinting teeth (connecting mobile teeth with adjacent teeth to ensure immobility) and other methods is also used.
A separate stage of surgical treatment is prosthetics. This is done to restore the functionality of the dentition, distribute the chewing load evenly, and prevent displacement and further loss of teeth. In some cases, a temporary prosthesis can be used to quickly unload the chewing surfaces and eliminate mobility during the recovery phase.
How to restore teeth with severe periodontitis
In severe cases of the disease, the risk of losing a tooth or an entire row of teeth is very high. Tooth extraction for periodontitis is indicated in cases of excessive mobility, when the unit is barely held in the bone and moves in all directions around its axis. If it is impossible to save the tooth, orthopedic treatment is carried out - prosthetics supported by natural teeth or implants.
For single defects or restoration of a tooth segment, two-stage implantation with delayed loading is used. Implants are implanted after a course of gum treatment and restoration of bone volume. Bone parameters are restored through osteoplastic surgery. After new bone tissue is formed (after 6 months), implants are implanted, the prosthetic system is fixed after they have fused with the jaw bone ( after 3-6 months
). Treatment may take about a year.
In case of complete edentia, one-stage implantation methods with immediate loading demonstrate high efficiency. The ability to install implants in deep bone layers that are not subject to inflammation allows you to avoid osteoplasty and sinus lifting. Treatment will take no more than a week.
Treatment and prevention of periodontitis at home
After successful treatment of periodontitis, it is necessary to pay increased attention to oral hygiene. To do this you should:
- Visit your dentist regularly to remove plaque and tartar;
- eliminate caries and fill dental canals at the slightest manifestation of pathological processes;
- use hygiene products designed to prevent gum disease;
- After each meal, use dental floss and mouthwash with an antiseptic;
- follow other rules for the prevention of periodontitis.
A few words about the importance of periodontitis prevention
Treatment of periodontitis is a complex and lengthy process, sometimes it can last for several years. And naturally, carrying out the necessary procedures will require you not only time, but also significant financial expenses. Both time and money costs can be avoided if you prevent the development of periodontitis.
To effectively prevent the development of periodontitis, dentists advise following the following simple recommendations:
1. Regularly carry out high-quality dental and oral hygiene at home and from time to time - professional teeth cleaning in dentistry.
2. Contact the dental clinic at the first signs of not only periodontitis, but also caries, and undergo treatment on time.
3. Monitor your diet: it must be balanced and your menu must contain foods containing vitamins and minerals.
4. If you lose even one tooth, do not postpone the prosthetic procedure.
5. Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist.
Also, for effective prevention of periodontitis, you should avoid stressful conditions, strengthen the body’s immune system, and protect your gums from injury. Follow these simple rules, and then you won’t have to waste time and money on periodontitis treatment.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Asepta Parodontal - specialized products for the treatment of periodontitis
has developed a whole range of drugs for the treatment and prevention of gum disease. It includes:
- Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, which helps eliminate inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Contains a unique complex of medicinal extracts and active ingredients;
- Asepta Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth. Provides gentle care for sensitive enamel and gums prone to inflammatory processes. Thermal mud in the paste helps heal damaged tissue and relieve irritation;
- Asepta mouthwash is intended to relieve symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and toothache caused by infection. The antimicrobial components of the drug help relieve inflammation and pain, and also have an antiseptic effect;
- Asepta Fresh mouthwash eliminates inflammation and bleeding of gums, prevents the formation of dental plaque, and also gets rid of pathogenic bacteria that cause bad breath;
- Asepta gel with propolis has an intense anti-inflammatory effect, reducing the sensitivity of enamel and promoting the healing of trophic ulcers. Effectively strengthens periodontal tissues and is suitable for patients of all ages.
- The adhesive balm in this series eliminates the causes and symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the mouth. The sticky base ensures a longer and more effective effect of the drug, allowing it to remain on the gums for a long time;
- Asepta vitamin and mineral complex contains all the necessary substances and active components for healthy teeth and gums.
Take care of your health with professional hygiene products!
Treatment with antibiotics, dental ointments and gels
Drug therapy is possible after professional teeth cleaning as prescribed by a doctor. Antibiotics should be taken in recommended doses in the absence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
In some cases, during treatment, injections are prescribed simultaneously with the drugs Traumeel and Lincomycin.
