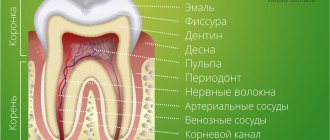
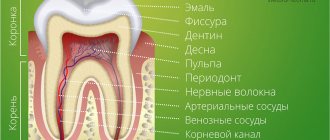
The dentofacial system is an important component of the human masticatory apparatus. It meets morphological and functional characteristics, such as number, size, shape, color, structure of dental units. There are a number of genetically determined or external factors that lead to disruption of these characteristics. Dental anomalies can have various consequences: some lead to periodontal pathologies, various forms of caries, others seriously limit chewing function, cause injury to the mucous membrane, and others cause aesthetic problems.
Improper growth of teeth results in speech and bite defects and breathing problems. As a result, the patient’s general health seriously suffers, and psychological problems arise.
Reasons causing anomalies
Anomalies of the dental system are very diverse and include both anomalies of dental units and incorrect formation of the dentition, as well as abnormalities in the development of the jaws. The most frequently diagnosed abnormalities of dental units. They can be caused by a wide variety of reasons, including both exogenous (caused by external factors) and endogenous (formed as a result of the physiological state of the patient).
Endogenous causes
Endogenous anomalies are formed as a result of genetic and endocrine disorders.
- Many structural features of the dental system, leading to improper development of teeth, are genetically determined. This can occur through direct inheritance (abnormal number and shape of teeth, edentia, diastema), through inheritance of a mismatch in the size of the jaw bones, through inheritance of a mismatch in the size of the jaw and teeth (crowding of teeth or sparse arrangement of teeth). Dental anomalies of this type include disorders associated with hereditary and congenital pathologies (clefts of the soft and hard palate, cleft lip, Down syndrome, Vaanderburg syndrome, Seckel syndrome, Shershevsky-Turner syndrome).
- Another part of the endogenous causes of dental anomalies are problems of the endocrine system, such as hypothyroidism (in later stages), hyperparathyroidism, hypocortisolism. Their frequent symptoms may be delays in the eruption and replacement of teeth, and disturbances in the formation of the enamel layer.
Exogenous causes
Exogenous (external) causes of dental anomalies are, for the most part, external unfavorable factors that affect the baby’s body during the formation of tooth germs. There are prenatal (prenatal), postnatal (postpartum) and intranatal (associated with childbirth) periods.
- An example of a prenatal factor is a pregnant woman living in poor environmental conditions. Various developmental disorders of the fetus can also occur as a result of the mother’s poor lifestyle.
- Factors in the intranatal period may include complicated labor, birth injuries, consequences of asphyxia and oligohydramnios.
- In the postnatal period, dental anomalies develop as a complication of pathologies in early childhood. These include childhood infections, rickets, hypovitaminosis, and micronutrient deficiency.
All these reasons are of a common nature. Local factors that affect dental development include everything related to improper oral care, feeding errors or bad habits. Among them are feeding too soft food, prolonged sucking of a pacifier or finger in early childhood.
Childhood injuries and caries with complications lead to dental anomalies.
The death of tooth germs or the development of supernumerary teeth can occur due to osteomyelitis.
Anomalies in the number of teeth
All anomalies in the number of teeth are divided into three types:
- hyperodontia (excess of dental units above normal);
- edentia (complete absence of teeth);
- hypodontia (insufficient number of teeth).
Hyperodontia
Hyperodontia is a disorder of the formation of the dentition, which is expressed in the presence of supernumerary teeth (over 32 dental units in an adult). The cause of the disease may be a violation of the mechanism of formation of tooth germs in childhood or infancy. Hyperodontia mainly affects the incisors of the upper jaw. Other teeth are involved in the pathological process less frequently. Extra dental units grow small and have a cone shape.
The disease can be true or false.
- With true hyperodontia, the formation of extra dental units occurs in the human jaw.
- False hyperodontia occurs when the loss of primary teeth is delayed, which interferes with the normal growth of permanent teeth.
With polyodontia, teeth may erupt away from the dentition or next to a correctly positioned dental unit, which leads to its gradual displacement. The dentition can be seriously deformed, which leads to serious diction problems.
If supernumerary teeth interfere with the development of normal teeth, they must be removed. Broken teeth are corrected by installing braces.
In those rare cases when a row violation does not occur, the supernumerary tooth is preserved. Prosthetics are used to correct the shape.
