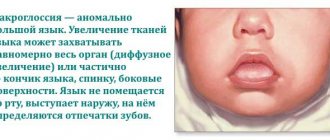
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Localization
Close attention is paid to the site of swelling. The varied nature of the disease harms a specific area of the muscular organ. If the root is affected, problems with the large intestine can be assumed. Pathology in the middle indicates improper functioning of the duodenum or small intestine, as well as the stomach. When imprints of chewing organs are visible on the sides, the patient is advised to balance the diet. More about this.
Along the edges
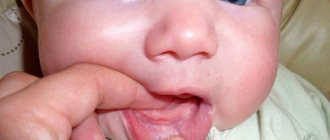
Is your tongue swollen around the edges? In such a situation, marks from the side teeth are visible on it. This most often occurs when a deficiency of nutrients in the body is diagnosed. Also, the edges are affected when problems with the thyroid gland occur. If water is retained in the body, there will also be dents on the sides of the organ. Most often this is diagnosed in diabetics, with inflammation or enlargement of the liver. It happens that this condition is typical for a diseased spleen, excess weight, and improper digestion.
On one side of the tongue
A symptom such as one-sided swelling due to a certain disease. It can be triggered by various factors: chronic diseases, bacterial or fungal infection, neoplasm, herpes virus and other ailments. It happens that one side swells as a result of injury. This could be a bite, burn, or surgery. Often Quincke's edema or allergies affect a specific area - an area on the right or left side.
Under the tongue
When swelling affects the area under the muscle organ, this most often indicates improper functioning of the salivary glands. Many provoking factors can lead to this condition. Among them are infection, mumps, sand in the salivary glands, HIV, herpes, influenza, poor hygiene, parainfluenza of both types.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
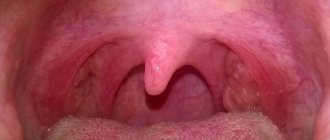
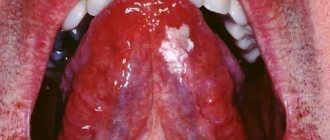
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Swollen after puncture
Many patients complain that their tongue is swollen after piercing. In most cases, this swelling is not pathological. The tongue was injured during the puncture process, and slight swelling is completely natural and natural. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations of the specialist who performed the puncture, keep the oral cavity clean, and rinse your mouth with antibacterial drugs. However, if the swelling does not go away within 4-5 days, and purulent exudate forms at the puncture site, you should immediately consult a doctor, since various complications often arise with tongue piercing.
Normally, healing after a puncture occurs within two weeks. During this period, the tongue may swell, hurt, and the patient may experience a feeling of discomfort, burning, and soreness. In the future, all these unpleasant symptoms will disappear, and after two weeks the wound should heal without a trace, and the swelling should go away.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of tongue swelling are its increase in size and swelling. In difficult cases, the patient has difficulty breathing, and there is a sensation of a foreign object in the mouth. The mucous membrane becomes loose, with prominent papillae, and tooth marks become noticeable on the lateral surfaces. Blood vessels become clearly visible on the lower part of the tongue.
Swelling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Change in taste sensations.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane.
- The appearance of heaviness when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of lips.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Paleness of the skin.
If the problem is not detected in a timely manner, the tongue continues to swell, does not fit in the oral cavity, and falls out. The help of a doctor cannot be neglected. If the tongue is swollen and this process persists for several days, it is dangerous to self-medicate or wait until the problem goes away on its own.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Treatment
For the most effective treatment and quick relief of the patient’s condition, the real cause of the swelling should be established. Let's consider treatment options depending on the causes of swelling:
- Swelling of the tongue caused by mechanical trauma usually goes away on its own within a few days. During this time, you should limit your consumption of spicy and hot foods and rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions.
- If the swelling is caused by glossitis, first of all you need to relieve the inflammation. It is necessary to rinse your mouth thoroughly, take antibiotics and antifungal drugs.
- In the presence of infectious diseases, the underlying disease should be treated, and a swollen tongue as a concomitant symptom will go away on its own.
- In case of an allergic reaction, the patient should eliminate contact with the allergen as quickly as possible, give an antihistamine, a sedative, and call a doctor.
- In case of anaphylactic shock, call an ambulance immediately, as seconds may count.
- In case of metabolic disorders and thyroid diseases, the underlying diseases should be treated first of all. The swelling of the tongue will go away on its own as the patient recovers.
- For genetic disorders, treatment is symptomatic; the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs to alleviate the patient's condition.
- In the presence of malignant tumors, treatment is carried out by an oncologist; it includes treatment of the underlying disease and relief of the patient’s condition.
- Very often tongue piercing . In this case, a small tumor is considered normal, because piercing is, in fact, the most common mechanical injury to the tongue. The piercing specialist must prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. Swelling after a piercing usually goes away on its own as the wound heals.
Allergic
A swollen tongue due to allergies most often occurs after taking medications, as well as when eating certain foods. If the cause of swelling is a medication, you should immediately stop taking it and replace it with another drug. In parallel, antihistamines and calcium supplements should be prescribed.
If you are allergic to food, you should do the same - stop taking foods that cause allergies, start taking antihistamines.
You can also use folk remedies against allergies. However, it should be remembered that swelling of the tongue and lips, swelling of half the tongue, as well as swelling under the tongue can cause suffocation, so self-medication should be done very carefully and only in cases where the swelling is small and does not make breathing or swallowing difficult. In all other cases, you should consult a doctor immediately.
The most effective folk remedy is rinsing the mouth with a decoction of sage, calendula or chamomile. They have an antibacterial effect and help calm the inflammatory process.
Juice from raw potatoes also helps reduce swelling. You should rinse your mouth with freshly squeezed juice.
