Content:
- Causes
- How does pathology manifest itself?
- How is the treatment carried out?
- Surgical techniques
- Additional treatments
- Preventive measures
If the gums have become detached from a wisdom tooth or any other unit, you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
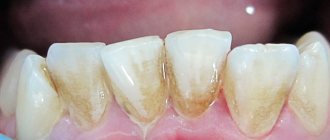
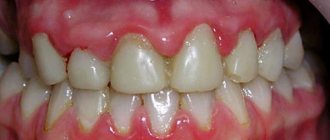
When the soft tissues subside, the neck remains unprotected and exposed. It is not covered with a thick layer of enamel, so it immediately begins to react sharply to temperature changes. The situation is aggravated by the fact that food debris gets into the formed periodontal pocket. They accumulate there and serve as an ideal breeding ground for pathogens. If such a pocket is not cleaned in a timely manner, it will increase in size. Then it will come to edentia.
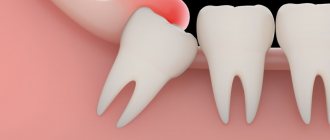
Eruption of wisdom teeth: inflammation and consequences
The figure eight on the lower jaw begins to create problems from the moment of eruption, when the crown rests closely on the adjacent tooth or is tightly covered with a hood. When the hood becomes inflamed, favorable conditions are created under it for the proliferation of pathological microorganisms, and the gums are involved in the process. This manifests itself as pain during chewing or when accidentally biting the mucous membrane. It happens that a wisdom tooth partially erupts, and one or more tubercles rest against the hood, injuring it. In this case, the inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth will have to be treated by removing the hood or the tooth itself. If the figure eight is healthy and does not interfere with the adjacent tooth during eruption, then the dentist makes an incision in the hood so that the tooth can erupt calmly.
How to treat inflammation of the hood and gums near the wisdom tooth at home? To do this, you will need to regularly rinse, rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions and take analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief: Nimesil, Ketanov, Ibuprofen. If the hood is inflamed, you can rinse your mouth with weak solutions of the antiseptic Chlorhexidine, soda and saline solutions.
Causes
Exposed necks indicate periodontal damage. Most often the problem occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. When exposed to this factor, a person can very diligently monitor the health of his smile, but will still periodically encounter unpleasant dental symptoms.
- Mechanical and thermal damage. The habit of gnawing on foreign objects, eating too hot food, using a hard brush are all provocateurs that contribute to irritation.
- Poor oral hygiene. If the patient neglects basic hygiene rules, a lot of plaque is deposited on the crowns. Pathogenic microorganisms spread in it. The gums become irritated, turn red, and bleed. Gradually they begin to move away from the teeth. It is important to use a brush and paste twice a day, and undergo professional hygiene at the dentist’s office annually.
- Poorly performed prosthetics or mistakes made during filling. It is necessary that the dentures fit as tightly as possible to the bases and do not fall under pressure, otherwise the gums will be constantly injured and inflamed.
- Curvature of the bite, problems with teething “eights”, uneven edges of the crowns. All this causes the gums to move away from the tooth.
- Unbalanced diet. If a person eats only soft foods and sweets, he does not actively chew food. As a result, blood circulation in the oral tissues slows down, less saliva is released, and periodontal deposits are actively formed. These are the prerequisites for a recession.
- A large amount of tartar. Despite the fact that dentists recommend removing stones annually or even more often, many patients do this very rarely. You shouldn't wait until a serious problem arises. It is easier and cheaper to prevent it than to treat it later.
- Hormonal imbalance. Most often, this reason concerns women, for example, during pregnancy, menopause, and breastfeeding. With hormonal fluctuations, the mucous membranes become especially vulnerable. Even minor mechanical impacts cause recession.
Don't forget about the negative effects of tobacco smoke. According to statistics, smokers are much more likely to suffer from gum disease and exposed necks. They accumulate plaque faster. Therefore, if you want to have a healthy smile and visit the dentist less often, stop smoking.
Recession classification
Receding gums are classified according to their causes into the following types:
- Traumatic - appears as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membranes. As a rule, the injury is associated with a hard toothbrush and improper brushing technique, which leads to systematic damage. Other common causes of injury include incorrectly installed orthopedic structures - veneers, crowns, etc. Sometimes injury is associated with protruding edges of fillings and elements of braces. It is important to understand that bite defects are also a common cause of recessions: improper distribution of chewing load leads to changes in tissues. Injuries can also be associated with direct pressure on the gums of the teeth. And finally, another group of injuries includes burns, for example, those associated with unsuccessful home bleaching.
- Symptomatic - in this case, the prolapse is associated with some pathological process and serves as its symptom. Usually we are talking about diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease. They affect mucous membranes and soft tissues, disrupting their trophism. The situation is aggravated by dental deposits in the places where the gums adhere to the tooth; as a result, the tissue simply peels off from the surface of the tooth and the tissue level drops. More rare pathologies manifested by gum recession include other diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, leukemia.
- Physiological - it develops as a result of a general metabolic disorder, including metabolic disorders in periodontal tissues. In this case, we are talking about the natural processes of aging. However, sometimes receding gums develop at a young age due to the individual structural characteristics of the dental system. The most striking example is a shortened labial frenulum, which leads to tissue tension.