Hypodentia
Hypodentia is a deficiency of dental units. This disorder occurs most often due to the death of tooth germs in the fetus. A small number of teeth causes a shift in the midline, the formation of wide gaps between teeth (diastema and three), and shortening of the dentition. All this adversely affects the bite. Possible ways of correction are prosthetics.
Edentia
Adentia is a complete or partial absence of teeth. With edentia, the continuity of the dentition is disrupted, which leads to difficulties in chewing and speaking. The reason is a violation of the development or death of tooth germs under the influence of genetic factors or under the influence of unfavorable external factors during the formation of the dental plate in the fetus (the formation of the germs of permanent teeth in the fetus occurs after the 17th week of intrauterine development). The disorder is corrected using prosthetics or dental implantation.
Why does bone tissue decrease when teeth are missing?
So, let's talk a little about the causes of bone loss.
One of the problems is the so-called bone deficiency. It is very important to understand that bone is the same living tissue of the body as all other organs, although it is very hard and has its own laws of life, growth time, etc.
The roots of the teeth are located in the bone of the alveolar process on the upper jaw and in the alveolar part on the lower jaw, they provide the retention and stability of the teeth. When we talk about bone deficiency, we mean the partial or complete absence of that bone tissue.
The alveolar bone has such a structure and structure that in the absence of teeth it simply dissolves or resorption occurs. Also, bone loss can occur with periodontal disease, even in the presence of teeth.
Removable dentures greatly increase the rate of alveolar bone resorption due to large or improper pressure on the gum and bone, pressure for which they were not designed.
All this can lead to the fact that there will be nowhere to place dental implants.
Anomalies of magnitude
There are two forms of this type of deviation, including macrodentia (increase in the size of dental units) and microdentia (small teeth).
Macrodentia
With macrodentia, the size of dental crowns is significantly increased. The cause of the disorder is, in most cases, dysfunction of the endocrine system, which is characterized by the fusion of several rudiments together. The disease is localized mainly in the area of the upper incisors. Large teeth interfere with the process of eruption and growth of neighboring dental units, which leads to their abnormal arrangement and crowding. Giant teeth are found on or outside the dentition line. This is a serious cosmetic defect that causes serious functional impairment and psychological disorders. Pathologically enlarged teeth are removed, and the growth of adjacent teeth is corrected using prosthetics or braces.
Microdentia
Microdentia – teeth that are too small. The disorder mainly affects the upper lateral incisors, but may affect the incisors of the lower or both jaws. The cause of the anomaly has not been studied, but it is reliably known that it develops in genetically predisposed patients. With the problem of small teeth, patients develop too large interdental spaces, which significantly disrupts the aesthetics of the dentition. To correct the pathology, incorrectly growing teeth are removed or covered with crowns.
Overview of correction methods
Each method of correcting crooked teeth has its own characteristics. To figure out how to correct very crooked teeth, consider all the means that are used for this:
- Braces. These are small plates made of ceramic or metal that are attached to each individual tooth and connected to each other with a special arch. The plates apply uniform pressure on the teeth, gradually leveling their position. Most models of braces are installed on the front part of the teeth, so the plates are visible when speaking. But there are also special, lingual braces. They are placed on the inside of the teeth. This design is more expensive, but it does not spoil the smile at all.
- Mouthguards. These are removable plastic structures that the patient can remove and install himself. It is important that the more often the trays are used, the faster a positive result will be achieved. Typically, mouthguards are used to correct crooked front teeth. The mouth guards themselves are used to correct the bite in children, and they are often placed on adults only to consolidate the achieved result.
- Trainers. Removable devices that are worn at night. They are used only to correct minor malocclusions and crooked teeth.
- Plates. Made from plastic or metal. They are attached to teeth or crowns with special hooks. Most often used to correct bite in children with small defects.
Veneers. In fact, these are onlays that do not eliminate a tooth defect, but only hide it. Therefore, the question of whether veneers will correct crooked teeth can have only one answer: it is physically impossible if the entire dentition is deformed. But in fact, installing veneers on crooked teeth will help if their surface is uneven. In this case, veneers will simply hide the desired areas- Lumineers. Their installation also allows you to correct minor defects. In fact, lumineers are similar to veneers: they are also glued to the surface of the tooth to level it. But lumineers are thinner than veneers, although this does not affect their strength.
