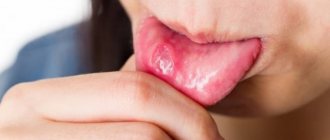
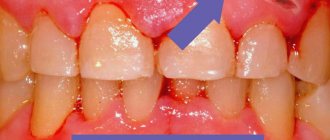
Folded tongue: photos and symptoms
Usually the anomaly is detected in early childhood, but it also occurs in adults, since sometimes this problem does not bother the patient in any way, and the person is not even aware of its presence. The signs of the disease are as follows:
- Macroglossia, or enlargement of the tongue, which can affect a person's speech and chewing function. Usually the patient keeps his teeth in an open position.
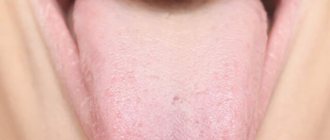
- Folds and grooves appear on the surface, which are covered with papillae.
- The tongue is significantly thickened.
- The back and tip of the tongue are smoothed, the filiform papillae have atrophied.
- Increased sensitivity (especially in people who have undergone infectious diseases and surgical operations).
- Regular tingling and pinching sensation.
- Lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Smell from the mouth.
The folds, in turn, are different: transverse, deep longitudinal (and not very deep), fringed. Usually the main longitudinal fold (it is the largest and deepest) runs from the tip along its midline. The remaining folds lead exactly to it.
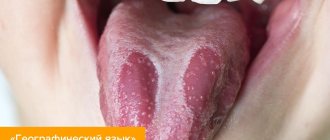
Sometimes this pathology accompanies desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue) - this is inflammation, as a result of which some areas of the organ become several shades lighter or acquire a gray tint. In general, the picture of the organ resembles a map, which is why it got its name.
Therapeutic measures
If scrotal tongue is an independent disease, then no special therapy is required. There is usually no discomfort, no pain occurs, so a person with a mottled tongue does not even notice his problem. In case of concomitant diseases, complex therapy is required, which is selected individually.
When the inflammatory process develops, drug therapy is usually prescribed. The treatment regimen includes:
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics as needed;
- the use of corticosteroids to relieve acute inflammation;
- in case of a fungal infection, antifungal drugs are indicated;
- To intensively cleanse the oral cavity and relieve inflammation, rinses with the use of herbal remedies are prescribed;
- use of cooling gels and analgesics in case of increased pain;
- carrying out immunostimulating therapy.
To eliminate inflammation, applications with chlorhexidine are prescribed. It is also recommended to treat the tongue with drugs with keratoplastic properties. This group of products includes glycerin and retinol solution.
Furrows can be removed mechanically using a laser. The procedure involves smoothing the grooves, as a result of which the tongue acquires an anatomically correct shape and becomes smooth. Surgical intervention is advisable in case of intensive increase in the size of the tongue. The procedure involves suturing the grooves. During the recovery stage, it is necessary to observe “speech rest” and adhere to a gentle diet.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Possible causes of pathology
The exact causes of the anomaly are unknown. But there are a number of factors that can provoke the appearance of pathology:
- chronic diseases of the liver, stomach, duodenum;
- skin diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- bone marrow diseases;
- acute infections;
- violation of the mucous membrane of the tongue and its trophic function;
- lack of vitamins and essential microelements in the body;
- collagenosis;
- human reaction to vaccination;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, lactation).
Localization of cracks in the tongue
Inflammation of the papillae on the tongue, cracks, spots and other unpleasant symptoms can be located in different ways. The location of the lesions makes it possible to determine why they appeared, and sometimes to make a diagnosis based on the tongue. Additional diagnostic measures are not excluded, but are mandatory. Inflammation is a symptom to contact a specialist.
Over the entire surface of the tongue
If there are many cracks in the organ, they are small, arranged in a disorderly manner - this may indicate diseases of the large intestine, and in a chronic form. When damage is accompanied by dry mouth and constant thirst, consultation with an endocrinologist is required.
On the tip
Inflammation on the tongue, localized in the area of its tip, often appears due to mechanical injuries, burns from hot food, and stomatitis. Sometimes the cause is disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. A weakened immune system facilitates the formation of cracks, which are caused by slightly biting the tip of the organ.
In the middle
The cracks in the middle part of the lingual surface are most clearly captured in the photo; they are the deepest. In the center of the organ, folded, diamond-shaped glossitis appears more noticeably. Malfunctions of the immune system lead to dry mouth: the mucous membrane dries out and cracks form.
