Why do ulcers appear on the gums, and is it always dangerous?
There are many possible reasons. To understand how dangerous the appearance of certain lesions on the gums is, you need to look at additional accompanying symptoms:
- in case it is trivial mechanical damage. The gums can be damaged by hard food, a toothbrush, or a foreign object. These lesions may resolve in 3-5 days. If a person does not brush his teeth, then infection is added to these damages, and healing may take several weeks.
- Sometimes ulcers can appear as a result of wearing orthodontic structures, braces or removable dentures.
Causes of scratches on gums
The periodontal tissues and periosteum of the lower and upper jaw are in close contact with the mucous membrane of the gums. Mucosal tissue not only plays a protective function, but also serves as a conductor for metabolic reactions.
The tooth is nourished due to reliable blood supply and innervation in the gums, and any slightest damage will always result in a painful sensation. Thanks to this, the dentist can determine the location of the lesion and its parameters.
A scratch, be it a microcrack that is not visually visible, is a reason to seek specialized medical help. In the oral cavity (on the surface of the tongue, cheeks) there is a large amount of foreign microflora, which, if they get into the scratch itself, cause serious problems for the teeth and the body as a whole.
There are three reasons that cause gum damage:
- Mechanical factor - when the oral mucosa is damaged by hard food during eating (for example, when the gums are crushed with hard food: crackers, sweets, seeds) and during therapeutic measures (the gums are damaged during dental treatment - touching with a needle, drill, etc.). Mechanical damage (scratches) is more often caused by young children who carry unknown things to their mouths, gnaw or chew them.
- Chemical factor - when the mucous membrane is exposed to various chemical compounds (acids, alkalis).
- Thermal factor - ingestion of too hot food or water causes burns, and exposure to cold damages teeth.
One should take into account the fact that the mucous membrane becomes more susceptible when the human body’s immunity is reduced. Typically, this condition is caused by concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, benign and malignant neoplasms, sexually transmitted diseases.
In children
Since gum scratches more often occur in children who want to “taste” everything, their parents should carefully examine the oral cavity every day for the presence of such scratches. In children, the immune system is still weak and the protective mechanism in a small body may not work, and then a small scratch may be complicated by swelling and redness of the soft tissues around the lesion. Externally, the child will be restless due to soreness in the mouth.
The teenage generation has a high risk of bruises (street fights, football, bad falls). Vivid symptoms of damage include severe pain in the mouth, bleeding gums, a knocked out tooth, etc.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
Causes of sores in the mouth
Purulent ulcers in the mouth can appear for various reasons. They are often the result of dental diseases.
The list of reasons may include the following:
- viral infections (herpes simplex or herpes zoster);
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- irritation of the mucous membranes from smoking and certain foods (nuts, cheese, citrus fruits);
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- chemotherapy drugs;
- frequent stress and nervous tension;
- oral injuries;
- hormonal changes.
First aid
If the temperature rises, you can take an antipyretic drug. In the future, before visiting a doctor, nothing should be done. Do not take antibiotics yourself or try to get into the ulcer with any object.
How to relieve symptoms of ulcers
- do not eat sour and salty foods
- food should be warm, no hot dishes or drinks
- Care should be taken to ensure that the child does not put dirty hands in his mouth
- teeth should be brushed, but make sure that the bristles do not touch the gums with ulcers
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal solutions (oak bark, chamomile) 3-4 times a day
You should be careful when using antibacterial solutions. They must be prescribed by a doctor. If such solutions are used incorrectly, they can provoke the development of thrush. The antibacterial agent will “kill” the beneficial microflora, which can result in a fungal infection.
Prevention of ulcers
- professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year
- Regularly replacing your toothbrush
- Proper brushing of teeth at least 2 times a day
- using additional hygiene techniques such as irrigators, dental floss, and tongue scrapers
- Children should be monitored for bad habits such as putting dirty fingers and other objects into their mouths
- It is important to treat your teeth in a timely manner. Microbes that are found in carious teeth and rotten roots can serve as a source of infection for ulcers
If you have problems in the oral cavity, contact the specialists of the Center for Family Dentistry!
How can you get rid of sores in your mouth?
