Lip cancer is a malignant neoplasm that consists of elements of the integumentary epithelium of the red border of the lips. A tumor on the upper lip appears rarely. Over time, lip cancer spreads to the bones of the lower jaw. Atypical cells are transported with lymph to the lymph nodes, resulting in the appearance of new malignant foci.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital carry out early diagnosis of lip cancer using modern research methods. Oncologists provide radiation therapy and perform gentle surgical interventions. In the later stages of lip cancer, complex therapy is used. Early diagnosis of a malignant lip tumor and adequate therapy can not only save the patient’s life, but also avoid cosmetic defects after surgery.
Lip cancer - what is it?
Depending on the type of tumor growth, the following forms of lip cancer are distinguished:
- Papillary;
- warty;
- Ulcerative;
- Ulcerative-infiltrative.
A malignant tumor of the lip in 95% of cases is represented by keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. In 5% of cases, histologists have squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer of the lip mucosa. A tumor of the lip, which from the inside, on the mucous membrane, is characterized by a malignant course (infiltrative growth and early metastasis to regional lymph nodes).
A tumor of the lower lip most often affects the border of the lower lip. A crack, ulcer or swelling forms on it, which looks like a wart. The disease is predominantly diagnosed in people over 60 years of age.
Cancer of the upper lip occurs less frequently than the lower lip, but the tumor is more aggressive. Upper lip cancer has a high risk of metastasis and spreads quickly. This is explained by the fact that the malignant tumor is located close to the nasal cavity, where the blood supply system is developed. A tumor on the inside of the lip is dangerous because it quickly grows into the soft tissue.
Melanoma on the lip is 10 times less common than squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, but is characterized by a high degree of malignancy. Basically, the tumor is located on the red border of the lower lip. It penetrates deeply into tissues, quickly transfers to nearby tissues and gives metastases.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists make a diagnosis of lip cancer using the following methods:
- Examination with the naked eye and using stomatoscopy;
- Cytological examination of impression smears from a tumor ulcer;
- Histological examination of lymph node punctate.
After establishing the primary diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out.
Pharmacy products for removing warts
You can buy medications at the pharmacy that will help you deal with warts at home.
Among them:
- Super clean . The product is an alkaline solution that has a chemical effect on the growth, causing cauterization.
- Cryopharma, Wartner . These agents cause cryodestruction of the wart; as a result of cold exposure, the neoplasm is frozen.
- Solcoderm . A drug containing acids that have a cauterizing and mummifying effect on pathological tissues.
- Immunomodulators – Viferon, Oxolinic ointment will help increase immunity and the body’s fight against the virus.
- Antiviral agents – Isoprinosine, Interferon.
The use of cauterizing agents on the lips and face is extremely undesirable; application of these agents to the oral mucosa is especially dangerous.
Causes of lip cancer
Lip cancer develops for many reasons:
- From smoking;
- After a long stay in the sun;
- As a result of inflammatory processes of an infectious and non-infectious nature;
- Under the influence of high temperatures;
- In the presence of microtraumas;
- Due to prolonged exposure to chemicals.
Lip cancer often develops from smoking. Men get lip cancer much more often than women. Currently, the trend is changing, because many women suffer from tobacco addiction. Doctors believe that lip cancer develops due to smoking strong cigarettes for a long time.
The average smoker smokes at least ten cigarettes a day. In this case, the paper surface is constantly in contact with the lips. The skin here is especially delicate and sensitive. Microcracks appear on its surface. They are invisible to others and do not cause problems for the smoker. Damaged areas of the epithelium are affected by tobacco smoke. It contains a lot of harmful substances. Skin cells begin to degenerate.
The cause of mechanical trauma that causes lip cancer can be improperly made dentures, the habit of holding various objects with the lips (nails, the mouthpiece of a smoking pipe), or biting the lower lip. The mechanism of development of lip cancer is as follows: a long-term non-healing crack, wound, inflammation on the lip, papilloma develops into leukoplakia, Manganotti cheilitis, keratoacanthoma, warty form of dyskeratosis or other precancerous diseases. Against this background, lip cancer occurs.
Gymnastics
Gymnastics is appropriate only after complete recovery. Not earlier than 2 weeks after the injection.
How to do:
- Pull your lips out with a tube.
- Stretch as wide as possible.
- Compress.
- Sing vowel sounds.
Gymnastics are performed 2-3 times a day for 3-4 minutes. A specialist will show you specific exercises.
Precancerous diseases of the lips
Lip cancer does not occur on healthy mucous membranes. Malignant neoplasms develop against the background of obligate or facultative precancerous diseases. Obligate precancerous diseases include:
- Abrasive precancerous cheilitis Manganotti;
- Warty precancer of the red border;
- Limited precancerous hyperkeratosis of the red border.
