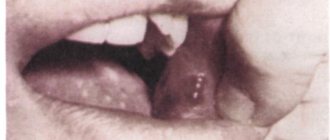
Causes of cheilitis
The inflammatory process can begin for multiple reasons. One of the most common of them is mechanical injuries: for example, accidental biting can cause inflammation.
The development of the disease can also be provoked by:
- unfavorable environment (people who spend a lot of time outdoors and are exposed to wind, frost and other weather conditions are more likely to suffer from cheilitis);
- aggressive action of cosmetics or an allergic reaction to some of their components;
- lack of vitamin B2, which is responsible for the division and growth of epithelial cells;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, lack of immunity.
Meteorological
Reason . Exposure to cold air, strong wind. It occurs more often in men, especially those who suffer from general weather sensitivity or work outdoors.
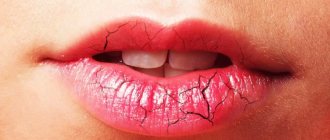
Symptoms . Peeling, itching and dryness, as well as erosions and crusts on the lips. Cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Treatment and prevention. If possible, minimize exposure to cold and wind. Use protective cosmetics for lips. Take B vitamins internally, as well as PP. Use special wound-healing ointments externally and often rinse your mouth with extracts of chamomile, oak bark, and calendula.
Types of the disease, their symptoms
There are a large number of types of disease, each of which has its own symptoms. Cheilitis happens:
- catarrhal, resulting from injury. Its characteristic symptoms are redness, peeling, swelling and soreness of the lips.
- eczematous, developing due to the occurrence of eczematous processes. The reason is an allergy to a certain type of food, cosmetics (lipstick, cream).
- glandular, associated with an abnormality of the salivary glands. It happens that cheilitis on the lips accompanies periodontal disease, lupus, etc. The lower lip often suffers and begins to peel.
- meteorological. It is caused, as the name suggests, by weather conditions (high air humidity, strong wind, decreased or increased temperature, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, etc.).
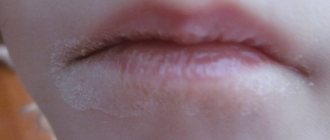
- exfoliative, characterized by a chronic course. It is divided into two forms - dry (the blood supply to the lips is disrupted and, as a result, dry scales are formed, which can be easily removed, but after a few days they appear again) and exudative (the border swells and becomes inflamed, crusts appear).
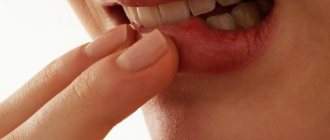
- angular, called jam. Due to streptococci, inflammation begins in the corners of the lips. Vitamin deficiency and frequent licking of lips can also provoke it.
- atopic, accompanying atopic dermatitis. The red border of the lips flakes and itches, the lips crack.
- hypovitaminosis, which occurs due to a lack of B vitamins. Dryness and a pronounced burning sensation affect not only the lip area, but also the entire mucous membrane of the mouth, including the tongue. In this case, the mucous membrane turns red, and vertical cracks form in the area of the red border.
Regardless of the type of cheilitis, common symptoms will be:
- peeling of the lips, observed both only near the border and over the entire surface;
- swelling and swelling, burning and itching in the lips, the appearance of cracks and crusts on them.
Why does my lip hurt?
Cheilitis
Cheilitis is a large group of inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane and skin of the lips. They arise primarily or develop against the background of other pathologies. Typical signs include pain and burning in the lips when eating, opening the mouth, peeling, hyperemia, the appearance of cracks, crusts, and bleeding ulcers. The symptom can be provoked by the following types of cheilitis:
- Exfoliative.
It is formed against the background of neurotic disorders and is more often detected in women. It affects the red border without involving the mucous membrane, corners of the mouth, areas adjacent to the skin of the chin and nasolabial triangle. It manifests itself as a burning sensation, dry lips, and the formation of scales. The pain is more pronounced in the exudative form, also accompanied by swelling of the lips. - Glandular.
