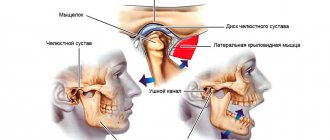
Does your jaw click when chewing or when at rest? This is an alarming symptom that indicates certain pathologies of the dental system. It is imperative to consult a dentist, since wasting too much time can lead to inflammation of the joints, loss of teeth and other negative consequences that will have to be treated surgically.
Noise
Most people believe that tinnitus and pain are caused by a cold or flu.
In reality, this is not the main cause of ear pain and many other factors can give rise to the inflammatory process.
Ringing in an adult
From time to time, ringing in the ears can bother absolutely healthy people and have no reason in the form of pathologies or inflammation. This often happens after overwork, lack of sleep or psycho-emotional stress.
But if ringing in the ears bothers you quite often, for no apparent reason, there is reason to believe that there is a serious problem in the body.
Tinnitus is mainly associated with the following diseases:
- Hypertonic disease . The ringing can occur on one or both sides. It occurs as a result of spasm of blood vessels in the brain, as a result of which blood flow to the brain is reduced due to narrowed arteries.
- Osteochondrosis . This disease, like other injuries to the cervical spine, leads to impaired blood flow, which in turn causes ringing in the ears. By its nature, it can be similar to an indistinct noise or resemble the clinking of metal.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Due to cholesterol plaques that obstruct the movement of blood through the arteries of the brain, a prolonged ringing in the ears and head occurs. It may also be accompanied by dizziness and nausea.
- A brain tumor. The tumor can put pressure on the brain stem or the cochlear part of the auditory nerve. At first, a noise appears, similar to ringing or squeaking, but in the future, this can develop into complications that threaten hearing loss.
- Traumatic brain injuries . During serious head injuries, swelling may occur, which can cause ringing in the ears. In such cases, patients compare the ringing that appears with a whistle or squeak.
Aching when chewing
The main cause of aching pain in the ears is inflammation of any part of the ear area. At different stages and forms of inflammation, pain can have different intensity.
In addition, the causes of aching pain are:
- Perforation of the eardrum.
- Eustachite.
- General or local intoxication of the body. General intoxication implies poisoning of the body as a whole, and local intoxication occurs due to the entry of various chemical reagents into the ear area.
- Water ingress.
- Diseases of the nervous or cardiovascular system.
- Injuries.
Dull, goes to your head
The presence of dull pain often indicates the presence of pathologies that arise as a result of infection in the body or in the ear canal.
In addition to this, there are a number of other reasons that result in dull pain in the ear:
- Barotrauma . This is a disorder that can result from differential pressure on the middle and inner ear. It can also be caused by a runny nose.
- Sulfur plug. When the ear canal is blocked by wax, complications may arise over time, leading to dull pain.
- Blockage of the eustachian tube. The first signs of this problem are very similar to the formation of a wax plug. Subsequently, the patient develops a stuffy ear and, over time, develops a feeling of dull pain.
- Inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
- Injuries.
- Diseases in the oral cavity . Diseases such as carious lesions of chewing molars cause dull pain in the ear.
Why does it shoot when swallowing?
Shooting in the ears can be due to the following reasons:
- Noise in the ears and head, causes and treatment. Folk remedies and medications for ear noise
- Progressive eczema.
- Cellulite. When soft tissues are damaged, swelling and compacted formations occur, which cause shooting pain in the ears.
- Otitis.
- Accumulation of mucus in the middle ear cavity.
- Labyrinthitis. May occur as a complication due to influenza, mumps, measles and chickenpox.
- Neuritis of the facial nerve.
- Caries. Due to the fact that the teeth are located quite close to the hearing organs, many dental diseases affect the ears.
From harsh sounds
Pain and discomfort in the ears from sharp sounds are a consequence of increased hearing sensitivity. A condition in which the patient experiences pain from sounds is called hyperacusis.
This pathology occurs against the background of hearing impairment. However, these are not all the reasons why ear pain occurs during sharp sounds:
- Damage to the facial nerve.
- Inflammation of the middle and inner ear.
- Pathological processes in the brain.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
Pulsating
The main causes of throbbing pain in the ears are divided into four groups:
- Hearing diseases:
- Otitis.
- The appearance of sulfur plugs.
- Cardiovascular disease:
- Hypotension and hypertension.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Defects in the structure of blood vessels.
- Hearing injuries and traumatic brain injuries.