On the side surfaces
The hidden cause of cracks in the tongue along the edges may be diseases of the liver and gall bladder. Damage on the lateral surface is a common symptom of anemia, thyroid pathologies, and gastrointestinal disorders. There are also tooth marks on the edges; they appear due to the fact that the organ swells and is easily injured.
Treatment of folded (scrotal) tongue
The anomaly usually does not bother its owners, however, sometimes they complain about its appearance: cracks.
A folded (scrotal) tongue requires especially careful care. Because food residues may be trapped in the folds. Because of this, bad breath occurs, as well as accompanying unpleasant symptoms: burning and inflammation.
In addition, the grooves may bother people who have suffered acute infections or surgical interventions. The reasons in this case are also clear: the overall tissue reaction in the body decreases, and the sensitivity of the surface of the folded tongue increases significantly. Therefore, it reacts painfully to chemical irritants and drugs.
If the patient does not properly care for the diseased organ, then the inflammatory processes can drag on, and this is a very favorable place for the development of fungal infections.
The dentist treats this pathology. It is he who will select oral care.
Sometimes a folded tongue requires surgery. This happens in cases where the organ is too enlarged and interferes with the patient. The operation involves excision of part of it.
So, in general, drugs are used to eliminate related problems:
- Fungal and bacterial diseases: anti-inflammatory, antifungal drugs, immunocorrectors, antiseptic treatment.
- Candidiasis: clotrimazole cream, shading with aniline dyes, 10% sodium borate solution in glycerin.
- Painful sensations: antiseptic rinses, mouth baths with citral solution, application of medications with anesthesin.
Complications of the disease
If, according to you, glossitis of this form does not pose a particular danger to humans, then this does not exclude the development of complications. The grooved tongue makes the oral cavity vulnerable to infections. Most often, fungi from the genus Candida settle in folds. In this case, the symptoms expand significantly. Candidiasis leads to the appearance of ulcers that are painful. Erosion of the oral cavity interferes with the normal absorption of food and negatively affects the general well-being of the patient.
Staphylococci and streptococci also thrive in the oral cavity when fimbriated furrows appear. Bacteria actively multiply, causing general intoxication of the body and the formation of abscesses. An intense inflammatory process leads to a deterioration in the patient’s condition: increased body temperature, weakness, loss of appetite.
Any weakening of the immune defense leads to the development of inflammatory reactions. Folded glossitis does not require drug therapy, but its complications force the use of aggressive medications.
A mottled tongue in itself does not cause discomfort. You need to consult a specialist if your tongue has acquired a bright red color, and the process of chewing food is associated with pain. Plaque, unpleasant odor and burning sensation in the mouth indicate the addition of a secondary infection. If the necessary therapy is not carried out at this stage, then the organs of the digestive system may be involved in the pathological process.
There are other complications of the disease that are more of an aesthetic nature. If the organ increases in size, the bite may change. This is especially noticeable in young children. If a folded tongue has recently begun to interfere with conversation, then you need to consult a specialist. Incorrect bite, impaired diction, psychological complexes - this is only part of what progressive pathology can lead to.
The category of aesthetic problems includes excessive salivation, distortion of the oval of the face, cracked lips and dry mucous membranes. An enlarged tongue is more likely to be injured. Regular damage to the mucosa can cause the development of tumor processes.
Features of care
If you have this pathology, you do not need to self-medicate; careful care and supervision by a specialist are required. In general, you should take care of your oral cavity as follows:
- general oral hygiene;
- rinsing;
- if the patient uses removable dentures, they should also be thoroughly cleaned after eating;
- it is necessary to avoid spicy, salty food, it should not be too hot or cold;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- You need to brush your teeth with a special paste;
- the toothbrush should be made of synthetic materials: this will help avoid damage;
- regular visits to the dentist.
Such careful care will help neutralize the oral cavity from bacteria, which will prevent their proliferation and the occurrence of associated infections.
Author:
External manifestations
In normal condition, the human tongue is clean and moist, with symmetrical edges and a uniform surface. As the disease progresses, these parameters change.
Depending on the pathology, the surface may become dry and glossy . The organ takes on an unhealthy pigmented hue . There is an upward change in size.
When the tongue protrudes, its deviation from the midline is noted. In some cases, pain and a pronounced change in surface relief occur. The epithelium may become covered with cracks and ulcers.