Diagnosed in people with developmental defects and acquired diseases of the minor salivary glands, caries, and periodontal diseases. The lower lip is most often affected. Initially, slight dryness is detected, which is subsequently replaced by painful erosions, deep bleeding and weeping cracks. - Contact allergic.
It is potentiated by cosmetics, formed by the habit of holding various objects in the mouth, and develops in people of certain professions (for example, musicians who play wind instruments). Severe itching, redness, and swelling of the lips prevail. The resulting blisters burst with the formation of painful erosions and cracks. - Meteorological.
Occurs under the influence of sunlight, less often - wind and cold. The exudative form is accompanied by burning, itching, and the appearance of small blisters, in place of which painful erosions remain. For the dry form, the presence of erosive defects is uncharacteristic; pain appears against the background of burning and dry lips. There is a danger of developing precancerous diseases and malignancy. - Atopic.
Diagnosed in patients with neurodermatitis and atopic dermatitis. Concerned about hyperemia, peeling, itching. Pain occurs when cracks form in the corners of the mouth. The listed manifestations are complemented by peeling and dryness of the face. - Hypovitaminosis.
It is provoked by a lack of B vitamins, especially B2. The skin of the lips is dry, hyperemic, covered with small vertical cracks that hurt and bleed. The mucous membrane is reddened, slightly swollen. The tongue is enlarged.
Herpes
The red border of the lips and the corners of the mouth are the favorite localizations of herpes simplex. The patient feels a burning sensation, tingling, and bloating. In the affected area, rashes form, which are a collection of small bubbles. As the changes progress, unpleasant symptoms increase, and pain is added to them. Then the bubbles open individually or after merging into one or more multi-chamber bubbles. In their place, erosions of irregular shape appear, painful when touched or when moving the lips.
Oral lichen planus
Involvement of the lip (mainly the upper lip) is characteristic of a rare atypical form of the disease. Papules, plaques or ulcers, erosive defects of irregular configuration, covered with fibrinous plaque, are found on the skin and mucous membrane. The pain syndrome is most pronounced in the presence of ulcers and is accompanied by a burning sensation. Several forms of lichen planus are often combined with each other or transformed into one another, so lesions can be present not only on the lips, but also on the gums, tongue, and oral mucosa.
Lip pain
Traumatic injuries
Acute damage to the mucous membrane or skin of the lip occurs as a result of injury from foreign objects or biting. It is quite rare. Manifested by the formation of a hematoma or erosive defect. The pain persists for 1-3 days. With secondary infection, erosion transforms into an ulcer, surrounding tissues swell, and pain intensifies.
Chronic trauma is possible when carious anterior teeth are damaged by sharp edges. It occurs with swelling, slight pain, and a feeling of discomfort. With prolonged injury, an ulcer forms. It is possible to develop a local or widespread inflammatory process with increased pain, swelling, and the appearance of purulent discharge.
Lip bruises are usually the result of fights. Children often develop as a result of falls. They are characterized by rapidly growing swelling and may be accompanied by abrasions of the mucous membrane due to sudden contact with the teeth. Painful sensations are pronounced in the first minutes after the injury, and then gradually subside. Recovery occurs after 1-2 weeks. Lip wounds are often lacerated and manifest as acute, raw pain and bleeding.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Repeated shooting intense pain impulses, reminiscent of an electric shock, are observed when the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved. The pain spreads to the upper lip, upper cheek, upper jaw. When the 3rd branch is affected, similar sensations occur in the area of the lower lip, chin, lower jaw, and lower cheek. The duration of an attack of neuralgia ranges from a few seconds to 2 minutes.
Lip cancer
At the initial stage of lip cancer, there is no symptom. A painless, sometimes itchy ulcer or area of compaction forms on the lip (usually the lower lip). Pain occurs when nearby tissues grow. Becomes constant, progresses, reaches significant intensity. Upon examination, an ulcer with uneven edges or a node in the form of a wart or cauliflower inflorescence, covered with cracks and ulcers, is revealed.
Cheilitis in children
Depending on the age of the child, he may experience a certain type of cheilitis.