- Tumors of the brain, hearing organs or in the neck area.
Stabbing
Stitching pain can occur due to reasons such as:
- Perforation of the membrane.
- Inflammation of the outer ear
- Injury.
- Entry of a foreign body into the ear canal.
- Boil.
- Inflammation of the middle ear.
- Barotrauma.
- Accumulation of exudate.
- Obstruction in the eustachian tube.
- Oncological diseases.
Diagnostics
If the crunch is prolonged and causes pain, you must immediately make an appointment with a gnathologist. The doctor diagnoses problems to create a complete picture of the disease:
- Palpation of joints;
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- Electromyography and x-ray or tomography of the jaw;
- Bite examination;
- Blood test (to determine the presence of inflammatory processes);
- Compiling an anamnesis based on the patient's testimony.
Causes of crunching
Patients often complain to doctors: “When I swallow, my ears crunch.” Also, with this phenomenon, other symptoms may be observed, such as pain, tinnitus. Before prescribing treatment, a diagnosis is required.
Why does my ear crunch when swallowing? This phenomenon can be objective and subjective. Phonendoscopic diagnostics allows you to determine the type of sound. Subjective noise is felt only by the patient, and objective noise can be heard by the attending physician; these noises are rare in the otolaryngological field.
- Why there is ringing in the ears: 5 most common reasons
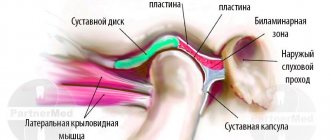
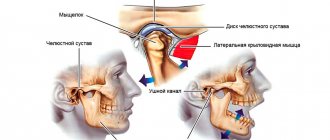
Why does my jaw click when I open my mouth?
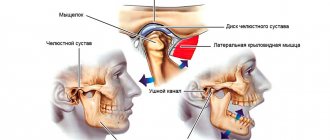
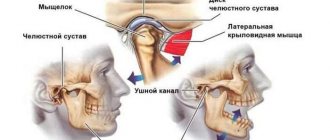
Most often, such clicking is caused by jaw arthritis. This pathology affects the cartilage layer of the joint or meniscus. Accordingly, the meniscus becomes thinner, the fibers become looser, and the cartilage can partially fuse with the articular head. As a rule, the clicks in this case are multiple, resembling a crunch.
The sound is formed as a result of the movement of the articular heads, which overcome the boundary in the form of folds of the cartilage disc. This crunch can be muffled, and therefore only audible to the person himself. Very often the jaw crunches when the mouth is opened sharply, when subluxation of the joint occurs. With some difficulties, but the jaw can be returned to its place. But sometimes this is impossible on your own - the patient is diagnosed with a dislocation, and here the help of a surgeon will be required.
Treatment
If there is a crunch in the ear when chewing, treatment can be performed using different methods. Only a doctor can choose the right one. The method of therapy depends on the cause that provokes the crunch:
- In case of dysfunction of the auditory tube, drug treatment is necessary, which involves taking anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs, vasoconstrictor medications in the form of ear drops. The normal patency of the ear canal can be restored using Politzer blowing. If irreversible structural changes occur, surgical intervention is likely.
- For aerootitis, experts advise using ear drops with a decongestant effect. If there is a purulent process, antibacterial agents are used.
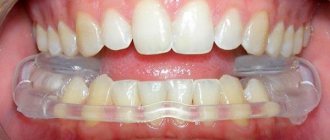
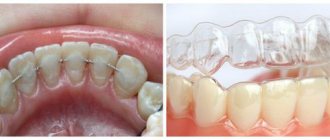
- If you have an incorrect bite, you need the help of a dentist. It should be noted that treatment can be performed at any age, but restoration of anatomical and aesthetic function allows you to get excellent results with early access to a specialist. Braces allow you to restore your bite.
- For diseases of the nervous system, treatment should be carried out using sedatives and nootropics. Such medications are taken only as prescribed by a specialist, when the cause leading to the change has been identified.
- If a foreign body is present, it must be removed. Then the unpleasant symptoms disappear immediately. The removal is performed in the otolaryngologist's office. If the foreign body is sulfur plug, rinsing is performed.
Symptoms
The occasional occurrence of clicking sounds is not usually a reason to visit a doctor. If the crackling is constantly present or is accompanied by noticeable discomfort, you should look for a provoking factor.
