Dental fissures are natural depressions on the surface of premolars and molars, i.e. chewing teeth. They are located between the dental cusps involved in chewing food and can be of a wide variety of shapes and depths. According to their structure they are:
- funnel-shaped - open, wide and, as a rule, well mineralized. Such fissures are quite easy to clean with a toothbrush, and in general deposits do not linger here;
- cone-shaped (gutter-shaped) - narrower grooves in which food debris can accumulate for a long time;
- teardrop-shaped (flask-shaped) - the most insidious form of fissures, in which a wider cavity is hidden under an externally narrow gap that collects dental deposits.
Fissures are provided by nature itself to reduce the mechanical load on the teeth - if they were completely flat, they would quickly crack and collapse from constant pressure on each other. In addition to distributing the chewing load, fissures help move food around the mouth during chewing.
What is dental fissure sealing?
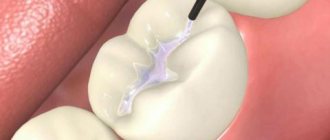
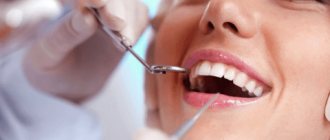
Fissure sealing is a safe dental procedure during which a specialist fills the natural crevices of the chewing surface of the teeth with a special liquid polymer (sealant). The fissure of the tooth is sealed with a sealant, which prevents the accumulation of food debris in the cavities of the recesses, which helps prevent the formation of plaque and reduce the risk of developing caries.
According to statistics, timely sealing of fissures can reduce the formation of caries by 90% or more. Therefore, sealing the tooth fissure with a sealant is recognized as an effective method of preventing dental disease and its complications - pulpitis, periodontal inflammation, tooth loss.
What is a fissure of a tooth?
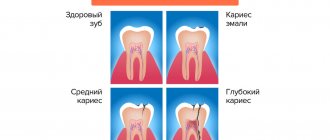
In Latin, fissure means “gap”. But this is a literal translation. In reality, fissures are more like grooves or grooves located among the cusps that make up the molar tooth. That is, they are of natural origin. However, these grooves change throughout life. At first they are shallow and have a smooth, flat bottom. Over time, the grooves between the sides of the tooth's cusps move downward, forming a deeper, inward-facing angle.
Thus, a fissure is a notch on the surface of a chewing tooth that cuts its enamel. This phenomenon can lead to caries. In such grooves, framed by the sharp edges of the tooth, food debris quickly accumulates, which can rot. Rotting causes the fissures to deepen.
Brushing your teeth will not help remove stains. Bacteria living in the oral cavity cope with plaque, but produce acid, which negatively affects the teeth and leads to the formation of caries.
Modern sealing methods
The fissure sealing procedure begins with a thorough diagnosis of the general condition of the oral cavity. During its implementation, specialists from the Dental Center on Shabolovka assess the condition of the tooth enamel, the presence or absence of a carious process, the depth and structure of the fissures themselves. After this, one of the methods of sealing the tooth grooves will be selected - non-invasive or invasive.
- A non-invasive sealing technique
is used for open fissures. It does not involve additional opening of natural grooves, and comes down to simply filling visible gaps with dental sealant. - The invasive technique
is used in the presence of deep or closed fissures, the condition of which cannot be monitored visually. To do this, they are first “opened” and then sealed with sealant.
Both sealing methods are safe for the patient's health. At the same time, the non-invasive technique is absolutely painless and does not require the use of anesthesia. While during invasive sealing, the patient may experience discomfort and unpleasant sensations caused by micropreparation of the surface tissues of the tooth. Therefore, the procedure can be performed using local anesthesia, which eliminates any pain.