Newborns suffer from a catarrhal disease caused by the prolonged presence of a pacifier or bottle in the mouth. Plus, saliva accumulates on the nipples of the lips, irritating sensitive baby skin.
If the disease is ignored, hoping that it will go away on its own, cheilitis will develop into an exfoliative form, accompanied by the formation of scales, which the child will not be able to remove himself (parents are highly discouraged from interfering in this process, since attempts to tear off the crusts can cause cracks, which will only aggravate the situation ).
Constant sucking of the mother's breast is an equally common cause of the development of the disease: during feeding, cracks form on the nipples, into which bacteria penetrate, which causes cheilitis.
Actinic
Reason . Increased sensitivity of the red border of the lips to ultraviolet radiation. The disease appears in the spring-summer season, and by autumn it disappears by itself.
Article on the topic
Lipstick: history of creation and subtleties of use
Symptoms .
The red border of the lower lip swells, becomes bright red, powdered with small white scales. Sometimes small bubbles appear, after opening which crusts form. Patients are concerned about itching, burning, and less often sore lips. Treatment and prevention . You should not only reduce your exposure to sunlight, but also start constantly using sunscreen cosmetics. Ointments with hormones (hydrocortisone, prednisolone, etc.) can be used topically. Inside - vitamins. Rinse your mouth with herbs.
Prevention methods
Careful oral hygiene
To prevent the appearance of cracks, you need to protect the skin and mucous membranes from adverse effects. To do this, you should get rid of the habit of licking your lips and corners of your mouth, using medicinal cosmetics for dry skin and hygienic lipsticks. To prevent infection from getting onto the skin of the lips from the oral cavity, it is necessary to brush your teeth at least twice a day, as well as treat caries and inflammatory gum diseases.
Changing your diet
If pockets begin to appear in the corners of the mouth, it is necessary to limit the consumption of spicy, sour and salty foods that irritate the mucous membranes and skin. You can add non-acidic fruits and vegetables to your daily diet, as well as foods containing iron and riboflavin (beef, liver, dairy products, cabbage, potatoes, peanuts, almonds, etc.).
Up to contents
Causes of cheilitis
Exposure to adverse weather conditions.
The disease often develops as a result of exposure to unfavorable climatic factors, which include ultraviolet radiation, too low or high air temperature. For this reason, cheilitis often affects people whose work involves regular exposure to fresh air.
Development of an allergic reaction.
One of the reasons for the development of cheilitis is an increase in the sensitivity of the lips to various irritants, mainly of chemical origin.
In this case, the area of the red border of the lips is most often affected and, less often, the mucous membrane. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and do not undergo treatment, the disease can spread to the skin surrounding the lips. Most often, the disease develops due to the use of lipsticks. This is explained by the fact that their composition includes the dye eosin and specific fluorescent substances. The plastic of dentures, aromatic fillers included in toothpastes, etc. can also act as irritants. The disease mainly affects women aged 20-60 years.
Presence of an underlying disease.
Cheilitis on the lips can be a symptom of some disease and manifest itself against the background of neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis. Eczematous cheilitis is formed with various eczemas, macrocheilitis - with neuritis of the facial nerve in combination with a folded tongue. The most common cause of the disease is dermatoses. The skin of the lips, mucous membrane and red border can also become inflamed with systemic and infectious diseases (psoriasis, tuberculosis, lichen planus, erythematoses, etc.).
Up to contents
Allergic
Reason . Increased sensitivity of the red border of the lips to chemicals, for example, dyes contained in toothpaste, lipstick, dentures. Women get sick more often.
Symptoms . It begins with violent swelling and redness of the red border of the lips, which then becomes covered with abundant scales and crusts, and painful cracks form in places.
Treatment and prevention . Drugs that reduce the body's sensitivity to allergens, antihistamines, and vitamins are used. Externally apply lotions from a 2% solution of boric acid, zinc ointment, anti-inflammatory creams containing glucocorticoids, salicylic acid, sulfur. Avoid substances that irritate the oral mucosa and red border of the lips. After eating, rinse your mouth with infusion of chamomile or soda.