How to treat wounds in the mouth if they appear and cause discomfort. Initially, you need to determine the true causes of their occurrence. This will help not only choose the right treatment, but also reduce the risk of relapse. If simply stomatitis has formed, it is not difficult to recognize it, but a purulent wound in the mouth of unknown pathogenesis is a reason to consult a doctor. Particular attention should be paid to lesions that do not heal for more than 10 days.
For a quick recovery, use:
- medicinal ointments with anti-inflammatory effect;
- antibiotics if the cause is a bacterial infection;
- complex of vitamins;
- rinsing with oral antiseptics;
- protective applications;
- painkiller injections;
- laser cauterization.
What happens in the mouth after tooth extraction?
A wound formed in the mouth creates problems:
- it can bleed for quite a long time;
- food can get into it and cause repeated injury;
- it can fester, infecting surrounding tissues.
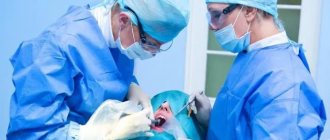
How long does it take for gums to heal after tooth extraction under normal conditions? After the surgeon removes the tooth, the healing process begins, and the ligament surrounding the removed tooth begins to contract. A blood clot forms in the wound itself, which will protect it from infection. After a couple of days, granulation tissue begins to form, which over time is replaced by osteoid tissue. As a result, after 2–2.5 weeks the edges of the wound come closer together, and then young bone is formed, over which the gums take shape.
Why do gums hurt under dentures?
Among the main reasons influencing the development of gum pain after prosthetics are:
- Incorrectly installed prosthesis. Errors in choosing the size and shape of the structure cause discomfort. Crowns press and rub the gums. The situation is aggravated by the fact that with frequent consumption of solid foods, toffees and other foods, the position of the structure changes, which causes chafing and wounds on the mucous membrane.
- Allergic reaction. Intoxication occurs if the patient has a tendency to be allergic to cobalt, copper, chromium, nickel and metal alloys. It is also enhanced when installing metal ceramics.
- The case is dangerous. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, there is a risk of developing Quincke's edema.
- Diseases of the gums, mouth and teeth. If a foreign object is installed during an infection of the oral cavity, the disease can develop into gingivitis, fungal stomatitis, cyst, candidiasis, caries. Symptoms may vary. For example, soft plaque accumulates under the denture; when you press the plate, the pain intensifies, the gums bleed and swell. Periodontal tissues are deeply affected, and ulcers appear on the alveolar processes.
Signs that your gums are inflamed
To decide what to do if the gums under the denture become inflamed, it is necessary to correctly diagnose the pathology.
The main symptoms indicating an inflammatory process are:
- Redness appears in the prosthetic area. It can spread to surrounding tissues.
- Drops of blood are noticeable when brushing your teeth, turning into constant bleeding.
- Feeling of discomfort, pain when chewing food.
- It is possible to relieve inflammation for several hours, then the situation worsens again.
- Gradually, bad breath begins to appear, which does not disappear after the usual procedure of brushing your teeth.
- The tongue feels swelling of the gums.
If the situation repeats frequently, then the pathology is likely complicated. In advanced cases, the main symptoms include chills, hyperemia of the surrounding gum tissue, increased body temperature, and the gums of the entire part of the dentition become inflamed.
The patient may notice a change in the angle of the artificial tooth, as well as the appearance of gum pockets. Pieces of food get into them, which creates a negative environment for the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
In case of an allergic reaction to the prosthetic material, a rash, burning, dryness, and itching on the skin of the face is observed. You should immediately seek help from your doctor.
Treatment of scratches and wounds on the gums
What to do if you cut your gum? If the scratch is without foci of inflammation and other signs of complications, then you can get by with treatment at home using traditional medicine and the use of local antiseptics. Treatment of with chlorhexidine or furatsilin when rinsing promotes healing of the scratch and will become a serious obstacle to infection.
Treatment activities will include:
- drug treatment;
- folk remedies for wound healing;
- surgical care.
Drug treatment of injured areas
Many dentists do not advise self-medication and delaying consultation, especially when the child has cut the gum. At the stage of specialized care, the doctor will examine the surface of the mucous membrane, the nature of the cut in the gums and tell you how to treat it.
For difficult-to-heal mouth ulcers, dentists use ointments with an antiseptic effect :
- gel "Metrogil denta";
- gel "Cholisal";
- "Levomekol" (antibacterial agent);
- medicinal paste “Parodontocide”;
Metrogyl and Cholisal
For deep cuts, in order to prevent purulent infection, antibiotics :
- penicillin antibiotics (Amoxiclav);
- tetracyclines (Doxycycline, Tetracycline);
- tyrothricins (Grammidin).
