When to take an antibiotic for teeth
Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections.
It is important to note that we are talking specifically about bacterial diseases, not viral or fungal ones. Antibiotics are powerless against viruses or fungi. Therefore, if we are talking about a viral or fungal disease, then in such cases it is appropriate to use antiviral and antifungal drugs, respectively. Antibiotics are also used in dental practice when a tooth hurts. At the same time, it is important to understand in which cases the pain is of infectious (bacterial) origin, and in which – non-infectious.
A common type of toothache is due to pulpitis. It occurs when caries has already eroded the top layer of enamel. The resulting hole reaches the pulp of the tooth, which is why the latter begins to hurt when exposed to various irritants - thermal, chemical or mechanical. In this case, antibiotics are useless. In order to relieve pain due to pulpitis, anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
In cases where a dead tooth hurts, there is a high probability that the cause is bacteria. As you know, dead teeth (with filled canals) cannot hurt on their own. If such pain occurs, it means that bacteria have grown in the cracks or cavities of the tooth. Microorganisms multiply, infect the gums and lead to the accumulation of pus. The latter exerts pressure, which leads to pain. The above pathology is nothing more than a gumboil. The antibiotic for flux is selected by the doctor after diagnosis. After all, it is necessary to establish the type of pathogenic bacteria so that the antibiotic for flux will work for sure.
Antibiotics in dental practice are also used in the following situations:
- After surgical operations . Tooth extraction and other surgical interventions are sometimes complicated by an infectious process. To avoid bacterial infection, surgical treatment is accompanied by antibiotic therapy.
- Periodontal diseases . Advanced variants of periodontal pathologies are sometimes complicated by purulent periostitis (flux). To avoid such developments, treatment of periodontal diseases is sometimes accompanied by the use of antibiotics.
The above cases are not the only ones in which antibacterial drugs are used. These medications are prescribed by the doctor based on the clinical picture, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient. In some cases, antibiotics are also prescribed for preventive purposes - when there is a possibility of a bacterial infection. These risks are assessed by a doctor.
Content:
- Forms of release of antibacterial agents used in dentistry
- Contraindications to treatment of flux with antibiotics
- What undesirable effects are possible during the course of medication?
- When you can't do without antimicrobials
- Which antibiotic to choose
- Danger of overdose
- Why you can’t self-medicate
Antibiotics are drugs that exhibit pronounced antimicrobial properties.
They block the growth and spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Dentists prescribe drugs from this pharmacological group for inflammatory gum diseases, purulent processes, and during the recovery period after surgical interventions in the oral cavity. Antibiotics also help with flux. A patient with an inflamed tooth root should not independently select an antibacterial composition. It is important to consider:
- degree of spread of the pathological process;
- associated disorders;
- sensitivity of the pathogen to active antimicrobial compounds;
- speed of regenerative processes.
If you take the wrong antibiotic for flux, the disease will continue to progress. This will disrupt the intestinal microflora. Therefore, never self-medicate.
Antibiotics for gumboil and toothache: types of drugs
Today in dental practice various antibiotics are used for gumboils and toothache. Let us remember that antibiotics are usually divided into classes. Let's look at the most popular types of antibiotics for purulent gum disease.
Nitroimidazoles
Nitroimidazoles are synthetic antibacterial drugs that exhibit high activity against anaerobic microorganisms (bacteria living in conditions without oxygen). The most popular drug in this group is metronidazole, which has been used since the 60s of the last century.
The mechanism of action of nitroimidazoles is associated with disruption of DNA replication and protein synthesis of microbial cells. Such violations are incompatible with the life of the bacterium.
Representatives of this group of antibiotics are active against most anaerobic bacteria (both gram-positive and gram-negative). Some types of protozoan microorganisms and the bacterium Helicobacter pylori are also sensitive to nitroimidazoles. The latter is the cause of the development of gastritis and gastric ulcers (as well as tumor lesions of the mucous organs of the gastrointestinal tract).
Fluoroquinolones
This is a group of drugs that exhibit antibacterial activity against a wide range of bacteria. It is noteworthy that fluoroquinolones are not considered antibiotics in the classical sense of the word. The fact is that antibiotics (even synthetic ones) always have analogues of natural origin. Fluoroquinolones have no natural analogue. The most popular representatives of fluoroquinolones include ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, moxifloxacin, lomefloxacin, levofloxacin and others.
The mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones is reduced to inhibition of a number of important microbial enzymes. This leads to disruption of DNA synthesis and death of the bacterial cell.
Lincosamides
Lincosamides are a group of antibacterial drugs that includes antibiotics such as lincomycin and clindamycin. The mechanism of action of lincosamides is reduced to suppressing protein synthesis in bacterial walls.
Antibacterial ointments for flux
Lincomycin ointment
Lincomycin ointment is very good for soft tissue infections
It helps very well with infections of soft tissues, including in the oral cavity. This determines the popularity of using the drug in dental practice. Use Lincomycin after rinsing the mouth. To do this, apply a small pea-sized amount of ointment to the affected area. The number of rubbings depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and can be 2-3 times. Treatment continues for an individually selected time.
Metrogil Denta
Gel Metrogyl Denta
Used strictly in dental practice. To relieve pain and signs of inflammatory and purulent inflammation, you will need to apply Metrogyl Denta to the gum tissue twice a day. Be sure to do this with strictly sterile sticks or gauze. The use of this antibacterial ointment can last up to 10 days.
Levomekol
Levomekol ointment has a good antibacterial composition
It has a good antibacterial composition, due to which the inflammatory process quickly disappears and tissues heal. Quickly helps with the formation of pus. Levomekol should be applied three times a day. The ointment is used in a special way:
- First you will need to rinse your mouth to free it from any remaining food;
- It is also advisable to brush your teeth, this will also reduce the number of harmful organisms on the mucous membrane and enamel under the affected gum;
- after this you need to take a strictly sterile bandage, onto which a small pea of Levomekol is applied;
- the compress is applied to the sore spot for three hours;
- if the flux has been opened, it is allowed to inject the medication directly into the affected cavity;
- The ointment can be used until the patient recovers completely.
Attention! When using Levomekol, it is important to monitor the cleanliness and hygiene of the oral cavity, since a large number of bacteria accumulate under the compress. If they are not removed, inflammation may worsen.
Oflomelid
Oflomelid ointment suppresses the activity of pathogenic microflora
Also refers to antibacterial ointments that can suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora. Oflomelid is used only once a day, regardless of the severity of purulent inflammation. The duration of use of the antibacterial agent depends on the rate of release of pus and the patient's response to the treatment.
Attention! Ointments can be used at the same time as oral antibiotics. But such a combination can only be selected by a dentist.
Antibiotics for tooth root inflammation
For toothache caused by inflammation of the tooth root, doctors also prescribe fluoroquinolones (as for gumboil). In addition, for inflammatory pathologies of the tooth root, antibiotics of the penicillin and tetracycline series are also used. Let's take a closer look at them.
Penicillins
These are the first antibiotics that were discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. The main mechanism of action of penicillins is bactericidal. These drugs disrupt the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a component of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to the death of the bacterium.
Currently, different types of penicillin antibiotics are used in dental practice. The most common are amoxicillin and ampicillin.
Tetracyclines
Another class of antibiotics that was discovered a long time ago - back in the 40s of the last century. Tetracyclines act against a wide range of bacteria, both gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. The mechanism of action of tetracyclines is inhibition of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Microorganisms stop synthesizing vital proteins, which is why they die.
How long do antibiotics work for toothache?
The therapeutic effect of antibiotics occurs within the first three days. If relief does not occur during this time, then a decision is often made to prescribe another drug.
The minimum course of antibiotics is 5 days. In this case, an individual course of therapy is established for each patient depending on a number of factors.
Sometimes antibiotics do not work and the patient does not feel a therapeutic effect from taking them. Let's consider typical cases when antibacterial drugs do not work:
- Insufficient dose of medication . When carrying out antibiotic therapy, strict adherence to the dosage is an important condition. If you take less than what your doctor prescribed, there will be no effect. In other words, there was not enough active substance to suppress pathogenic flora. Please note that the dosage of the antibiotic also depends on the age and weight of the patient. The heavier the patient, the more drug is required to achieve the required drug concentration in the blood.