Procedure for applying sealants
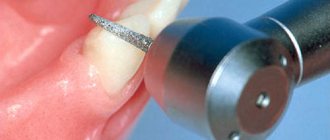
Sealants are usually applied to fully erupted teeth. A distinction is made between invasive and non-invasive fissure sealing. The procedure for applying sealants begins with professional teeth cleaning using cleaning pastes and brushes, followed by thorough drying of the enamel surface. Then, if necessary, the fissures are treated with an antiseptic or a special acid, under the influence of which the shell of the enamel prisms is destroyed, and the enamel acquires higher adhesive (cohesive) properties. After washing and drying again, the fissures are filled with liquid sealant. Then the material is cured using a special lamp, after which the dentist sands off the excess sealant. An invasive procedure is carried out if the carious process has already begun in the fissures. During its implementation, carious cavities are treated with bur, and damaged tissue is removed. Then sealing is carried out as in a non-invasive procedure.
How sealing occurs: stages
To achieve the maximum preventive effect, the sealing procedure is carried out in several mandatory stages, the sequence of which depends on the chosen technique.
The non-invasive sealing method involves the following steps.
- Thorough cleansing of the treated area from food debris and plaque.
- Drying the tooth surface and fissures.
- Isolation of the treated area from the penetration of saliva with special dental rollers.
- Applying a 32% solution of orthophosphoric acid to the fissure area, which makes the enamel slightly rough, which ensures good adhesion of its surface to the sealant.
- Phosphoric acid is kept on the tooth surface for 30–40 seconds, after which it is thoroughly washed off with distilled water, and the fissures are dried again.
- Carefully apply dental sealant (sealant), which immediately hardens under the influence of a UV lamp.
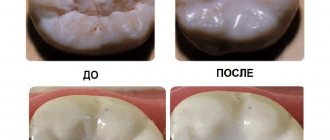
- Removal of excess sealant by grinding and subsequent polishing of the chewing surface of the tooth. As a result, the sealed fissures look as natural as possible and do not create any discomfort for the patient.
Invasive sealing is very similar to non-invasive sealing, with the only difference being that it involves a few additional steps.
- Cleansing from dental plaque.
- Opening of fissures through micropreparation.
- Drying and isolating the treated area.
- Treatment with 32% phosphoric acid solution.
- Filling open fissures with filling material.
- After the filling material has hardened, the cracks are sealed with sealant.
- Treatment of fissures with a UV lamp.
- Removal of excess material, grinding and polishing.
Regardless of the chosen sealing technique, after the procedure, remineralization and fluoridation of the teeth can be carried out. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve a high level of dental caries resistance and reliably protect them from disease.
What material is the sealant made of?
To seal fissures, special dental sealants are used, which are characterized by good fluidity, allowing them to penetrate even the smallest crevices of the tooth surface. Essentially, these are modern polymers based on methacrylate and polyurethane. Each of them has its own properties, wear resistance, and can harden naturally or under the influence of a UV lamp. Often their composition is additionally enriched with fluoride ions, which strengthens tooth enamel, thereby inhibiting the development of the carious process.
Sealants for sealing fissures differ not only in their composition, but also in their transparency.
- Transparent sealants
allow you to visually monitor the condition of fissures. But due to their colorlessness, they are practically invisible on the surface of the tooth, which makes it difficult to assess the condition of the sealant itself. - Opaque sealants
are sealants that contain titanium dioxide. They are painted in a pleasant milky white color, are hardly noticeable on the chewing surface of the teeth and allow you to monitor the general condition of the sealant during use.
Any sealant composition is well tolerated by the human body, does not cause allergic reactions and does not harm tooth enamel.
Fissure sealing in children: pros and cons
Sealing the tooth fissure with sealant can be done at any age. This procedure is especially indicated for children whose tooth enamel is just beginning to form and the accumulation of plaque in the fissures often provokes the onset of the carious process.
The problem is that a child's baby teeth have a low level of mineralization, which makes them especially vulnerable to tooth decay. Therefore, a preventive examination and the first fissure sealing in children are recommended to be carried out 6 months after the eruption of baby teeth. The effect achieved during the procedure will last for 1 – 2 years, during which it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination by a dentist every 6 months.
Among the advantages of early fissure sealing, the following points can be highlighted.
- The presence of sealant does not disrupt the natural development of the tooth.
- Sealants do not reduce the level of natural mineralization of enamel.
- Sealing the gaps does not have any effect on the formation of a correct bite in the child.
In both children and adults, the presence of sealants in fissures does not cause a feeling of discomfort or stress on the tooth.
