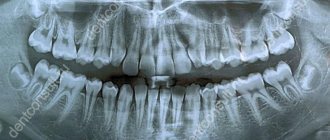
An x-ray is the dentist’s main tool in making the correct diagnosis. However, a conventional orthopantomogram or targeted photograph has limited diagnostic potential and does not provide complete data on the condition of the teeth and maxillofacial area. But technologies are constantly being modernized and today, more informative technology has come to the aid of conventional radiography - dental computed tomography (CT).
What does a 3D dental x-ray show?
3D dental tomography is a highly accurate diagnostic method that makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the dental system in different projections. Volumetric images obtained with CT allow the specialist to enlarge, rotate and examine the area of interest from all sides and at different depths:
- The entire maxillofacial apparatus.
- A dentition or an individual tooth.
- Paranasal sinuses.
- Bone and periodontal tissues.
Dental CT allows you to detect inflammation, assess the homogeneity of the filling material and check the quality of installation of a filling, crown or implant, see the number of dental roots and their fragments, identify neoplasms, assess the degree of curvature of teeth, determine the exact parameters of bone tissue (height, width, density, etc.). d.). The information obtained allows the doctor to optimize treatment measures and predict the result.
Why are dental x-rays prescribed?
A 3D photograph of teeth is performed if the following indications exist:
- Injuries of the maxillofacial area.
- Preparation for endodontic treatment (structure of root canals, pathological processes in the periodontium, degree of pulp damage, etc.).
- Diagnosis of neoplasms (cysts, abscesses, granulomas, tumors).
- Anomalies of development and deformation of the maxillofacial apparatus.
- Quality control of filling and implant installation.
- Planning of orthodontic treatment (identification of impacted and dystopic teeth, analysis of the condition of the tissues around each tooth, etc.).
- Detection of hidden periodontal cavities and pockets.
- Implantation planning (assessment of jaw bone parameters, indications for sinus lift or osteoplasty, modeling the result of implantation).
- Endogenous pathologies of the maxillary sinuses.
Three-dimensional x-ray examination is the gold standard when planning any complex dental procedure or surgery. CT allows you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis, competently plan treatment or dental prosthetics, and monitor the results.
What equipment is used
To carry out 3D diagnostics, a three-dimensional computed tomograph SOREDEX Scanora 3D with advanced functionality is used. This is the latest generation equipment, which allows you to obtain three-dimensional images of the anatomical structures of the maxillofacial region in a few seconds, with the least radiation exposure for the patient.
The program analyzes the obtained multiplanar sections and builds them into a 3D model, thanks to which the specialist is able to accurately assess the condition of the dental system, detect all pathological processes occurring in this area and competently plan a treatment regimen.
A virtual 3-dimensional model of the scanned area can be recorded on any digital media (CD, flash drive), which allows the attending physician, if necessary, to view diagnostic data or involve related specialists in the analysis of the received information.
Orthopantomogram during implantation
As part of implant treatment, a panoramic image is taken more than once. First, an X-ray examination is carried out at the preparatory stage - the doctor carefully examines the resulting image, assesses the condition of the bone tissue, selects places for implants, and makes a verdict on the need for bone grafting. If we are talking about one-stage immediate loading protocols, then patients are usually sent for a computed tomography scan of the jaw - a 3D image provides more detailed information about the clinical picture.
3D diagnostics makes it possible to study a more detailed three-dimensional image
You will have to undergo a repeat examination after implantation. In this case, OPTG will give the doctor the opportunity to assess the quality of the operation performed, monitor the process of engraftment of artificial roots, and recognize possible complications in the later stages of their development. Several photographs may be required during the osseointegration period of the implants.
Possible harm
Cone beam dental computed tomography is the safest and fastest diagnostic method. Thanks to the use of a conical X-ray beam, the radiation dose received during the study is 10 times less than when using spiral CT. And the pulsating mode of the X-ray beam further reduces the radiation dose. The three-dimensional computed tomograph SOREDEX Scanora 3D is one of the safest devices in terms of X-ray radiation dose - only 0.035 m3v.