Facultative precancerous diseases with greater potential for malignancy are:
- Erosive and verrucous leukoplakia of the lip;
- Papilloma;
- Keratoacanthoma;
- Cutaneous horn.
Malignant neoplasms of the lip can develop against the background of optional precancerous diseases with less potential malignancy:
- Flat leukoplakia of the lip;
- Chronic ulcers;
- Ulcerative and hyperkeratotic forms of lupus erythematosus and lichen planus;
- Chronic cracked lips;
- Post-X-ray cheilitis;
- Meteorological and actinic cheilitis.
Background conditions that are precursors to lip cancer include scars after burns, trauma, surgery, and benign neoplasms.
Heilith Manganotti
Abrasive precancerous Manganotti cheilitis occurs in older people. Small, round erosions appear on the lips, which do not heal for a long time. They have a smooth surface of yellow-red or bright red color. In some cases, a bloody or serous crust appears on the surfaces of erosions. If you remove it, the opened wound bleeds a little. Touching erosions does not cause pain. Once erosion appears, it does not heal for several weeks or months. After disappearing, soon enough new erosions appear in their place or nearby.
Manganotti cheilitis is diagnosed by external examination and questioning of the patient. This disease has symptoms similar to those of herpes, leukoplakia, lichen planus or lupus erythematosus. For differential diagnosis, oncologists scrape the affected area of the lip and send it for a thorough histological examination. This scraping makes it possible to detect emerging cancer cells in a timely manner and prevent the development of a malignant neoplasm of the lip.
Leukoplakia and lip hyperkeratosis
Leukoplakia of the lip is a lesion of the mucous membranes with keratinization of the epithelial tissues. Unfavorable factors that contribute to the development of leukoplakia may be alcohol abuse, smoking and eating very spicy foods. Leukoplakias of the lower lip most often develop in the mucous membranes at the corners of the mouth.
Hyperkeratosis of the lips appears as a limited area from 0.2 to 1 cm in diameter. Its surface is smooth, covered with thin, tightly packed grayish-white scales. Scraping cannot remove them.
Other causes of bumps and their types
- Retention cyst is a common disease. The cyst is filled with clear liquid and protrudes above the mucous membrane, from the inside. Its structure is dense, but when pressed, the cyst flattens. Then it returns to normal again. The tumor does not hurt, its size is constantly changing (it decreases or increases). Sometimes the cyst bursts on its own, and fluid enters the oral cavity. But this situation will not solve the problem, since over time the ball will reappear in its place. In order to get rid of the problem, you need to visit a dentist. The doctor probes the salivary canal and completely removes the cyst, suturing the edges of the wound.
- Herpes is a disease caused by the simple herpes virus. It causes white bumps to appear on the lips. The balls are watery inside. Additional symptoms are increased body temperature (but not in every case), pain and burning in the lips. Once the ball is ripe, it bursts. Liquid exudate flows out of it. Then the wound becomes covered with a purulent crust. Herpes is characterized by multiple rashes. The virus is always present in the patient’s blood, long-term remission is possible, but under favorable conditions the herpes virus attacks again, and rashes begin.
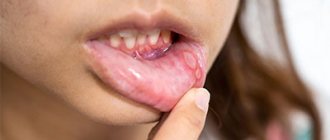
- Papilloma on the tongue is a benign neoplasm that looks like cauliflower forks. They do not manifest themselves in any way except for aesthetic discomfort. Papillomas can appear on the inside and outside of the lip. They are caused by the human papillomavirus. These can be flat pinkish seals, reaching up to 1 - 2 centimeters in size. Warts are black. In this case they are localized in the singular. If papillomas do not cause visible aesthetic discomfort, then they do not need to be removed.
- Hemangioma is a common tumor on the outside of the lip. Usually a bluish bump that can reach large sizes in diameter. Hemangioma is formed due to the proliferation of blood vessels. The anomaly may be congenital or acquired. Removal is the only surgical solution.
- Injuries – this also includes thermal burns. Often, after an unsuccessful bite or after a fall, a ball appears on the lip. The integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised and it is severely injured. As a result, a transparent blister, ulcer or growth on the mucous membrane may appear. The ball dissolves on its own; if this does not happen, then the help of a specialist is required.
- Fibroma is a benign tumor that is formed from fibrous tissue. It grows for quite a long time and is not noticeable at first. It is a nodule on a stalk or on a wide base. The seal is pink in color with a smooth surface. It can only be removed surgically.