- Restoration and prosthetics of crooked teeth. This is a special type of treatment in which each tooth is straightened individually with crowns or composite material. Under the light of a special lamp, it quickly hardens and is completely indistinguishable from an ordinary tooth. The only disadvantage of composite restorations for crooked teeth is that the material can be stained with food coloring.
Sometimes even braces or veneers are not enough to straighten crooked teeth. A crooked tooth can be corrected with a crown, but if the dentition is deformed due to the eruption of a wisdom tooth or anatomical abnormalities of the jaw, surgical intervention may be required. For example, straightening the dentition in some patients can only be done by removing a wisdom tooth, which puts pressure on neighboring teeth and moves them.
Shape anomalies
There are pathologies in the development of dental units, due to which they acquire an unnatural shape. These disorders are named after the scientists who first described them. The following types of dental shape anomalies are found: spiny teeth, Pflueger teeth, Fournier teeth, Hutchinson teeth.
- Spiked or awl-shaped teeth. With this pathology, the teeth acquire a cone-shaped shape. Wide at the base, they gradually narrow and, towards the cutting edge, become sharpened into a spike shape. This problem is combined with microdentia. There are irregularities and stains on the surface of the teeth. The disease affects the front and lateral incisors. The disease occurs in childhood and is caused by genetic factors in combination with external factors. Among them are vitamin D deficiency and endocrine system problems.
- Hutchinson's teeth are characterized by a modified crown shape of the incisors. Externally, they have the shape of a barrel, since the neck is significantly thickened. The cutting edge of the teeth acquires an arched notch. The enamel layer also suffers, which is present only on the sides and absent in the center.
- Fournier's teeth are a form of systemic hypoplasia of dental units associated with metabolic disorders at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. The barrel-shaped shape of the teeth is preserved, but the notch of the incisal edge is absent. The color of the enamel is not disturbed, but the enamel layer is underdeveloped, which can be seen during microscopic examination.
- Pflueger's teeth are a disorder that affects permanent dental units. Their crowns take on a conical shape. Thickening develops in the cervical region, and the chewing surface is significantly underdeveloped. The chewing function of the teeth is completely preserved.
- Turner anomaly. With this pathology, there is no enamel on the teeth. They have an abnormally lumpy surface, and replacement tissue, dentin, forms in the exposed areas.
Systemic hypoplasia with a violation of the shape of the teeth has three degrees of development. The third degree is the most dangerous, in which the crown is severely deformed and the enamel layer decreases. In this case, the defective teeth are removed and replaced with dentures. It is also possible to restore affected teeth using reflective components.
Several stages of caries development
How does the initial stage of caries manifest?
The first stage is the initial stage of caries - when a chalky stain appears on the tooth, such a concept used to be present. At this point, the tooth enamel loses its transparency and becomes completely white. Hence the name - as if drawn with chalk. This carious spot may become pigmented or darken. In this case, it is believed that caries has stopped in the enamel and the destruction process no longer proceeds. This is a controversial theory, since only a dentist can assess the condition of a tooth.
What are caries spots? According to the modern classification, these are enamel caries and dentin caries.
Previously, there was such a classification: spot stage, superficial, medium and deep caries. But regardless of classification, any caries is worth treating.
The second stage of caries after the stain is enamel caries
When the carious process occurs only in the tooth enamel, this is superficial caries.
The third stage of caries - a dark spot on the tooth
If a patient comes and says that I react to sweets, he will have the most favorable treatment outcome
The third stage or middle caries looks like a dark spot on the tooth. In this place, the enamel has already been destroyed, and the disease goes deep into the tooth. This occurs when dentin caries appears.
Anomalies of hard tissue structure
An altered shape, abnormal size or color of enamel is formed against the background of an abnormality in the structure of the hard tissues of the dental unit. Among such anomalies are:
- Hypoplasia (underdevelopment of tissue). The initial degree of the disorder is manifested by the presence of chalky spots on the enamel and areas where tissue deficiency is observed. Subsequently, all kinds of pits, grooves, and recesses appear on the surface of the enamel. The defect affects all teeth in the dentition.
- Hyperplasia (excessive tissue formation). Pathology also affects all teeth at the same time. It is characterized by areas where tissue growth is observed - tubercles, sagging enamel. The consequence of the pathology is a change in the shape and size of the teeth, a violation of the occlusion (the line of contact of the upper and lower jaws).