However, despite the safety of the study, CT also has contraindications. If we just talk about dental tomography, it is not performed during pregnancy (in the 1st trimester). 3D dental x-rays with contrast are prohibited for pregnant and lactating women, patients with endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies), renal failure and intolerance to iodine-containing drugs.
Current promotions!
Implantation in installments regularly
The promotion operates regularly and applies to patients who require implantation.
X-ray is far from the only type of diagnosis, but it is very informative. It is based on the ability of ionizing gamma radiation to penetrate tissue. As a result, a picture of the organs being examined is displayed on the film or monitor of the device.
There are several types of x-ray examinations. They differ in scope, equipment used, methods of providing visual information and other parameters.
Types of X-ray examinations
- radiography
(short exposure time to an image (photo) on film or electronic media); - fluoroscopy
(information is displayed directly on the monitor during the examination and is analyzed by a doctor); - tomography
(photo series of layer-by-layer X-ray images), including computed tomography (CT).
Depending on the area of examination:
- mammography
- x-ray of the mammary glands; - angiography
- study of blood vessels; - cholecystography
- a picture of the gallbladder; - fluorography
- lungs.
Photos of the dental offices of the clinic Our Dentist in Krasnogorsk
(images are clickable)
X-ray in dentistry
X-rays are widely used in dentistry, and this is not just the desire of the doctor, but also a requirement of the treatment protocol. Dental photographs are taken for diagnostic purposes, in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis, in case of dental trauma, at various stages of implantation and bite correction, and in other clinical situations.
Depending on the purpose of the research, dentists use x-rays in the form.
- Sight shots
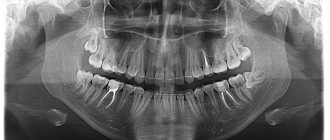
. They are printed on film or displayed electronically. The sighting image shows 1-2 teeth. - Orthopantomograms
. The picture shows all the teeth of two jaws in a direct projection. - CT
(computed tomography). The device makes many sections, and you can set any area to be examined: from one tooth to both jaws. - TRG
(teleradiograms). The device takes pictures in special positions and angles (used in orthodontics and maxillofacial surgery). - Joint examination
: pictures and computed tomography, needed for gnathologists and maxillofacial surgeons.
The dental clinic “Our Dentist” has two modern devices for x-ray examinations:
- high-frequency digital visiograph for targeted images of teeth;
- orthopantomograph (for so-called “panoramic” photographs).
Are dental x-rays performed for pregnant women?
When asked whether it is possible to take a dental photograph at any stage of pregnancy, modern medicine answers in the negative. Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication to any x-ray examination, unless there is a threat to the life of the mother.
Any X-ray examination, including CT, is accompanied by radiation exposure to the patient’s body. Its value can vary within very wide limits, but it cannot be absolutely zero. A special protective apron significantly reduces the negative impact of ionizing gamma radiation, but cannot completely eliminate it.
Even a small radiation exposure can negatively affect the formation and development of the fetus. Therefore, targeted and panoramic photographs of teeth during pregnancy are not taken in normal situations (during planned and emergency treatment).
However, as part of emergency care, when there is a real threat to the life of a pregnant woman, an x-ray can be done in a hospital setting. For example, if a woman is involved in an accident, she will be taken to a hospital and if there are suspicions, for example, of rib fractures and damage to internal organs (lungs or heart), an X-ray or computed tomography (depending on the equipment of the clinic) will be taken. In this case, all the doctors’ actions are aimed at saving the victim, since the risks to her life many times exceed the potential harm to the fetus.
There are also emergency situations in dentistry, when a photograph of a tooth during pregnancy must be taken to confirm a preliminary diagnosis and provide emergency medical care.
