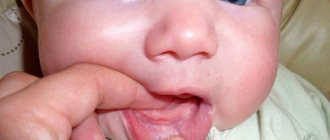
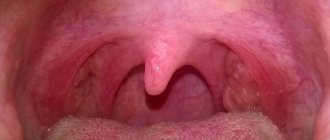
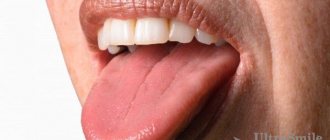
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
2.What are the types of urticaria and Quincke's edema?
There are several different types of urticaria and angioedema:
- Acute urticaria and acute angioedema
. This is hives or swelling that lasts less than six weeks. The most common causes of this reaction in the body are food, drugs, latex or infections. Insect bites or some kind of internal disease are another cause of acute urticaria. When it comes to foods, the most common causes of hives are nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries, soy, wheat and milk. Especially if they are all consumed in their raw form. Medicines that may cause hives or angioedema include aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen), high blood pressure medications, or pain relievers (codeine). - Chronic urticaria or Quincke's edema
. In this case, the hives or swelling last for more than six weeks. Usually the causes of this type of urticaria are more difficult to determine than in the case of the acute form of the disease. In fact, the cause of chronic urticaria may be the same, but perhaps it is all due to an autoimmune disease, chronic infections, hormonal disorders or malignant neoplasms. - Physical urticaria
. This is a rash caused by direct physical impact on the skin. For example, from cold, heat, sunlight, vibration, pressure, sweating or exercise. In this case, hives usually appear in the area where the skin was directly exposed and rarely occur elsewhere. In most cases, physical hives go away within an hour of stopping exposure. Cold allergy is one of the most common forms of physical urticaria. - Dermatographism
is hives that appear when the skin is rubbed or scratched too hard. Such urticaria can begin simultaneously with other forms of this disease. - Hereditary angioedema
. This is a painful swelling of the tissue. The disease is inherited.
Visit our Allergology page
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
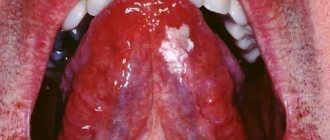
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Diagnostic procedures for urticaria
Diagnosis of acute urticaria is usually quite simple. An examination and questioning of the patient about his medical history is sufficient. Finding out the reason is not so easy, and for this purpose additional research is carried out:
1. Laboratory tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood biochemistry (liver tests - ALT, AST, bilirubin, rheumatic tests, blood glucose);
- stool examination (coprogram);
- bacterial cultures from the nasal and pharyngeal mucosa.
2. Instrumental research:
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- endoscopic examinations of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract (gastroscopy, colonoscopy).
3. Allergy tests:
- intradermal tests with allergens;
- cold and heat tests;
- physical stress tests, line drawing, tourniquet application.
4. Immunological methods.
5. Consultations of related specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- endocrinologist;
- rheumatologist;
- gynecologist and others as necessary.
First of all, it is important for a specialist to establish what nature the urticaria is – allergic or non-allergic. In the allergic form, one can clearly trace the connection between the symptoms and the introduction of the allergen. It is confirmed by skin, allergy and immunological tests.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
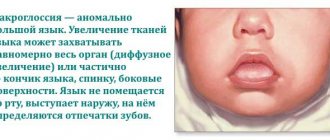
What language should be normal?
A child who is completely healthy has a uniform pink tongue, without areas of inflammation. There should also be no plaque on the mucous membrane normally. Parents should be alert to the following changes in the tongue:
- Limited areas of inflammation;
- Neoplasms of various types;
- Uneven plaque, which consists of tiny particles of food and dead epithelium;
- Excessive growth of the epithelium in certain areas of the uvula.
You should pay attention to the localization of spots and areas of inflammation. This also has important diagnostic significance, since each part of the tongue is associated with the work of a specific organ.
- Liver and gallbladder – spots and plaque on the sides of the tongue;
- Intestines - changes affect the base of the uvula;
- Buds - spots located between the root and the middle of the tongue;
- Lungs - there are spots on the front of the tongue;
- The heart is connected to the tip of the organ.
