From this article you will learn:
- what do white spots on gums mean?
- why does a white coating appear on the mucous membrane,
- what to do if your gums turn white.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
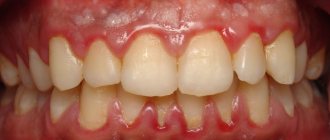
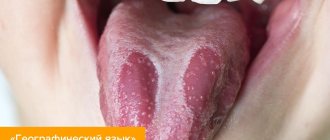
A white spot on the gum is a symptom of diseases of the oral mucosa, which is most often characteristic of a disease such as leukoplakia. And this is not such a harmless disease (as it may seem at first glance), but it has its consequences and requires certain therapy. According to the International Classification of Diseases, leukoplakia is classified as a precancerous disease of the oral cavity, i.e. in some cases, mucosal lesions can become malignant.
But there is a similar variant of damage to the oral mucosa, in which a white coating may appear on the gums, tongue, mucous membrane of the cheeks and palate. In some cases it can be easily scraped off, but in later stages of the disease it is usually firmly attached to the mucosal surface. The appearance of such white plaque on the gums, tongue and other parts of the oral mucosa indicates the development of oral candidiasis.
Why does light plaque form on the gums and what does it mean?
Ideally, the gums should have a uniform pinkish color. If suspicious white spots appear on the oral mucosa, you should be wary - most often they indicate the presence of some pathological processes in the body. The reason for the formation of white plaque on the gums may be a low level of hygiene or, for example, a whitening procedure. However, a similar symptom can also be provoked by a serious illness - leukoplakia, abscess, oncology. Read further in this article about possible causes of the problem and ways to solve it.
Light plaque on the gums is not a reason to panic
Plaque on the oral mucosa is a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. In the absence of any pathological processes in the body, such a symptom may indicate insufficient hygiene. Usually natural plaque can be detected in the morning after waking up, in which case it can be easily removed with a regular toothbrush and paste. Its presence on the tongue and gums is a completely natural and normal phenomenon, which provides a certain degree of protection of the oral cavity from pathogenic microflora. However, if a person does not systematically brush his teeth and take care of his oral cavity, the plaque on the teeth near the gums will very soon begin to harden and eventually turn into tartar, which can only be removed in the dentist’s office.
White plaque on the gums, why does it occur?
Another question is if you can’t remove the film yourself. In such cases, it usually has a dense consistency and can appear either in the form of a continuous covering or in the form of plaques. This symptom indicates the presence of any pathological processes in the oral cavity or in the body, so in this case you should definitely consult a doctor. It will be possible to cope with the problem only after making an accurate diagnosis, and any attempts to eliminate plaque on your own will not lead to the desired results, if they do not aggravate the situation at all.
Can stomatitis go away on its own?
Patients often delay visiting a doctor, hoping that stomatitis will go away on its own. Stomatitis in non-advanced forms can actually go away on its own within a week. But given the risk of complications and, as a rule, a fairly high degree of discomfort from which the patient suffers with this disease, it is much wiser to seek help from a doctor and receive competent medical care.
Correctly prescribed treatment, following the recommendations of the attending physician, will bring rapid relief and improved quality of life. In addition, this will speed up the process of curing stomatitis, avoid the unpleasant consequences of untimely treatment, and also, thanks to diagnostics, learn about the causes of stomatitis and, if necessary, take care of your health. It is difficult for a patient who does not have special knowledge to assess the severity of his disease and the causes that caused it, so seeking medical help is necessary.
Possible consequences and complications of stomatitis
Recurrent stomatitis can be cured quickly if you follow your doctor’s recommendations. But sometimes patients may experience some complications:
- lung diseases;
- damage to the entire mucosa;
- digestive problems;
- loss of some teeth.
Typically, such complications are the result of self-medication or lack of treatment, which is why you should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
What other symptoms may appear?
If the issue is not a low level of oral hygiene, and plaque cannot be removed on your own, we are talking about a specific pathological condition. In this case, patients often experience associated symptoms. Among the most common signs of the problem are bad breath, itching, swelling and redness of soft tissues, the appearance of small ulcers and other growths on the gums. To prescribe the necessary treatment, the doctor first needs to examine the patient’s oral cavity, take into account accompanying complaints, and, if necessary, take tests and scrapings.
Only tests can determine the true cause of the problem.
Common causes of white plaque on the gums
So, why does light plaque appear on the teeth, near the gums and in other areas of the oral mucosa and what does this mean? As noted above, the most common cause of the problem is insufficient care. Among other common provoking factors, experts highlight the appearance of tumors on the gums, the consequences of dental procedures and exacerbation of diseases. Let's look at all these reasons in more detail.
Factors leading to symptoms in adults
Light plaque on the mucous membrane in adults is a fairly common occurrence after professional whitening. Also, a thin film on the gum can form after rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic. This is a temporary phenomenon that disappears on its own within a few days. Also, a similar problem can arise due to a lack of certain minerals and vitamins in the body after tooth extraction. In the latter case, the symptom in question becomes a complication that occurs due to infection of the wound. In such a situation, the gum tissue also swells, is covered with a light film, and the person suffers from severe pain.
So, the most common pathological conditions leading to the formation of whitish plaque on the gums are listed below:
- stomatitis: in addition to plaque on the mucous membrane, inflamed areas with ulcers and erosions appear,
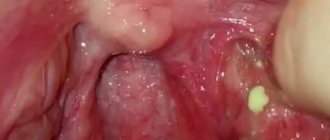
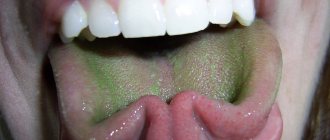
The photo shows candidiasis in the mouth - leukoplakia: soft tissues thicken, and white plaques appear on the mucous membrane itself, which gradually harden1,
- candidiasis (thrush): plaque is characterized by a cheesy consistency, is easily removed, but without treatment it soon forms again,
- Oncology of the gums: in this case, a hard plaque is formed, which most often appears in the form of numerous nodules.