For example, if a pregnant woman is suspected of having phlegmon, a dentist at an outpatient medical institution calls an ambulance and sends the pregnant woman to a hospital - there is a greater choice of equipment and diagnostic capabilities. Hospital doctors decide on a case-by-case basis whether to take a dental photograph despite pregnancy, or whether to use another diagnostic method.
In our clinic, we do not take any, including panoramic, dental photographs during pregnancy, as this is absolutely contraindicated.
Dental X-ray during pregnancy: how to do without it?
When treating some dental diseases, dental x-rays are required, but during pregnancy, as we have already found out, they cannot be done. For example, when treating pulpitis, targeted images are taken three times: for diagnostic purposes, during treatment and after permanent filling of the canals. What to do in this situation?
It is impossible to delay the treatment of pulpitis until childbirth: this is fraught with the development of severe inflammation, pain and complications in the form of periodontitis and even phlegmon, which, in turn, is a life-threatening disease. In such cases, doctors use other diagnostic methods:
- electroodontometry
(to check the vitality and condition of the pulp); - apex locator
(to “see” the top of the tooth and measure the length of the canals); - clinical methods
(examination, percussion, assessment of response to stimuli, and so on).
After making a diagnosis, the doctor begins treatment. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, two scenarios are possible.
In difficult cases, the doctor removes the pulp (neurovascular bundle) and temporarily fills the canals with medicinal paste with calcium. The tooth cavity is closed with a temporary filling and observed. Depending on the clinical picture and stage of pregnancy, for example, when delivery is still far away, the doctor may change the medicine several times, each time applying a temporary filling.
After giving birth, the patient comes for an appointment, an X-ray is taken to assess the situation, and a decision is made about permanent filling of the canals with subsequent installation of a filling.
Second option. With “fresh” uncomplicated pulpitis, treatment can be carried out completely. The doctor makes a diagnosis, confirming it using electroodontometry, administers injection anesthesia, removes the neurovascular bundle, passes, expands, processes and seals all canals, using an apex locator for control. A pregnant woman is given a temporary filling, and after a few days, if there are no complaints, it is replaced with a permanent one. After giving birth, the patient comes for an examination and a control x-ray.
A pregnant woman had her teeth x-rayed: what will happen?
If you had a dental x-ray done during pregnancy, you shouldn’t be scared either. One dental photograph during pregnancy is unlikely to significantly harm the baby.
As a rule, dental X-rays are done for pregnant women at very short notice, when the woman herself does not yet know about her own interesting situation and, naturally, cannot inform the doctor about it. In most cases, at these early stages, x-rays do not have a negative effect on the embryo. In the worst case, with serious defects, the pregnancy simply will not develop.
If a dental X-ray during pregnancy was taken for emergency reasons at a later date, you need to contact your gynecologist. He will prescribe the necessary studies, and further management of the pregnancy will depend on the diagnostic results.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of a situation where urgent or emergency dental treatment is needed, it is necessary.
- Undergo a full examination and sanitation of the oral cavity at the stage of pregnancy planning.
- Visit your dentist regularly (preferably once every 3 months) for medical examinations.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene before and during pregnancy.
- Treat caries and gingivitis in a timely manner to prevent the development of more serious diseases (pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, periostitis, phlegmon).
- Follow the diet, daily routine and doctor’s recommendations.
- Carry out hygiene procedures thoroughly and regularly several times a day.
Dear ladies! We are waiting for you for a free consultation for pregnant women at the “Our Dentist” clinic. Our doctors will be happy to conduct a preventive examination, professional hygiene, removal of tartar, and, if necessary, treatment.
Make an appointment by phone or through the website, and our dentist will be yours!
Your calls are always welcome! 8 915-367-04-47 - call, make an appointment, come for a free initial consultation, and Our Dentist will become yours!
Dear patients! All prices on the site are valid only at the time of publication. The specialist will inform you about the exact cost and scope of necessary procedures after consultation.
Author of the material: Chief Dentistry Doctor “Our Dentist” Oleg Nikolevich Sharmay.