In the photo you can see different types of bumps on the lip. But you should not make an independent diagnosis; this should only be done by a doctor based on an examination and the necessary tests.
Symptoms of lip cancer
There are local and general signs of lip cancer. Local symptoms of a malignant neoplasm can often be seen on the lower lip. When the pathological process is located on the mucous membrane of the lips, facing the vestibule of the mouth, the tumor has a pronounced malignancy. General signs of lip cancer can develop if the tumor is not detected in a timely manner and treated inadequately in the later stages of cancer.
First symptoms
The first signs of lip cancer usually go unnoticed. First, you can determine the enlargement of the mental lymph nodes. You can notice this by feeling the lower jaw. The next early sign of lip cancer is a swelling of a dense consistency. Itching occurs in it. This neoplasm is usually mistaken for a herpetic rash.
A small ulcer with a crust forms in the center of the swelling, which does not cause pain. If it is removed, the patient feels quite severe pain, and upon closer inspection, he may find a bleeding base, which is formed by tubercles.
Local signs of tumor
Symptoms of lip cancer are:
- Dyskeratosis of the lips;
- Papilloma;
- Erosion;
- Cheilitis.
In most cases, dyskateriosis looks like cracks and ulcers. The erosions are covered with a crust and resemble herpes in appearance, but, unlike it, they do not heal after a certain period of time. Some patients have no ulcers or erosions. Instead, a small compaction appears, which over time grows and becomes covered with a crust.
On the red border of the lower lip, away from the midline, a patch or formation may appear that protrudes above the surface. An erosion or ulcer with a granular surface and a roll-like edge forms in the center of the tumor. The formation has a dense consistency and gradually increases in size, eventually acquiring an irregular shape. Its boundaries are unclear.
Exophytic lip cancer predominantly develops from a warty form of productive diffuse dyskeratosis of papilloma. With exophytic growth, the tumor has a dense consistency, often covered with flat scales. Endophytic growth of a cancerous tumor is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with uneven, dense edges. It often appears against the background of destructive dyskeratosis, quickly infiltrates the soft tissues of the lip and is prone to metastasis.
Symptoms of the disease should be a signal to immediately contact oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital. Lip cancer, treatment of which is started on time, is completely cured in 90% of cases.
Causes of warts
The appearance of warts is caused by infection with papillomavirus or HPV.
Since the skin on the lips is quite thin, it is therefore easily permeable to viruses.
It should be noted that signs of infection with the human papillomavirus do not always occur.
The better the immune system, the less likely it is that symptoms of the disease will appear.
And yet, most of the world's population is infected with HPV.
The incubation period for the development of the disease can be several months or years.
As soon as the immune system fails, the first signs of infection appear.
Activation of the virus is accompanied by the formation of warts.
As a rule, growths appear on the area of the skin or mucous membrane where the pathogen entered the body.
Infection can occur both through sexual contact and through household contact.
Can the virus be transmitted by kissing on the lips?
The most common cases of infection are:
- intrauterine infection of the fetus if a pregnant woman is infected with papillomavirus
- shaking hands or kissing an infected person (if there are wounds or abrasions, the risk of infection increases)
- the use of personal items of an infected person (toothbrush, dishes, lipstick) is unlikely, since the pathogen is not stable in the environment
- sex accompanied by oral sex
- visiting common areas (swimming pool, sauna, shower)
People at risk are those who:
- patients with diabetes mellitus or other pathology of the endocrine system
- suffer from obesity and metabolic disorders
- taking antibiotics for a long time
- have chronic diseases
- suffer from increased sweating, especially on the feet, as this is where plantar warts often form
A malfunction of the immune system can occur for the following reasons:
- If there is a deficiency of essential substances in the body
- After suffering stress or physical exhaustion
- In case of hormone imbalance: during puberty, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, during treatment with hormonal drugs
- In case of chronic lack of sleep and overwork
- Due to a recent infectious disease
- If a person abuses smoking and alcoholic beverages
Stages
Currently, the generally accepted classification of lip cancer is TNM (T-size of the tumor, N-damage to the lymph nodes, M-metastases). Based on the size of the tumor, there are 4 stages of lip cancer.