Based on the severity of a recession, it is also classified into three categories:
- light: tissue loss up to 3 mm;
- average: 3−5 mm;
- heavy: more than 6 mm.
Based on the localization of the pathological process, recessions are divided into localized and generalized. In the first case, receding gums are associated with trauma and spread to one or more closely spaced teeth. As a rule, the outer side of the teeth is affected, and the defect is noticeable when smiling.
In the generalized form, the pathology covers the entire dentition on one or both sides. It is more often observed in elderly patients, as well as in people with periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Ask a Question
How does pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms depend on how far the gum has receded from the tooth. Most often patients complain of:
- increased bleeding and soreness of the gums;
- bad breath that cannot be eliminated with standard hygiene products;
- taste of pus;
- separation of purulent masses from the inflammatory focus;
- the appearance of deep periodontal pockets;
- loosening of individual units.
In the first days of the disease, patients may not experience any significant discomfort. They are just beginning to notice that in certain areas of the jaw the tissue seems to have sagged and become less voluminous. Because of this, the crown part of the tooth, on the contrary, looks elongated.
If the gums have peeled off, there is no need to try to do anything on your own. Without qualified help, it will still not be possible to cope with the recession. Postponing competent therapy until later is fraught with even more serious violations.
How is the treatment carried out?
Some people think that they can be cured with regular rinses. Unfortunately, it is not. The first step is to make an appointment with a dental hygienist. The doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the surface of the crowns and subgingival area in one session.
The following methods are used to remove stone:
- Instrumental. Involves the use of special scrapers that remove deposits. It is considered outdated and is extremely rarely used by doctors, as it is traumatic.
- Ultrasonic. Using an ultrasonic scaler, the doctor crushes the stones into tiny particles. This equipment produces waves of the required frequency, which easily destroy dental plaque.
- Sandblasting. It is the most modern and safe. The doctor delivers the cleaning solution under high pressure. Abrasive particles wash away deposits from crowns and effectively flush out existing pockets. The advantage of the technique is to achieve the effect of teeth whitening by one or two shades.
If the hygiene procedure does not help and the problem is serious, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Surgical techniques
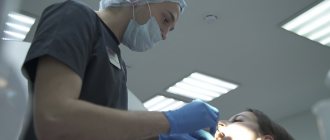
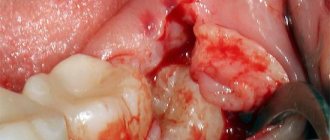
In advanced situations, plaque removal alone is not enough. Then there may be a need for open or closed curettage. It is indicated if the gums are very severely detached from the dental neck and the bone structure is changed.
The dentist-surgeon treats the lesion with an antiseptic, makes a small incision and removes purulent deposits and affected tissue . Then the gum is sutured. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious and can communicate with the doctor, but does not feel pain.
For a speedy recovery after curettage, antibiotics and mouth rinsing with an anti-inflammatory solution are prescribed. If the pain after surgery is very severe, the patient can use painkillers.
Additional treatments
Considering that gums become inflamed for various reasons, it is important to try to find out the provoking factor. Then the risk of relapse of dental pathology can be reduced to a minimum.
If the doctor determines that the disorder is related to hormonal levels, it is necessary to select hormonal therapy . In case of malocclusion, consultation with an orthodontist is indicated. If the diet is unbalanced, the patient is told what the diet should be like after recovery.
Often, when fighting gum that has receded from a tooth, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, glucocorticosteroids, and antiseptics are used. It is very important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions and does not engage in amateur activities. An integrated and responsible approach to treating recession is a guarantee of a speedy recovery.
If the tissues become so inflamed that the teeth begin to loosen, splinting may be required. If there is a deficiency of bone tissue, their deficiency is compensated with special compounds.
Forecast
Proper and timely medical care will help restore the integrity of periodontal tissues, prevent gum destruction and tooth decay.
Recession requires mandatory treatment. Ignoring pathology can lead to tooth loss. In addition, possible complications may include:
- lymphadenitis;
- damage to the bone tissue of the jaw;
- periostitis;
- heart diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- respiratory diseases of infectious etiology.
Prevention of the development of the disease is as follows:
- quality oral care;
- balanced diet;
- strengthening the immune system;
- systematically undergoing preventive examinations;
- professional oral hygiene every six months.
Preventive measures
To prevent gums from moving away from the tooth, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- use a properly selected brush and paste;
- visit the dentist in a timely manner;
- prevent tartar from forming;
- no smoking;
- eat more solid foods;
- Healthy food.
At the first sign of a recession, you should see a doctor. Then the disease can be stopped very quickly.
Home care and postoperative period
After treating gum recession, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, rinses, topical gels, and other topical treatments to prevent complications and speed up the healing process. It is also important to prefer gentle, soft food at a comfortable temperature, and perform regular hygiene according to the recommendations of a specialist.
The dentist will recommend replacing your hard toothbrush with a soft one, and as healing progresses, you will likely need a toothbrush with medium-hard bristles. In addition, the doctor will definitely show the correct cleaning movements and tell you what pressure will be optimal. In many cases, such measures are sufficient to eliminate the causes of exposed tooth necks, as well as maintain treatment results.