Online consultation with a doctor
If you are concerned about the condition of your teeth. Painful sensations arise, gums bleed for a long time, and seals have appeared on the jaw. You are concerned about previously installed dental implants. And there was a need to take a 3D photo of the teeth. Then, after receiving three-dimensional visualization, it is better to go for an examination or consultation with a dentist to interpret the images and compare the results with your current complaints. It is impossible to independently understand the nuances of a 3D image, much less make a diagnosis. The specialist will explain the situation and give recommendations before the in-person appointment.
Advantages of the method
- The ability to rotate, enlarge, and examine images in any projection and section, which is impossible with conventional 2-dimensional scanning.
- The examination lasts only a few seconds (8-20 seconds).
- Complete diagnostic information.
- Maximum security.
- Digital information format.
- Detection of any pathological processes at an early stage.
- No prior preparation required.
- 3D reconstruction without distortion or artifacts.
- A wide range of purposes - from endodontic dental treatment and implantation to maxillofacial operations.
Features of treatment in early and late stages
Obstetricians and gynecologists say that dental treatment during pregnancy is safest in the 2nd trimester. And the maximum danger from dental interventions is in the first trimester. And at the same time, doctors are convinced that the risk of harm to the fetus from progressive dental diseases is much higher than the risks from treatment. Therefore, in case of deep caries or pulpitis, you must contact the dentist immediately, regardless of the stage of pregnancy. If symptoms of early caries appear, you can delay the visit to the doctor until 20 weeks. But at 36-38 weeks (if there is no severe pain and purulent inflammation), it is better to refuse dental interventions. Treatment during this period can provoke premature birth.
Important: if the pregnancy is short and the pregnancy is not yet visually noticeable, be sure to inform the dentist before starting treatment that you are expecting a baby. Otherwise, he will not be aware of the need to take extra precautions during pain relief and X-ray diagnostics.
Is there an alternative to CT
There are many other diagnostic imaging methods (x-ray, orthopantomogram, ultrasound, etc.), but only CT provides the possibility of highly accurate, separate images of all types of tissue at different angles and to different depths. Although a panoramic dental photograph remains an equally important diagnostic tool for a dentist today, it can only provide a general overview. In turn, a 3D tomogram allows you to obtain not a single flat image of the jaw, but a whole series of sequential multiplanar images in different projections and without the distortions inherent in a panoramic image.
Example:
due to the different density of bone structures exposed to X-ray radiation, it is impossible to see less dense bone in a 2-dimensional image; accurate information is provided by a 3- D image of the teeth.
How does the procedure and decoding work?
To take a 3D photograph of teeth, a standing or sitting patient needs to bite a special plate and fix his position in the device using a fixing stand. During the entire scanning time, you must remain absolutely still.
The tomograph sensor makes a series of revolutions around the patient’s head for 8-20 seconds, producing about 200 images in different projections. Processing digital data takes 5-15 minutes, after which the information is written to a disk or flash drive. No preparation is required, you just need to remove all metal jewelry from your neck, ears, and hair before the procedure.
Preparing for dental computed tomography
Before the CT procedure of the upper or lower jaw, no special preparatory procedures are required. However, before the procedure, the patient may be asked to remove any jewelry from the body, as well as metal prostheses and sound-amplifying devices that may interfere with the normal examination.
It is also advisable to inform the radiologist about the presence of non-removable metal-ceramic structures in the oral cavity. This will allow the specialist to pre-set the equipment in order to minimize the likelihood of image distortion. Women should also inform the diagnostician about the presence of pregnancy.
A prerequisite is to fix a special apron made of X-ray protective material on the patient’s chest. In this case, the participation in the procedure of a highly qualified specialist who has a certificate in the specialty “Radiology in Dentistry” is of particular importance.
Unfortunately, not all modern clinics meet this condition. If a nurse is allowed to perform a CT scan of the jaw in Moscow without the necessary professional training, this may result in low-quality images being obtained and increased radiation exposure to the patient. That is why, before conducting a diagnosis, you should definitely make sure of the professionalism of the specialist.