Along with antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory treatment is indicated, including the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs :
- Ketorolac;
- Nimesulide;
- Diclofenac.
This therapy is aimed at reducing the inflammatory response and pain.
A frequent question: “What to do when you scratch your gum, it’s swollen and you have bad breath?” If the gums are scratched and have an unpleasant odor, this indicates an infection in the mouth. If there is a complication, then surgical intervention , the purpose of which is to release pus from the scratch and then treat it with local antibiotics.
Folk remedies for wound healing
If the patient has scratched his gums, but does not want to seek medical help, a solution may be to take folk remedies that will quickly eliminate signs of inflammation and relieve tissue swelling.
- Dried St. John's wort in combination with flax seeds and oak bark will cope with an infection in the mouth. By killing the infectious agent, this decoction will restore beneficial microflora. Use 1 time per day for a week.
- Pieces of propolis relieve the inflammatory reaction. Used in alcohol infusion or made in the form of plates, attached to the inflamed area of the gums for 30 minutes. Use daily until inflammation disappears.
- Compresses with calendula have a similar effect to propolis.
- Using a solution of potassium permanganate to relieve inflammation, 2 times a day, for a week (especially for pulpitis, stomatitis, gingivitis).
Treatment of scratches in a child
Since children are susceptible to infection, self-medication is not the right solution. If a child exhibits the corresponding symptoms of gum damage, you need to contact a dentist to decide on further treatment measures.
Even a microcrack in children is an indication for consultation. The doctor will examine you and tell you how to treat the inflamed scratch.
What problems may arise after tooth extraction?
Many patients experience swelling and pain in the gums during the first time after tooth extraction, but in most cases these problems quickly disappear. If the removal was traumatic, recovery may take longer. What factors influence the rate of wound healing?
- Her condition immediately after the operation, determined by the qualifications of the surgeon.
- The addition of a secondary infection, in most cases provoked by the patient himself.
- The patient has diseases that affect blood clotting and prevent the formation of a blood clot.
Therefore, it is so important to seek qualified dental care - in a reputable clinic, with an experienced surgeon who does not make annoying, unforgivable mistakes during surgery.
What to do if your denture rubs
It’s not just the first days of installation that are difficult for many patients. Often, removable dentures constantly rub against the gums due to their irregular shape. In this case, therapeutic treatment will not be successful, so dentists carry out a correction or a complete change of the prosthesis.
The plate is filed at the points of contact with the mucous membrane. Thus, the load on the gums will be redistributed and the problem will be solved.
After the manipulations, the specialist recommends a remedy to relieve inflammation caused by rubbing. For example, a gel for lubricating gums. It is important to see a doctor immediately, otherwise complications are possible - inflammation of the inner layers of the jaw apparatus, healthy periodontal tissues.
Complications after a cut on the gum
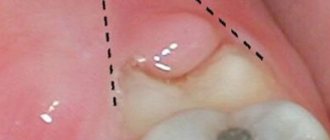
Deep cut on the gum photo
Sometimes after an injury, a person may notice pain at the site of the scratch. The gums become very swollen, small bumps appear, making it difficult to chew, and aching discomfort and burning occurs. A mark forms near the base of the tooth, which is surrounded by inflamed tissue. Redness and increase in volume are noticeable to the naked eye. You should immediately contact your dentist if you experience the following symptoms of exacerbation and inflammation:
- The scratch becomes white and rises above the surface of the gum.
- Cloudy contents or ichor ooze from the wound.
- The pain becomes tugging or throbbing and spreads to other areas of the jaw.
Most likely, a pathogenic infection or harmful microorganisms got into the cut on the gum, and a purulent inflammatory process began. This point cannot be left unattended: infected exudate can penetrate the root of the tooth, disrupt blood circulation in the periodontium and lead to the formation of acute gingivitis, pulpitis or other complications.
In addition, the person has constant pain, which prevents him from sleeping normally, preventing him from eating and smiling. A characteristic sign of inflammation is an acute reaction to certain foods: pepper, salt, spices or vinegar. The wound begins to itch more, pull and burn, practically does not heal and continues to increase in size. It can cause stomatitis and rashes in the mouth.