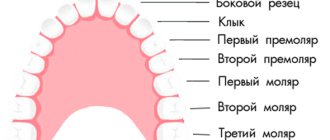
The vast majority of the adult population of the planet is familiar with toothache. It can manifest itself in different ways, including when pressure is applied to a tooth, when a person cannot bite even soft food.
| Causes of pain and accompanying conditions | Methods for eliminating toothache |
| Increased sensitivity of the tooth in the absence of external damage, pain occurs even with slight pressure | At home: rinsing with herbal decoctions, soda solution When visiting a doctor: remineralization (treatment with preparations containing calcium and fluoride), in some cases - building up new enamel |
| Damage to enamel (cracks, chips - including microscopic ones invisible to the eye), the appearance of severe pain when exposed to any factor | It is recommended to consult a doctor |
| Inflammation of the gums: pain occurs when pressing on a healthy tooth precisely because of the condition of the gums | At home: rinse with a water-soda solution, sea buckthorn oil lotions. If there is no effect, you should consult a doctor. |
| Inflammation of the upper part of the tooth (periodontitis), accompanied by independent, precisely localized pain and a general deterioration of the condition | Treatment at home is impossible; you need to see a doctor. During the first week after removal: rinse |
| Removal of the nerve: after depulpation, pain may persist due to injury to the fibers (the reason is unskilled intervention that led to tissue necrosis due to insufficient asepsis of the canals) | The persistence (especially the intensification) of pain requires immediate contact with a doctor in case of a medical error |
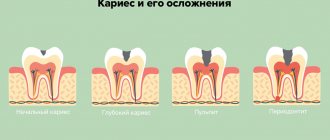
| A complication of caries is pulpitis, intense pain that intensifies when chewing, discoloration of tooth enamel (graying) | requires immediate medical attention; if delayed, tooth loss may occur |
Main reasons
Pain is a kind of “alarm” from the body, drawing attention to malfunctions in its functioning. The oral cavity is no exception: if a seemingly healthy tooth hurts when pressed, this indicates that something has happened to it. As a rule, the reason is damage to the crown, root, gums, or the presence of an inflammatory process. But provoking factors can be very diverse: injuries, infections, insufficient hygiene and even medical errors. Let's look at each case in more detail.
What complications may arise?
Pain in a dead tooth necessarily indicates the presence of some pathology that needs to be eliminated in a timely manner. Infection can lead to serious consequences:
- complete destruction and death of the tooth;
- chronic gum inflammation;
- development of periodontitis, gingivitis;
- the appearance of cysts.
In addition, failure to seek medical help in a timely manner can lead to the development of systemic infections that spread from the periosteum through the bloodstream throughout the body!
The tooth hurts when you press on it: after depulpation (nerve removal)
The pulp is nerve fibers and vessels that provide sensitivity and nutrition to the tooth. After their removal, the tooth is considered dead, and it may seem that this is the solution to any problem, because a dead tooth is unlikely to hurt. This is wrong. A pulpless tooth can be disturbing for several reasons:
- if the dentist, while cleaning the canals, punctured the root;
- when the thin end of the endoscopic instrument breaks off and remains inside the canal;
- in case the dental canals have not been completely cleaned and an infection remains in them.
In the first two cases, the pain is quite sharp: the pulpless tooth hurts not only when pressed, but even when touched lightly. If the dentist cleans the canals poorly, pain appears after some time. In any case, a tooth without a nerve that causes discomfort is a reason for a repeat visit to the dental office.
Periodontitis
Sometimes painful sensations occur in a tooth from which the nerve has already been removed. When pressed, the tooth hurts and aches. Many patients are perplexed as to how a fully treated organ can produce such symptoms. However, treatment is not always of high quality. The following mistakes may be made during canal filling:
- perforation of root canal tissues with an endodontic tip;
- incomplete cleansing of nerve tissue from the canal;
- poor quality disinfection of treated canals;
- insufficient tightness of canal sealing;
- the use of cheap fillings that can dry out over time.
All of the above reasons lead to various complications in the dental cavity. Of course, this does not happen immediately after treatment: it may take a month, and sometimes several years. However, such therapy will sooner or later make itself felt. The causing tooth will begin to ache at night, and then will react with pain to any pressure. The essence of periodontitis is the penetration of infection into the tissues of the dentoligamentous apparatus. Through the tip of the root canal, pathogenic bacteria enter the periodontium. There they slowly spread, forming cysts and granulomas of various types. Treating this type of inflammation is quite difficult and takes a long time, and a large percentage of such diseases require removal of the neglected organ.
When the first symptoms of periodontitis appear, dentists recommend following the following tips:
- If a tooth hurts when biting, it is strictly forbidden to apply heat to the sore spot;
- take one or two tablets of painkillers such as paracetamol, tempalgin, analgin;
- brush your teeth, removing food debris from the carious cavity of the affected tooth;
- rinse your mouth several times a day with a solution of potassium permanganate, soda or furatsilin;
- Do not take anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
In order to prevent unpleasant consequences for the health of the body, treatment of periodontitis should not be postponed and hope that the disease will disappear over time. A timely visit to the dentist will preserve not only the health of the tooth, but also the entire body, since periodontitis contributes to the emergence and spread of harmful substances. Of course, toxins will negatively affect the functioning of internal organs and a person’s well-being.
The LeaderStom network of clinics specializes in dental therapy, orthodontics and prosthetics. Our specialists try to cure even the most advanced cases of chronic pulpitis and periodontitis with maximum preservation of natural dental tissues. Treatment tactics depend on the degree of neglect. In the initial stages, the disease can be eliminated by refilling the canals. By eliminating the source of infection, dentists achieve stable remission of the tooth and restoration of periodontal tissue. If the inflammation process has covered a large area of tissue, and a purulent process has already formed near the apex of the root, then in this case either surgical intervention or removal of the diseased tooth is possible.