Most often, spots on the tongue are caused by problems with the digestive tract. Such changes are not necessarily a sign of serious illness, but it is worth consulting your doctor about this.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
When and which doctor to contact
Usually a doctor is consulted:
- if the rash spreads over a large area;
- when symptoms increase;
- when signs of general intoxication occur;
- if the urticaria does not go away on its own after eliminating the factor that caused it;
- if the disease becomes chronic or often recurs,
It is advisable not to delay your visit to the doctor and come when the first manifestations of the disease occur. Then it will be easier to establish the cause, and treatment will take less time. In addition, the doctor will recommend what to do to prevent hives.
A therapist or pediatrician, a dermatologist can provide assistance with urticaria, and an allergist is involved in targeted diagnosis and treatment.
4.How to treat urticaria and Quincke's edema?
The easiest way to deal with urticaria and angioedema is if you can identify and eliminate the factor that caused the problem. But this is not always possible. Typically, antihistamines are used to treat hives. They will help relieve the symptoms of the disease. Sometimes antihistamine medications need to be taken regularly to prevent the rash and associated swelling.
Chronic urticaria is treated with antihistamines or a combination of them. But if this does not give the desired result, sometimes the doctor prescribes corticosteroids.
In severe cases of urticaria and angioedema, an injection of adrenaline or steroid medications may be necessary.
What else can be done to treat hives?
While the course of treatment is ongoing and you are waiting for the redness and swelling to disappear, follow these simple recommendations.
- Do not use hot water. Let it just be warm.
- Wash with mild soap.
- You can apply cold compresses or apply a damp cloth to the affected areas.
- Be in a cool room.
- Wear loose, lightweight clothing.
Mechanism of disease development
Urticaria differs from other dermatological and allergic diseases in the presence of a clear and understandable relationship between exposure to an allergen and the appearance of rashes. Most often, patients can independently name the provoking agent - symptoms appear within a few minutes after contact with the provoking agent. If the causes of urticaria are unknown, then first of all it is recommended to pay attention to contact with animals and diet.
An immediate allergic reaction develops as follows: an allergen enters the body, mast cells are immediately sent to it - they cause the release of immunoglobulin E. When a mast cell is in conditions of increased immunoglobulin content, it produces histamines - substances that increase vascular permeability and cause swelling . This is a protective mechanism that allows the body to block part of the allergen, and remove part as quickly as possible.
The provoking factor may not be a substance, but a physical effect - heat or cold, stress. Allergies can also be caused by the presence of a source of infection in the human body.
In clinical diagnosis, acute and chronic forms of urticaria differ in duration - if episodes of urticaria are present for 6 weeks and are interspersed with periods of remission, then a diagnosis of chronic urticaria is made.
Our doctors
Orlova Tatyana Vladimirovna
Doctor - allergist-immunologist, pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
Shundeva Oksana Veniaminovna
Allergist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Causes of development and forms of urticaria
The main cause of hives is contact with an allergen. There are many factors that can provoke a pathological response of the immune system (this is an allergy). Most often, urticaria is caused by contact with such groups of substances as:
- Medicines, especially antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
- Dust.
- Animal fur or feathers.
- Plant pollen, poplar fluff.
- Substances that get under the skin from insect bites.
- Compounds that parasites secrete are most often caused by Giardia.
- Some substances contained in food products.
For the development of acute urticaria, short-term contact with the allergen is sufficient. The chronic form is characterized by frequent relapses and is associated with prolonged proximity to the substance causing the pathological reaction. Therefore, at the first manifestations of an allergy, it makes sense to conduct special tests, find out what exactly caused the rash, and exclude any contact with this substance.
In the chronic form, the rash and inflammation are less pronounced. After an exacerbation, the symptoms disappear for a while. Recurrent urticaria may be associated with the presence of a source of infection in the body and requires consultation with a specialist.
3.Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of urticaria or Quincke's edema is made after examination. Your doctor will ask you a few questions to find out the possible cause of your hives or angioedema and examine your skin. Depending on your health condition, you may need to consult an allergist, immunologist or dermatologist.
Skin tests may be done to determine which substance is causing your allergy. And routine blood tests are needed to determine the presence of some systemic disease.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!