Angioedema
Angioedema is of allergic origin and develops extremely quickly, sometimes in a matter of seconds. This is the most dangerous of all types of edema, as it often spreads not only to the tongue, but also to the larynx, causing attacks of suffocation.
With angioedema, not only the tongue often swells, but also the face, cheeks, lips, and eyelids. The patient's skin becomes bluish and the eyes begin to water.
If swelling spreads to the pharynx and larynx, it can cause asphyxia. The patient experiences difficulty breathing, to the point of being unable to breathe on his own. In this case, it is necessary to perform a tracheostomy or intubation. Since only a qualified doctor can do this, at the first sign of rapidly developing swelling of the tongue or face, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before her arrival, the victim should be given antihistamines, preferably administered intravenously. The airways should be cleared of accumulated mucus, facilitating easier breathing. The victim's head should be slightly elevated to avoid blocking the airway with a swollen tongue.
Causes
The tongue can become swollen for many reasons. Some do not pose a serious threat to human health and life, but some of them indicate the presence of a dangerous pathology. In this case, untimely treatment can lead to dangerous consequences, including death.
A tumor on the tongue occurs as a result of chemical exposure against the background of pathological processes.
The patient complains of attacks of nausea and vomiting, cough, abdominal pain, and disruption of the digestive system.
The provoking factor can be determined by taking an anamnesis, analyzing blood, urine and feces, and ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland.
The most common of them include 8 reasons.
Allergy
An allergic reaction is the most common cause of tongue swelling. It can be triggered by components of certain medications and food. In case of allergies, the organ enlarges on both sides equally over the entire surface. In this case, difficulty breathing and speaking occurs, and dizziness may occur.
An increase in the size of the tongue is almost always accompanied by a violation of the sensitivity of the taste buds.
Due to their swelling, the receptors that recognize salty, sweet or bitter foods cannot do their job. As a result, all food seems tasteless.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
Burns
Thermal burns caused by drinking hot drinks or food also lead to tongue swelling. Spicy food can also injure the mucous membrane.
There is no danger to the body; only unpleasant sensations arise that go away on their own after some time. During this period, it is better to refrain from drinking cold, hot drinks and foods, as well as from using spicy seasonings.
Insect bite
Occurs in rare cases. The tumor is observed only at the site of the bite. In this case, it is accompanied by painful sensations, localized mainly in a certain place. It also goes away on its own without the use of special medications.
Exposure to toxic or chemical substances
The tumor is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and pain in the abdominal area. After contact with chemical or toxic substances on the mucous membrane of the tongue, rinse thoroughly with running water and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Infectious diseases
Swelling and swelling of the tongue can appear as a result of the development of infectious diseases. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through microcracks on the surface of the mucosa. This is how herpes, candidiasis and syphilis arise. In certain cases, tongue swelling may be a side effect of scarlet fever.
Piercing, smoking and injuries from prosthetics
If your tongue is swollen, this can be caused by various everyday reasons, for example, piercing. Also, minor swelling is observed in cases where you bite your tongue while eating.
Hormonal imbalances
Swelling of the tongue is observed with various dysfunctions of the thyroid gland. This symptom most often occurs with hypothyroidism. In this case, the swelling does not go away on its own. Long-term treatment with hormonal drugs or surgery is required.
Disruption of the exchange process
A negative reaction of the body can be provoked by metabolic disorders or reduced immunity against the background of long-term infectious diseases.
A tongue tumor can also occur as a result of oncology, when a malignant neoplasm is formed in other organs or affects the tongue. Down syndrome and various genetic pathologies are also provocateurs of this unpleasant symptom.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
There are many reasons for a swollen tongue. This symptom does not always indicate the development of serious diseases, but in any case requires attention.
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of the tongue tumor and determine the need for therapy, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination. First of all, the specialist finds out when and under what circumstances the symptom occurred.
The doctor also identifies the presence of an allergic reaction to drugs or food, chronic diseases. Associated symptoms are being studied.
As an additional diagnosis, laboratory tests of blood, feces and urine may be prescribed to detect infection. If thyroid dysfunction is suspected, a hormone test and ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland are prescribed.
Swollen throat
If the tongue and throat are swollen at the same time, this condition is life-threatening for the patient. In the vast majority of cases, this condition occurs during anaphylactic shock (the most severe manifestation of allergies). Only an experienced doctor can remove a patient from a state of anaphylactic shock, therefore, at the first signs of swelling of the tongue and throat, you should immediately call an ambulance, especially if the patient has other dangerous symptoms - such as difficulty swallowing, bluish coloration of the lips and nails, swelling of the eyes and lips, small rashes, low blood pressure, nausea, shortness of breath or choking.
4.Treatment
The key is to reduce and, if possible, completely eliminate the likelihood of contact with the allergen. To relieve acute symptoms, antihistamines, desensitizing, decongestants, anti-inflammatory drugs are used, incl. hormone-containing. In most cases, the patient is hospitalized, mainly due to the risk of asphyxia.
Methods for drug correction of immune failure (immunotherapy) are being actively developed, but at the moment such treatment is very expensive.
Sign up for a consultation
2. Reasons
Angioedema type 1 is usually associated with an acute allergic reaction localized in the upper part of the body and occurring in response to contact with a provoking substance. It can develop both independently and against the background of a provoked allergic status - for example, with urticaria, hay fever, etc. In general, Quincke's edema is most often compared with urticaria, although in the second case the reaction from the skin is not so deep and pronounced.
Another, non-allergic form of angioedema is caused by inherited dysfunction of the immune system, as a result of which a violent and inadequate immune reaction can occur suddenly, spontaneously, in response to almost any more or less intense irritant (for example, cold or hot air, chemical fumes, etc. .).
Visit our Allergology page