- Insufficient duration of therapy . Strictly adhere to the regimen and duration of taking the drug. Some patients, feeling relief, decide to interrupt the course, which makes a mistake. Premature interruption of the course of antibiotic therapy is fraught with the development of antibiotic resistance - resistance of pathogenic and opportunistic flora to antibacterial drugs.
- Some concomitant diseases . Before prescribing medications, the doctor must have comprehensive information regarding the patient’s health. It is important to inform your doctor about all chronic and recent acute diseases that may affect the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy.
- Antibiotic intolerance . The patient may have individual intolerance to some types of antibiotics. Don't despair. If one antibiotic is not suitable, then there is always an alternative antibacterial drug. Sometimes a patient has problems taking an antibiotic orally (in the form of tablets, capsules or solutions). In such cases, a decision is made to inject antibiotics, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.
- Interaction with other active substances . The doctor must be informed about the medications the patient is taking. Some drugs cannot be taken together with antibiotics, as they neutralize the effect of the latter. In addition, drinking alcoholic beverages is prohibited during antibiotic therapy. Otherwise, the treatment will not bring the desired effect.
List of effective antibacterial agents for dental infections under the crown
After endoprosthetics and implant installation, some patients complain of discomfort. Pain and inflammation are a consequence of a violation of the technology for fixing artificial teeth and crowns: the dentist did not completely fill the cavity inside the problem unit or mechanical damage to the canal walls occurred. If the implantologist is poorly qualified, the pin may be installed incorrectly. Perhaps the smallest parts from dental instruments remain inside the canal.
There are several causes of the pathological process and pain syndrome:
- swollen gums or gumboil (acute inflammation);
- cyst - a cavity with fluid near the root of a problematic unit of the dentition;
- inflammation of the submandibular salivary glands;
- dental granuloma;
- a fistula on the gum is a hole through which purulent masses are released.
With the development of inflammation in periodontal tissues, an abscess forms at the root apex. Painful sensations are a consequence of the active accumulation of exudate and pressure on neighboring areas.
The main condition for eliminating discomfort is a timely visit to the dentist to remove the crown, clean the root canals, and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics can harm the body.
Before treating the canals, the doctor makes an injection into the gum, removes the prosthesis, and examines the affected area.
Effective antibiotics are prescribed to suppress the infection:
After the removal of a wisdom tooth, there is an increased risk of not only inflammation, but also bleeding from the socket.
If the patient takes the drug Warfarin to prevent thrombosis, then you need to warn the dentist: the doctor temporarily stops taking the medication for several days before and after the extraction of the “eight”, be sure to coordinate this action with the cardiologist.
It is important to know how to combine an antithrombotic agent with antimicrobial compounds.
What you need to know when taking antibiotics
Let's consider some facts about antibiotics that will help the patient avoid mistakes during antibiotic therapy:
- Taking antibiotics should not be combined with alcohol . Doctors prohibit drinking alcohol because alcohol increases the likelihood of side effects. It has been established that drinking alcohol during antibiotic therapy increases the likelihood of headaches, abdominal pain, tachycardia, and increased blood pressure. In addition, alcohol is an additional burden on the liver, which is already having a hard time coping with medications. Thus, drinking alcoholic beverages increases recovery time.
- Antibiotics, orange juice and milk . Few people know about this, but it is not advisable to take antibiotics with fruit juices (in particular, orange, grapefruit, apple or pineapple), as well as milk or dairy products. This is due to the fact that the above drinks impair the absorption of antibiotics. For this reason, the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment deteriorates. Therefore, after taking medications, refrain from drinking juices and milk for at least 3 hours.
- Antibiotics with meals . Some types of antibiotics should be taken on an empty stomach. For others there are no strict restrictions, and they are allowed to be taken with food. Read the medication instructions carefully and consult your doctor regarding your medication regimen.
- Medicines and antibiotics . The instructions for the antibiotic contain a list of drugs with which it is undesirable to combine it. Some combinations may weaken the effect of the antibiotic or increase the likelihood and intensity of side effects.
- Proper distribution of the antibiotic dose . The frequency of antibiotic intake per day is directly related to its effective concentration in the blood. For example, if the instructions say that the drug should be taken once a day, this means that after administration it remains effective for 24 hours. Thus, you need to take the antibiotic a second time the next day, at about the same time. If the instructions say that you need to take the drug 2 times a day, then the interval between doses should be 12 hours; if 3 times a day, the interval should be 8 hours.