Tooth hurts when pressed after filling
Slight pain after the doctor has given a filling to the patient is normal: during the sanitization of cavities affected by caries, the tissues receive microtrauma. The condition is easily treated with analgesics and goes away on its own in 2-3 days. But if a filled tooth hurts when pressed hard enough, then the problem is one of five reasons:
- high filling - the occlusion is disrupted, the tooth experiences excessive pressure and becomes painful;
- the dental pulp was burned when the filling was treated with a photopolymer lamp;
- a gap has appeared between the filling and the enamel, into which bacteria and food particles have entered, causing inflammation;
- the cavities affected by caries were not drilled out thoroughly enough, and it reappeared;
- I developed an allergy to the filling.
If the tooth under the filling hurts when pressed, this means that you need to make an appointment with the doctor again and have it filled again.
The treated tooth hurts when pressed after canal filling
Working with roots requires precision and accuracy from the doctor. If he incorrectly assessed the depth of the canals, then the following complications cannot be excluded:
- a tooth without a nerve hurts when pressed if the filling material extends beyond the apex of the root, gets into the gum and puts pressure on it;
- when the channels, on the contrary, are not completely filled, inflammation may begin in the voids over time. If a lot of time has passed after visiting the doctor, and the tooth aches and hurts, then the problem is the unsatisfactory filling of the canals.
The tooth under the crown hurts when pressed
Crowns and bridges can also cause many unpleasant moments for their owner. Normally, you may feel discomfort under the crown for several days after installation, but as you adapt, the pain gradually goes away. If a month later the tooth still aches a lot and hurts when pressed, and also if the pain under the crown appears suddenly, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
There are four main reasons:
- the crown became loose, food particles and plaque accumulated under it, and inflammation began;
- the crown is cracked or split;
- the tooth is poorly ground under the crown;
- The shape of the crown is chosen incorrectly; it puts pressure on neighboring teeth or gums.
When to see a dentist
If the pain syndrome, which should last no longer than a few days, does not go away within the specified period, you should immediately go to the doctor. Why do you need to consult a doctor: if you do not treat the “damaged” tooth, then not only will the pain intensify, but a lot of other serious complications will also develop. To determine the cause of the discomfort, a specialist will conduct a palpable examination, tap the tooth (so-called percussion), determine how viable the pulp is, and send it for an x-ray.
If the diagnosis reveals medical errors, the tooth will need to be treated again. In emergency situations, if conservative methods are ineffective, the “affected” unit will be removed and a crown, bridge or other suitable prosthesis will be installed in its place.
Important! When, immediately after the filling has been installed, the gums become swollen and the pain rapidly increases, you should immediately contact a dentist.
So, the fact that a tooth hurts after canal filling is a variant of the norm, but it may also indicate the development of a pathological process. It all depends on how long the unpleasant sensations last and what nature they have. If a tooth hurts when pressed immediately after installing a filling, the discomfort persists for longer than three days and the pain increases, this is a reason for an immediate consultation with a dentist.
A healthy tooth hurts when pressed
What should you do if, when pressed, a tooth that has not been sanitized, depulped, drilled or loaded with a crown hurts? Yes, this happens too. Here are a few reasons why a seemingly healthy tooth can be painful.
- Periodontitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the tissues around the teeth. When pressed, both the gums and the tooth hurt at the same time. If no action is taken, progressive periodontitis will lead to a reduction in the volume of the gums and even bone, and then the tooth will become loose and may fall out.
- Excessive enamel sensitivity. It is provoked by chemical teeth whitening, after which even a tooth with a nerve can ache when biting or drinking cold and hot drinks. Teeth with filled canals do not have this problem. You can make your enamel less sensitive at home by using remineralizing gels and toothpastes.
- Removal of a tooth. After surgery, the adjacent healthy tooth may hurt. This is due to damage to soft tissues and does not require any additional therapy other than that prescribed by the doctor.
What should you do if your tooth hurts when you press it?
Pain almost always accompanies the rehabilitation period after dental surgery. If the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the discomfort disappears on its own after 2-4 days, however, in some cases, pain can signal complications. The patient should return for a follow-up appointment if:
- immediately after the anesthesia wears off, severe and sharp pain appears;
- More than a week has passed after treatment, but the toothache does not go away;
- The rehabilitation period went well, but after 1-3 months pain appeared again.
The most important thing is not to endure, but to figure out where the pain comes from.
How to prevent pain after therapy
There are some simple preventive rules that will prevent possible negative consequences of treatment. The first thing is not to violate the doctor’s recommendations. If it is said that you cannot eat for two hours after taking it, then do not violate the instructions for even a minute.
If the doctor told you not to eat for 2 hours, you need to follow the instructions.
If you smoke, then in the next few days after treatment you should reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke as much as possible. It goes without saying that you should give up sweets.
You will also have to give up sweets for a while
Hot or cold foods should also be prohibited; they act as an irritant to the injured nerve endings of the tooth.
It is better to cool drinks and dishes that are too hot
In the first days, it is worth including more liquid and non-solid food in the menu, which is not necessary to bite into. Also, for the first time after treatment, reduce the load on the treated tooth. Chew them intensively; you definitely shouldn’t bite them.
- It hurts to chew on a tooth
Chicken broth is an excellent dietary dish that will not harm your teeth and gums
Of course, it makes no sense to use untested, questionable pain relief recipes. There is no need to run for a painkiller if the pain appears only occasionally, when biting, and immediately disappears. Of course, after treatment, avoid serious physical activity; it will be stressful for the body.