Table 1. Stages of lip cancer
| Stage | Tumor size |
| T1 | Less than or equal to 2cm |
| T2 | More than 2-4cm |
| T3 | More than 4cm |
| T4a | The tumor grows into the cortical layer of the bone, tongue muscles, maxillary sinus and skin |
| Т4в | The tumor grows in the bed of the masseter muscle, the pterygoid process, the internal carotid artery and the base of the skull |
If on the affected side there are single enlarged lymph nodes, the size of which is less than 3 cm, this is stage N1 lip cancer. At stage N2, enlarged lymph nodes are detected on the affected side, the diameter of which is more than 3 cm. If the patient has single enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side measuring 3-6 cm in size, this is stage N2a of lip cancer. At stage N2, oncologists determine multiple metastases to the lymph nodes. Their size is equal to or greater than 6cm. In the presence of bilateral metastases in the lymph nodes measuring 6 centimeters, they speak of the N2c stage of lip cancer. If the diameter of the lymph nodes exceeds 6 cm, this is stage N3 of the disease.
In the absence of distant metastases, oncologists determine stage M0 of lip cancer, if there are distant metastases - M1, in the case of distant metastases that cannot be assessed - MX. The diagnosis of “early stage lip cancer” is made in the presence of a tumor less than or equal to 2 cm, the presence of single enlarged lymph nodes less than 3 cm on the affected side and the absence of distant metastases. This is T1 N1 M0.
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).
Diagnosis of a tumor by a doctor in a hospital
What does lip cancer look like? It could be a small ulcer or a widespread tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of lip cancer based on the patient’s complaints, the results of an external examination and additional studies. The oncologist carefully examines and palpates the lips, cheeks, gums and regional lymph nodes. When examining the red border of the lips, skin and mucous membrane, use a magnifying glass.
How to identify lip cancer? Further examination is carried out using instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound examination;
- X-rays of the lower jaw;
- Panoramic tomography;
- Cytological examination of material obtained by taking fingerprint smears from the surface of the ulcer or histological examination of tissue obtained during a biopsy.
For lip cancer with lymphatic metastasis, a biopsy of the lymph nodes is performed. To exclude hematogenous metastases, chest X-ray and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs are used. When the diagnosis of lip cancer is confirmed, an X-ray examination of the chest organs, general clinical and laboratory examination (electrocardiography, blood and urine tests) are performed.
A PET-CT study (positron emission computed tomography) is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Determining the stage of lip cancer;
- Assessment of response to treatment;
- Detection of disease relapse during the observation period.
PET-CT is an innovative method that combines the capabilities of computer technology and radiology. At the Yusupov Hospital, it is used not only to diagnose lip cancer, but also to monitor tumor development and evaluate the outcome of treatment. Thanks to PET-CT, radiologists have the opportunity to very accurately carry out radiation treatment, significantly reduce the irradiation area, and minimize the impact on healthy organs and tissues.
In many cases, the use of PET-CT excludes a number of additional studies in the future. This allows patients of the Yusupov Hospital to save time and money. The issue of the need to use this method is decided individually for a specific patient at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. A comprehensive examination of patients using the latest diagnostic equipment, the use of modern methods of performing laboratory tests using high-quality reagents allows oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital to obtain reliable results and provide adequate therapy for lip cancer at an early stage.
Diagnostics
External signs of lip cancer, as a rule, are not enough to accurately determine the diagnosis, so the oncologist prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental tests for the patient.
- A smear or scraping from the surface of the ulcer to perform a cytological analysis of cells and determine the type of cancer.
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological examination of the removed sample to confirm malignant changes.
- Ultrasound of the neck to identify affected lymph nodes.
- X-ray of the lower jaw, chest to identify metastases or ensure their absence.
- CT scan of the facial skeleton to detect metastases in them.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Treatment of lip cancer
How to treat lip cancer? When treating the disease, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account many different factors: the patient’s age, histological type of tumor, features of the spread of the tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic provide multidisciplinary treatment for lip cancer:
- Surgical interventions;
- Radiotherapy;
- Chemotherapy.
Regardless of the chosen technique, they affect the lesion or tumor, areas of regional metastasis. For grades I and II of lip cancer, radiation treatment is performed, which includes external radiotherapy and surgery.
Treatment in the initial stages
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip is a common complex tumor process. Its treatment consists of two stages: removal of the main focus and the fight against metastases that have spread to neighboring tissues and organs. Radiation treatment can suppress the development of a tumor focus. The radiologist selects the method of radiation therapy individually, depending on the size of the tumor, stage of the disease, and age of the patient.
Removal using the Krail method
In the initial stage of the tumor, surgeons perform a wedge-shaped excision of the entire thickness of the lip under local anesthesia. In order to remove a defect on the lip, plastic surgery is performed - skin flaps are transferred from the patient's cheek. Removal of the lesion is performed using the Krail technique. The operation is performed at the first and second stages of lip cancer, when the tumor has not spread to nearby tissues. Surgical excision of carcinoma makes sense in the absence of metastases.