- Anomalies of amelogenesis (enamel formation) are expressed in the presence of brown or yellow spots on the surface of the teeth. Areas where the natural composition of the enamel is disrupted become especially sensitive. Microdentia develops against the background of pathology. The cause of the development of pathology is a deficiency of microelements that take part in the formation of dental tissue. Treatment consists of replenishing this deficiency. Additionally, local remineralizing therapy and physiotherapy are performed.
- Disturbance of dentinogenesis consists of dysfunction of the mechanism of dentin formation. The main symptoms of the disease are as follows: teeth become yellow-brown or grayish in color. The fragile dentin in these areas quickly wears off, causing tooth decay and then tooth loss. The disease occurs in genetically predisposed patients. The problem can only be solved by replacing the units destroyed by the disease with prosthetics.
Treatment methods
In cases where “short” teeth do not affect the functionality of the dentofacial apparatus, they are a purely aesthetic problem, and their correction is determined by the patient’s desire.
But if a functional problem is added to a cosmetic problem, the doctor must recommend mandatory treatment to the patient. Its method depends on the diagnostic results.
There are three main methods of treatment. Two of them are surgical – frenulum cutting and gum grafting. 3rd – prosthetic. Sometimes orthodontic correction is performed before microdentia treatment.
Lip frenulum trimming
If the cause of “short” teeth is a long frenulum hanging over the crowns, it is trimmed and sutured. The operation is performed under local anesthesia at any age .
Gum plastic surgery
The technology is used for microdentia of several adjacent teeth. A prerequisite for gum surgery is the healthy condition of the dental and periodontal tissues in the area of the operation.
Gumplasty or gingivectomy involves excision of the edge of the gum to expose part of the clinical crown and increase its height. As a result of the operation, the position of the gum line changes.
As an additional treatment after gum surgery, remineralization of teeth may be necessary, since the less mineralized part of the crown located under the gum may have increased sensitivity to mechanical and chemical influences. That is, the patient will suffer from hyperesthesia.
Veneers and Lumineers
Treatment of “short” teeth with veneers and lumineers is recommended for isolated, single microdentia, trema and diastema.
With the help of thin onlays fixed to the vestibular surface of the enamel, most visual defects can be corrected, and “short” teeth are no exception. Covering them with veneers and lumineers allows you to create the full effect of a normal size.
The advantage of the method is that with the help of veneering you can change the size of the crown in any direction, both in height and width. Its main disadvantage is the relatively high price, which increases when using lumineers or veneers made of high-quality materials, such as zirconium oxide, for example.
If none of the above methods are suitable for a particular case of microdentia, you can use prosthetics - installing artificial crowns or even bridges. The latter case requires the removal of a “short” tooth that cannot be corrected.
Color anomalies
Healthy, young teeth look snow-white due to a thick dentin layer and high-quality enamel, which has sufficient characteristics of whiteness, shine and transparency. Lifestyle, age, genetic factors, and ecology can slightly change the color of teeth from bluish to yellow. Small deviations are not considered pathology, although they indicate a change in the quality of the enamel.
Various pathological processes occurring in the body have a more significant impact on the condition of the enamel. The cause may be carious lesions, the use of medications, or a lack of certain microelements in the body. Teeth can take on a gray, pinkish, brown, purple and even black tint.
When starting to treat a patient, the dentist excludes the development of chronic pathologies. After a course of therapy and stable remission is achieved, other causes of discoloration of the enamel are eliminated. The final stage of treatment is a course of teeth whitening.
Specialists at the Consilium Dent choose the enamel lightening technique together with the patient. The selection criteria are age, condition of the enamel, and the wishes of the patient.
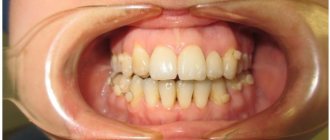
Position anomalies
Incorrect position of teeth always develops as a consequence of another pathology and forms an incorrect bite. May affect one or both jaws. Incorrect position of teeth makes chewing food and oral hygiene difficult. This can lead to digestive problems and the development of cavities. There are several options for the pathological position of teeth within or outside the dentition:
- External or vestibular position means that the tooth is located outside the dentition, closer to the vestibule of the mouth. This position is typical for canines and incisors and develops as a serious cosmetic defect.