Note! To avoid the development of complications, the procedure for sealing cracks should be carried out only by an experienced specialist – a dentist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Indications and contraindications
Since fissures are natural crevices on the chewing surface of every person’s teeth, we can say with complete confidence that their sealing is recommended for absolutely everyone. It is especially needed by small children, whose tooth enamel is just forming, and adults, who have deep and narrow fissures that are difficult to clean during daily hygienic brushing.
But we should not forget that natural cracks of a wide structure that communicate with each other can self-clean naturally. Therefore, if there is no threat of caries development, then they do not need to be sealed. In this case, only a dentist can determine the feasibility of the procedure. In addition, sealing may be refused if the following contraindications are present:
- The presence of a carious process that requires treatment.
- If visible fissures do not develop caries within 4 years.
- If a tooth has not fully erupted, its surface cannot be sealed.
- Unsatisfactory general condition of teeth caused by improper or insufficient oral hygiene.
Note! Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a dentist, who will help identify contraindications to sealing.
When should you resort to sealing?
The process of filling the grooves and grooves formed on the chewing teeth with a specialized product is called fissure sealing. The substance used during the procedure prevents the smallest microorganisms and pieces of food from entering the tooth grooves.
Essentially, the tooth is sealed and is inaccessible to the influence of harmful factors. The means by which sealing is carried out, as a rule, includes fluoride ions, and this makes the enamel resistant to the threat of caries.
The described procedure is performed for both adults and children. Both baby and molar teeth can be “sealed” with a special substance, since caries affects people of any age. However, in children the process of fissure mineralization is lower, so the possibility of enamel defects increases.
There are several indications for this procedure:
- the presence of teeth whose fissures have a complex structure and great depth, which leads to the accumulation of food debris in the grooves;
- the appearance of signs of caries;
- encountered when brushing teeth ;
- identification of pigmented fissures, that is, areas of enamel that are most susceptible to caries;
- the presence of teeth that are not yet four years old.
Indications for sealing are the appearance of weakly mineralized areas on the teeth, as well as the identification of areas susceptible to caries. A professional doctor, after checking the structure of the grooves, will immediately be able to determine the need for this procedure.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
On the other hand, sealing will be contraindicated if the oral cavity is not well maintained. First, you will need to remove tartar and plaque and teach the patient how to properly care for their teeth. Also, the procedure cannot be carried out if the tooth openings are very wide and connected to each other. In this case, the sealing material may not be applied correctly.
Prevention
According to statistics, 80% of sealants retain their integrity and tightness for 2 to 3 years after the procedure. Over the next 5–7 years, about 70% of sealants successfully withstand. After 10 years, only 30% of sealants remain intact and functional. Thus, modern sealants can serve the patient for a long time. The main thing is to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist in a timely manner and monitor their condition. To do this, you need to visit a specialist at least 1–2 times a year and regularly inspect the sealed fissures yourself. If you notice that part of the sealant has fallen out, you should immediately contact your doctor. Otherwise, it is enough to adhere to the general recommendations of a specialist and pay due attention to daily oral hygiene.
Author: Elena Kopylova Dentist-therapist, endodontist, pediatric dentist. Work experience more than 7 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Prevention of fissure caries at home
It is important to observe prevention not only at dental appointments, but also at home. Oral hygiene is a complex procedure. It includes:
- Individual cleaning with a medium-hard brush. The necessary components of toothpaste are active calcium (ROCS, Colgate, etc.) and fluoride (President Classis, Splat, etc.);
- Using dental floss to clean the interdental spaces;
- For more thorough hygiene, it is recommended to use an irrigator;
- After traditional brushing, do not forget to rinse your mouth with sodium fluoride solutions. The optimal fluorine concentration in the solution is 250 ppm.
The prognosis for fissure caries is favorable. Thanks to planned treatment, oral sanitation and good hygiene, relapse can be prevented and complications can be avoided. To improve the condition of your teeth, you need to take care of them, as well as adhere to a balanced diet and exclude carbohydrates from your diet. Remember: healthy teeth are the guarantee of a snow-white smile.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01