The decision to remove a lymph node is made by an oncologist surgeon if the primary tumor process has already been cured or if the lymph node is removed along with the removal of the main lesion. In some cases, surgeons remove the primary cancerous tumor, the affected lymph nodes and the vessels that connect them. The scope of the operation is determined collectively by the clinic's oncologists.
Due to the fact that metastasis can occur in a cross way, the lymphatic apparatus of the suprahyoid region on the left and right is removed. If the oncologist sees that there are cancer metastases in certain lymph nodes, he decides to remove them, and those that are located along the lymph outflow.
Treatment tactics for lip cancer depend on the stage of the disease:
- Preventive surgery at stages I and II of lip cancer is carried out exclusively in cases where it is not possible to control the dynamics of the disease and there are unfavorable prognoses regarding the spread of cancer;
- At stage III, in the absence of metastases, treatment is carried out using a combined effect on the lesion and adjacent areas;
- In case of spread of cancer cells and the presence of single metastases in the lymph nodes, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform combined treatment of lip cancer with subsequent surgery, plastic surgery and surgical correction of the lips;
- In stage IVC, palliative chemoradiotherapy is performed.
Candidates and doctors of medical sciences use innovative methods of treating lip cancer. The presence of modern equipment and competent medical personnel who are attentive to all the wishes of patients allows us to achieve good results in the treatment of lip cancer for many years. Lip cancer, treated in the early stages, is cured in 97-100% of cases. At stage III, 67-80% of patients can be cured. In the fourth stage of cancer and repeated relapses, complete recovery occurs in 55% of cases.
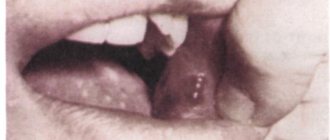
Malignant lump
A lump inside the lip can be a dangerous cancerous tumor. The disease usually affects older men. The tumor is large and growing rapidly.
Delivers severe pain. The patient experiences a sharp loss of strength and deterioration in health. The seal is covered with bleeding ulcers, can be bright red, plaques transform into gray or whitish growths.
After a biopsy and diagnosis is made, the lump is completely excised, and the patient is given a course of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. If the disease was detected in the initial stages, then complete recovery or long-term remission is possible.
Prevention
There are primary and secondary prevention of lip cancer. Oncologists recommend:
- Take precautions when exposed to the sun (wear a wide-brimmed hat);
- Stop smoking pipes and cigarettes;
- Maintain oral hygiene;
- Change working conditions;
- Do not drink strong alcoholic drinks.
For persons prone to dyskeratosis of the lips and cheilitis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct an annual preventive examination. Secondary prevention of lip cancer consists of regular dental treatment at the dentist, surgical intervention in the presence of dyskeratosis and cheilitis.
Treatment with traditional methods
Alternative medicine is often used as an adjuvant therapy.
The greatest therapeutic effect is achieved by:
- Sage. Used to prepare a decoction. To do this, 30 g of raw material is crushed, 0.5 liters of boiling water is poured in and boiled over low heat for 10 minutes. Afterwards, let it brew until it cools completely, filter and use for irrigating the oral cavity and as a lotion on the bump.
- Sea salt. Antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth are prepared on its basis. For 0.25 ml of warm water 1 tsp. salt.
- Propolis. Can be used in the preparation of a mouth rinse solution. Also based on it, ointments are made that improve nutrition and tissue regeneration, stopping the growth of pathogenic microflora. To do this, mix crushed propolis and butter in equal quantities.
- Calendula. On its basis, a tincture is made, which is subsequently used as a lotion or for irrigation of the oral cavity.
- Tea tree oil. Used to prepare compresses for the bump, which are kept overnight. To do this, mix 0.5 tsp. oils with 1 tsp May honey.
Lip cancer: treatment at Yusupov Hospital
Effective treatment of lip cancer in Moscow is carried out by doctors from the oncology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. Oncologists have many years of experience in treating malignant neoplasms of the lip. Surgeons are fluent in surgical techniques. The cost of surgery is lower than in other oncology clinics in Moscow, despite the high level of qualifications of doctors and modern equipment.
Radiotherapy is carried out using modern radiation installations from leading European and American manufacturers. In order to undergo a course of effective treatment for lip cancer at an affordable price, call the Yusupov Hospital. After the operation, surgeons at the Oncology Clinic perform lip plastic surgery using innovative surgical techniques.
How long does the result last?
The results last from several weeks to several years. On average from 4 to 18 months.
Duration depends on:
- individual characteristics,
- the chosen drug,
- compliance with the recommendations of a cosmetologist,
- number of procedures (the result of each subsequent procedure lasts longer).