- Oral or internal position. The teeth are deviated inward closer to the tongue. The disorder is typical for canines, incisors and premolars. May cause tongue injuries and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
- Mesial and distal position. Dental units are displaced forward or backward along the dentition, which leads to its shortening.
- Supra and infraocclusion are high or low positions of teeth relative to the occlusal curve. The cause of the disorder is underdevelopment of the alveolar process. It appears due to the presence of some obstacle that interferes with the normal formation of the tooth germ. Effective therapy is surgery.
- Tortoanomaly. The tooth is rotated around a vertical axis. The disorder is typical for incisors, canines, and premolars. The anomaly can cause injury to adjacent teeth. Dental units are rotated into the correct position using orthodontic structures.
- Transposition. The teeth change their location with each other. The disease affects canines that exchange places with premolars or lateral incisors. The disorder develops at the stage of tooth germ formation. The therapy is as follows: problematic teeth are removed followed by prosthetics.
- Crowding of teeth occurs due to lack of space when tooth germs are located too closely. Crowded teeth are closely adjacent to each other and rotate around their axis. Occurs in combination with macrodentia or with an undeveloped basal part. To eliminate the violation, some dental units are removed.
- Diastemas and tremas are wide spaces between teeth. The disorder develops as a consequence of an abnormal shape and size. The problem is treated with orthodontic methods or by installing veneers, which helps restore the aesthetics of the smile.
Misaligned teeth cannot always be cured using braces. Severe pathology, which is characterized by a skeletal disorder of the maxillofacial region, is treated with surgical reconstruction. The pathological fragment is transferred to the desired position and then secured. A fragment containing part of the dentition or the entire dentition can be used.
What is the disadvantage of rare teeth?
First of all, it is difficult to call rare teeth beautiful. They don't look aesthetically pleasing. This factor weighs heavily on many people.
In addition, due to rare teeth, the health of the gastrointestinal tract may deteriorate. After all, while eating, it is not possible to chew food thoroughly.
A number of rare teeth are not as strong as healthy ones. They are easy to injure and become infected.
Diagnostics
An experienced dentist diagnoses dental abnormalities after an external examination and questioning of the patient. To clarify the diagnosis and identify the causes of the disease, a more detailed examination of the dental system is carried out:
- The construction of diagnostic plaster models and odontometric measurements make it possible to accurately identify changes in the size of dental units and their characteristics, which indicate the presence of pathologies.
- The color and transparency of the enamel are determined using a photographic method.
- Computed tomography or teleradiography makes it possible to obtain information about the condition of abnormal dental units in order to determine further treatment tactics.
- Panoramic radiography of the jaws is an important diagnostic method
- Electromyography of the jaws helps to assess the functional state of the facial muscular system.
To carry out differential diagnosis, the patient is referred for consultation to specialized specialists: endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, geneticist. Based on the diagnostic results, the attending physician determines treatment tactics. Depending on the type of disorder and the complexity of the disease, the patient may need the help of a dentist, surgeon, orthopedist, or implantologist.
Prognosis and prevention
Consilium Dent clinic uses advanced methods of therapeutic, surgical, and orthopedic treatment of dental anomalies in patients. By skillfully combining them, experienced specialists are able to restore the aesthetics of a smile and ensure the normal functioning of the dental system, even if the degree of deviation is significant.
Prevention of anomalies in the formation and development of dental units begins during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus and is carried out throughout a person’s life. The main stages are as follows: monitoring the successful course of the prenatal period, caring for harmonious postnatal development, organizing a correct lifestyle while the baby is growing up, caring for dental health and general health throughout life. By conducting an annual preventive examination, the dentist identifies dental anomalies at an early stage, when the pathological process is still reversible.
Expert of the article you are reading:
How much does a perfect smile without gaps between teeth cost?
A perfect smile without gaps requires, first of all, a lot of patience and a little trust. Material costs depend on your choice and on the country where you want to be treated. Non-EU countries widely practice dental tourism, offering very competitive prices.
Braces, for example, in our clinic are not at all expensive (from 550 euros to 750 euros), you need to come to Moldova for adjustments. This is why we recommend that you evaluate how rational or economical the entire treatment will be.
Ceramic veneers cost 225 euros per tooth. Their advantage is that the treatment is carried out in one stage, which makes it very attractive to people abroad. To prepare teeth for EMAX ceramic veneers, we use a microscope and other magnifying devices, which makes the preparation (grinding) imperceptible, but the end result will surprise you to tears.