“When I saw a thick coating on the child’s gums, I was also very scared. If it doesn't come off after rinsing, don't try to remove it with a brush or your finger. We immediately went to the children's dentist, and the doctor immediately determined that we had stomatitis. We were prescribed rinses with antiseptics, and in just a week everything went away. The main thing here is to immediately run to the doctor, and it’s better not to do anything on your own.”
Nadezhda P.R., Krasnoyarsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
White spots on the mucous membrane can also indicate the presence of a cyst - penetrating into the canals, the infection leads to the accumulation of purulent masses at the apex of the tooth. The gum area turns white, and the person experiences acute pain when the sore spot is mechanically irritated. Wen and fistulas also often lead to the formation of plaque.
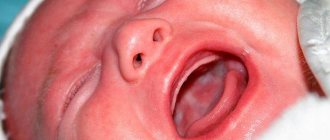
For what reasons can it appear in a child’s mouth?
The occurrence of a similar problem in children, including infants, usually indicates the development of candidiasis (thrush). The pathology is provoked by a fungus of the Candida species, which, against the background of a weakened immune system or other provoking factor, quickly spreads in the oral cavity. In this case, the child does not experience serious discomfort or pain, but the disease necessarily requires medical intervention.
Stomatitis is common in infants
Among other common causes of plaque in a child’s mouth, experts identify the following conditions:
- measles - white spots with a reddish edge,
- teething - the appearance of a light area on the gum,
- stomatitis – the main cause of the problem is most often insufficient oral hygiene or an incorrectly selected diet. A similar pathology is diagnosed in children, adolescents and adults.
It is also worth noting that a white film on the inner surfaces of the oral cavity may appear due to a lack of calcium and vitamins in the body. In any case, before starting symptomatic treatment, it is necessary to determine the source of the problem.
The most common diseases of the oral cavity in which ulcers appear
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis. The cause of this disease is bacteria that multiply when immunity decreases. Extensive ulcers appear on the gums, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise
- chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Up to 4-5 white spots first appear in the mouth, which later turn into ulcers. There is no temperature or other problems related to well-being. If such symptoms appear 1-2 times a year in small quantities, then there should be no cause for concern. Frequent occurrence is associated with weakened immunity and possible intestinal diseases, as well as allergies.
- acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis occurs in a child when he first encounters the herpes virus. Many bubbles appear on the gums, which, after bursting, turn into ulcers that merge with each other. The gums are always bright red, and the ulcers themselves are very painful, the temperature may rise
How is treatment carried out?
Treatment should begin with oral hygiene, and only after cleaning proceed to the main therapeutic measures. The choice of a specific treatment scenario directly depends on what specific problem the doctor will have to deal with. Obviously, if the cause of plaque is poor hygiene or teeth whitening, to get rid of the film on the gums, it is enough to rinse your mouth thoroughly - with plain water or chamomile infusion.
Chamomile infusion is great for rinsing
To treat stomatitis, I usually prescribe antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs, however, even in this case, much will depend on the form of the disease. If the cause of all the troubles is a fistula, then it will have to be opened surgically and the cavity cleared of purulent exudate.
On a note! Fungal infections are treated with special antifungal drugs: Nystatin, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole. Also, for a while, the patient will have to give up salty, bitter and acidic foods.
It is extremely important to start treatment for leukoplakia on time, since this disease often becomes a harbinger of oncology. In order to eliminate white plaques, an integrated approach is used - therapy is aimed at eliminating provoking factors. As part of the treatment, vitamin complexes are prescribed, and the affected areas are removed using an electric knife, laser device or radio waves. It is worth noting that liquid nitrogen is not used here because it leaves behind deep scars.
What can be done for prevention
The key condition that will help avoid not only the appearance of white bacterial plaque, but also most oral diseases, is regular and proper hygiene. You should brush your teeth at least twice a day, and after meals you should rinse your mouth with plain water or a special pharmaceutical product - these are the basic principles of maintaining oral hygiene. It is also worth minimizing the risk of injury to teeth and soft tissues by external factors. To do this, try to avoid sudden temperature changes when eating. For normal functioning of the body as a whole, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes from time to time.
Regular oral hygiene will help avoid problems
The appearance of a white film on the mucous membrane does not always indicate the presence of any problem in the body. Most often, this is just a consequence of insufficient oral hygiene. However, if after several attempts to rinse your mouth thoroughly the plaque still does not disappear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
- Anisimova, I.V. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips, 2008.
Gum healing
After tooth extraction, you need to be prepared for the fact that pain and swelling may intensify on the second day after surgery. But already on the 3rd - 4th day after the operation, the discomfort will begin to decrease. By this time, the wound healing processes are more active, and by touching the tip of the tongue to the hole, you can feel that a compaction has formed.
During this period, the following are actively developing:
- bone formation in the area of the removed tooth root;
- narrowing of the socket due to the “growth” of the gums;
- formation of the mucous membrane in the socket area.
Fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction persists for a week. It disappears on its own, without mechanical cleaning. Little by little, the mucous membrane begins to turn pink, gradually acquiring a healthy, natural color. Around the 10th day, wound healing is completed: healthy tissue is formed that covers the mouth of the hole. A small depression remains in the area of the removed tooth. The formation of bone tissue at the site of tooth extraction takes much longer - up to 6 months. Changes will be visible on an x-ray.