To relieve symptoms, the dentist prescribes gels and ointments:
- "Metrogil Denta" is an anti-inflammatory, analgesic agent;
- "Cholisal" - a gel to combat gum inflammation;
- "Kamistad" - for the prevention of gingivitis, relieving swelling, eliminating pain;
- “Gengigel” is a gel that increases blood circulation and promotes the regeneration of soft tissues;
- "Stomatofit" - to relieve severe pain;
- "Asepta" - to stimulate tissue regeneration processes;
- "Solcoseryl" is an antiseptic with a healing effect.
Clinical researches
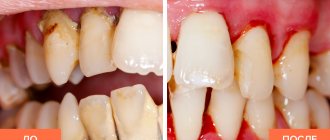
According to the results of the clinical use of the Asepta line of products: the examined patients, already at the first follow-up examination (after 1-2 days) of using the Asepta line of products, showed a decrease in complaints of discomfort in the gums. On examination, hyperemia and bleeding of the gingival papillae are noted. On the 7th day, complaints of gum bleeding persisted in a minority of patients.
Upon examination, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted, but bleeding persisted upon probing. On day 14, 2 patients continued to complain of bleeding gums when brushing their teeth; upon examination, a significant decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted. After the final application of the gel with propolis, normalization of clinical manifestations was revealed, which is manifested by the absence of bleeding during brushing and probing.
Improved dynamics of indicators allows us to recommend the Asepta line of products for the local treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Article “Treatment and hygiene features for mild and moderate periodontitis” by S.B. Ulitovsky head Department of PFS, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, A.A. Leontyev Associate Professor of the Department of PFS, Ph.D. PSPbSMU named after. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, aspirant, dentist, Department of Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
Symptoms of periodontitis
Symptoms of periodontitis can vary depending on the extent and severity of inflammation of the gums and tissues surrounding the teeth. The more severe the stage of the disease, the more the patient is concerned about the unpleasant manifestations of the pathology. At the initial stage, periodontitis causes virtually no discomfort. However, as symptoms progress, they become more severe. Typically, with periodontitis, the patient is concerned about:
- pain when food gets between the teeth;
- discomfort when chewing;
- feeling of itching in the gums;
- feeling of loose teeth;
- bleeding gums;
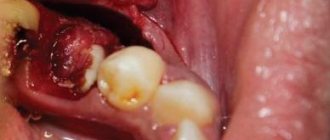
- discharge of pus from under them (in severe cases).
Up to contents
Types of periodontitis
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth; often results from mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - damage to several teeth also affecting the gingival and bone tissue.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - characterized by sudden pain attacks and rapid development of symptoms;
- chronic periodontitis is the transition of untreated acute periodontitis to a chronic form, in which pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease progresses and deforms the tissue.
Stages of the disease
There are 3 stages of periodontitis in adults:
- Initial
. The gums become inflamed, as evidenced by redness and bleeding. - Average
. The gums swell greatly, the neck of the tooth is exposed, a periodontal pocket is formed, the degree of bleeding of the gums increases and the first pain sensations appear in response to irritants. - Heavy
. The depth of the pocket reaches large sizes (up to 7 cm) and the tooth begins to become very loose.
Main signs of periodontitis
The presence of periodontal inflammation may be indicated by such obvious symptoms as:
- bleeding gums when brushing teeth or chewing food;
- feeling of itching of the gums;
- saliva viscosity;
- change in gum color to a redder, scarlet color (normally light pink);
- formation of a periodontal pocket (exposure of the neck of the tooth);
- the presence of purulent discharge;
- constant bad breath.
What contributes to the occurrence of the disease?
The reasons for the initiation of the inflammatory process of periodontal tissues may be:
- poor oral hygiene;
- untreated caries and gingivitis;
- proliferation of pathogenic bacteria due to large deposits of tartar;
- stomach diseases that change acidity;
- weakened immune system;
- hormonal disorders;
- diabetes;
- smoking.
Diagnostics
At the NovaDent clinic, a thorough diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out according to the following scheme:
Visual inspection
When examining a patient's oral cavity, the dentist pays attention to the quality of oral hygiene, the presence of bacterial plaques and their prevalence, the depth of periodontal pockets, the degree of resorption of supporting tissues and tooth mobility.
X-ray image
Provides the doctor with additional information about the extent of bone damage around the teeth, the presence of protruding crown edges and dangerous zones on the oral mucosa.
Blood analysis
Allows you to identify systemic diseases of the body that contribute to the development of periodontitis.
Smear of mucus from gums
Necessary for determining the presence of pathogenic microflora, its identification and volume.