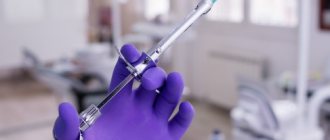
Injections for flux in adults
Tsiprolet
The medication must be administered intravenously by drip. It is first diluted in one of the special medical solutions, which may include sodium chloride, dextrose and Ringer's solution. Typically, a single dose of the drug for a purulent infection is 200 mg of the active substance; for a very severe condition of the mucous membrane, a dose of 400 mg of Tsiprolet can be used. The medication is administered twice a day. Treatment can be continued for 1-2 weeks.
- How to open the flux?
Biseptol 480
The drug Biseptol 480 in ampoules
The medication is a concentrate for preparing a solution for intravenous infusion. Biseptol 480 is diluted strictly before the procedure, having previously dissolved one ampoule in 125 ml of solution for infusion. Typically, no more than one ampoule of the drug is administered to the patient. The frequency of daily use should be determined separately for each patient. Therapy lasts one week.
Ciprofloxacin
The medication is a solution for intravenous use, administered by drip. Ciprofloxacin is administered at a dose of 200 mg or 400 mg, the dose depends strictly on the patient’s health condition. In this case, when prescribing the minimum dose, the drug must be instilled within 30 minutes, and at the maximum dose – at least one hour. With faster infusions, there is a high risk of side effects and anaphylactic shock. Therapy can continue for two weeks; for mild flux, Ciprofloxacin can be used for one week.
Attention! The drug in the form of an injection has the fastest effect on the site of the disease. But at the same time, it is worth understanding that it is better to use injections only in the middle and acute stages of the purulent process.
Video - Tooth flux
Adverse reactions from antibiotics
Antibiotics, like other medications, have side effects. Let's look at the most common problems that patients encounter from taking these drugs:
- Digestive problems . This is due to a disruption of the normal microflora. Antibiotics affect not only pathogenic and opportunistic flora, but also normal flora. A change in the balance of microflora leads to the development of gastrointestinal disorders. In particular, this is diarrhea, bloating, and sometimes constipation.
- Allergic reactions . After taking antibiotics, some patients experience allergic reactions. These include skin rash, runny nose, sneezing, watery eyes and swelling. In severe cases, severe allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock, are possible. It is noteworthy that disruptions in the functioning of the immune system (and associated allergic reactions) are often a consequence of intestinal disorders. Let us remember that a huge number of intestinal bacteria are directly involved in the functioning of the immune system.
- Headache . This is a relatively common side effect of taking antibiotics. Some patients who have never previously complained of headaches experience this symptom while taking antibiotics.
- Sensitivity to the sun . While taking antibiotics, it is not recommended to sunbathe or visit solariums. This is due to the fact that some antibacterial drugs act as photosensitizers - photosensitive components. This significantly increases the likelihood of getting a burn.
- Fungal infections . Since antibiotics also suppress the normal flora of the mucous membranes, this increases the likelihood of developing fungal infections. For example, oral candidiasis (thrush) is often caused by taking antibiotics.
- Teeth staining . Another problem caused by antibiotics is tooth pigmentation. Most often, this problem is encountered by patients taking tetracycline antibiotics. In some cases, such staining is irreversible, especially in childhood.
- Other side effects . The range of adverse reactions from antibiotics is not limited to the above effects. While taking these medications, the patient may experience joint pain, double vision, problems with the liver and kidneys (due to intoxication), and even depressed mood and depression.
Other ways to treat dental and oral infections
The advisability of antibiotic therapy is determined solely by the doctor after diagnosis. In some cases, it is impossible to do without antibiotics, since it is not possible to get rid of the pathogenic infection in other ways.
In some cases, for inflammatory pathologies of the teeth and oral cavity, antiseptic drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used. Folk remedies, for example, rinsing with herbal decoctions, have also proven themselves to be quite effective in the treatment and prevention of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. However, remember that traditional medicine cannot be used as the main type of treatment. They can be used as an additional measure to the main treatment.