If dizziness, noticeable pain, loss of orientation in space, or clicking occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor and determine the causes of this condition.
Before visiting a specialist, you need to assess the nature of the clicks and identify the circumstances that provoke the occurrence of this symptom. Thanks to this, it will be possible to make a correct diagnosis and select treatment much faster.
Soreness
Often, compression in one or two joints leads to changes in the structure of hard tissues (arthritis, arthrosis). This condition is always accompanied by pain.
The disease most often occurs as a result of infection, which over time can cause purulent melting of the bone.
Arthritis can also develop due to traumatic injury to the lower jaw. If untreated, the disease leads to joint immobility (ankylosis) after fusion of bone, cartilage and fibrous structures. The condition can only be treated surgically.
In the catarrhal and purulent stage, the primary task of the surgeon is to ensure the outflow of exudate. In this case, a sling-shaped bandage or an orthodontic structure in the form of a plate is often used.
Further treatment is based on medication, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
In what cases is expansion of the dentition indicated and what devices are used.
In this publication we will talk about the shortening of the dentition and the correction methods used.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/formyi/slivshiesya.html all the most important things about the treatment of fused teeth.
Which doctor should I contact?
When determining complaints about the occurrence of creaking in the ears, which is not accompanied by painful sensations, you should contact an otolaryngologist. If the specialist does not detect any abnormalities in the functioning of the ear parts, he will give the patient a referral to a phoniator. A specialist will determine through a series of tests whether the patient’s hearing has deteriorated.
In a number of special cases, when specialized specialists studying diseases of the hearing organs are unable to determine the cause of the creaking, an examination is indicated.
The patient can receive a referral to specialists:
- neurologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- traumatologist of maxillofacial surgery;
- dentist.
It is worth remembering that the manifestation of constant crackling in the ears is dangerous due to atrophy of the auditory nerve. Such a change leads to the development of hearing loss.
Preventive measures
The main preventive measure against the development of TMJ diseases is careful attention to the condition of the body as a whole.
Regarding the prevention of clicking in the jaw, experts recommend the following:
- treat dental diseases at the initial stages of their development;
- removed or damaged teeth should be immediately replaced with artificial analogues;
- After receiving an injury, immediately consult a doctor;
- treat ear, nose and throat diseases in a timely manner;
- Do not eat too hard and hard foods.
These simple tips will help you maintain healthy jaw joints for life.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Otitis externa
Most often, inflammation of the outer ear is bacterial in nature.
The causes of infection may be:
- trauma to the external auditory canal, for example, from a sharp or blunt object, or from a hearing aid;
- skin defects due to eczema, psoriasis, diabetes and other diseases;
- too thorough removal of earwax, which creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of microbes;
- frequent entry of water into the outer ear (“swimmer’s disease”).
Symptoms of external otitis:
- acute ear pain, aggravated by pressing on the tragus or pulling the earlobe;
- possible itching and a feeling of “stuffiness” in the ear;
- discharge of a purulent or bloody nature, sometimes having an unpleasant odor;
- examination reveals swelling and hyperemia of the external auditory canal;
- possible hearing loss;
- enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ear on the affected side.
The course of the disease may be complicated by a perforation of the eardrum, which cannot be determined without a visit to an ENT specialist.
External otitis of fungal origin is a common phenomenon, usually occurring in patients with low immune status or due to long-term use of antibacterial drops. It is characterized by severe itching, the formation of crusts, profuse thick discharge and the absence of a therapeutic effect from the use of antibiotics.
Separately, it is worth noting the localization of a boil on the skin of the external auditory canal or inflammation of the atheroma. The clinical picture is similar to otitis externa, but upon examination there is a more localized focus of inflammation with an opening from which pus and blood can be discharged.
How effective is therapeutic exercise?
After eliminating the causes of the disease, the doctor prescribes restorative exercises to the patient, or rather a set of exercises that will help improve the functionality of the masticatory muscles.
Joint exercises are performed after thermal preparation of muscle structures with a warm compress. The duration of the manipulation is no more than 10 minutes.
Good results can be achieved with the following exercises:
- Move your movable jaw forward and backward 10 times in each direction.
- Move your jaw first to the right and then to the left with your lips parted. Repeat at least 10 times.
- Press the chin area with your hand and try to forcefully lift your jaw up. The duration of the movement is at least 1 minute.
- Try pushing your jaw forward for 1 minute, pressing with your fingers on both sides of the chin.