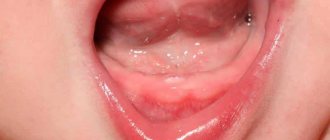
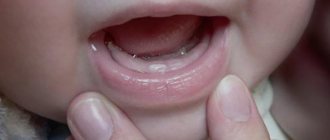
Teething is a process characterized by the axial movement of teeth from a non-functional position (from the bone jaw tissue) to a functional position (on the surface of the alveolar process and gums). Most often, the formation of a temporary bite causes a lot of inconvenience, not only to the baby, but also to his worried parents. In this article from the “Pediatric Dentistry” section, we will try to figure out in what order baby teeth erupt, and what symptoms accompany the development of this process.
Teething: sequence and timing
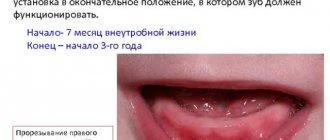
Normally, teething in babies occurs according to the scheme below:
- central incisors: at 6 months. – in the lower dentition, at 8 months. – on the upper jaw;
- lateral incisors: at 10 months. – in the top row, at 11-13 months. – on the lower jaw;
- first molars (at one year of age);
- canines in the upper row (1 year 4 months);
- canines in the bottom row (1 year 6 months);
- second molars on both jaws (2 years).
The timing of the appearance of the first teeth can vary under the influence of many factors, including:
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- the presence of Rh conflict;
- prematurity;
- receiving intracranial injury during childbirth;
- infectious diseases;
- congenital hypothyroidism;
- rickets;
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- neonatal sepsis;
- refusal to breastfeed the baby;
- noticeable weakening of the immune system.
It has been proven that in first-born children, teething occurs much earlier than in infants born at a later time. Boys' first teeth appear later than in girls, while in children of old-time mothers - significantly earlier than in babies born to young parents.
Otolaryngologist M.G. Goncharova
Red throat ” – with these complaints, parents often turn not only to an otolaryngologist, but also to a pediatrician. What is a red throat, and in what cases does it happen? In any case, a red throat implies inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane in the pharynx. What diseases does this happen with? The most common disease that causes hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa is acute catarrhal pharyngitis. At the same time, we see hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the pharynx, the side walls of the pharynx, and the soft palate. This condition occurs very often with respiratory viral infections, influenza, and childhood infections such as chicken pox, measles, and rubella. Redness of the back wall of the pharynx can also be caused by exacerbations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as biliary dyskinesia, chronic gastroduodenitis.
Sore throat in children
But such a simple disease as acute pharyngitis should not be confused with a more serious disease such as tonsillitis, because sore throat is usually called sore throat. Unlike acute pharyngitis, with angina, in addition to hyperemia of the posterior pharyngeal wall, we note hyperemia, filtration, edema of the anterior and posterior palatine arches. The palatine tonsils, which are located on the lateral surfaces of the pharynx, in this case increase in size, swell, and turn red.
At different stages of tonsillitis, either a whitish coating may appear on the surface of the tonsils, or purulent compartments may appear in the lacunae. Sore throat, unlike acute pharyngitis, is a serious infectious disease that most often occurs with fever and symptoms of intoxication.
What other diseases cause the “red throat” symptom?
In addition, a red throat can occur with various inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, such as stomatitis, or during teething in children. In this case, as with acute pharyngitis, the anterior and posterior palatine arches are not involved in the process and the tonsils are not involved.
The throat may be red even in the absence of any acute changes in the pharynx. Redness of the palatine arches or the so-called “congestive hyperemia of the palatine arches” may be a sign of a chronic inflammatory process or a sign of chronic tonsillitis. In this case, we see congestive hyperemia of the anterior and posterior palatine arches, hypertrophy of the lateral ridges of the pharynx without any acute disease. Depending on the symptoms, this condition may not require treatment at the time of examination.
What symptoms are noticeable to parents when their child’s throat is red?
Now let's talk about how the child behaves, and what parents can observe if the throat is red. If parents look into the child’s throat and see that the back wall of the pharynx is hyperemic, in this case it is very important to take into account the general condition of the child.
If the child’s condition is good, there are no symptoms of intoxication, there is no increase in temperature, he does not actively complain of a sore throat, then this non-serious condition can be regarded either as symptoms of acute pharyngitis, which require symptomatic therapy, or require treatment of an underlying disease, such as respiratory viral infection or any of the childhood infections.
In the case when a child actively complains of a sore throat, while he has an increase in temperature, symptoms of general intoxication, this condition must be differentiated from a sore throat, and in this case the child must consult a doctor and carry out active treatment, including (if necessary) general antibacterial therapy.
Treatment issues. What to give and when to give for a red throat.
As for the treatment and approach of parents to the problem of a red throat, it is very important to pay attention to the following points: a red throat is a symptom, I repeat, of a number of diseases, and in some cases, treating only the red throat itself will not lead to the desired result.
Therefore, active independent local therapy using antiseptics, local antibacterial drugs, sometimes even saline solutions, can lead to the development of pharyngeal dysbiosis.
Dysbiosis of the pharynx is a disruption of the normal microflora in the oral cavity, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in the protective functions of the mucous membrane itself in the oral cavity, and in this case it itself becomes an entry point for infection.
On the other hand, during self-medication, the adaptation of pathological microorganisms to antiseptics or local antibacterial drugs quickly develops, which in the future can significantly complicate the treatment of acute inflammatory diseases in the pharynx when necessary.
Therefore, before using any drug to rinse or irrigate the pharynx, you need to very clearly define the purpose of this treatment, because such a concept as “treating just a red throat” is unacceptable.
In some cases, a red throat may not be treated and does not require any special treatment, and the problem will be solved only by treating the underlying disease that led to the symptom of a red throat.
What inconveniences does the problem of red throat cause for parents?
Why is this problem inconvenient for parents? First of all, parents are worried about the fact that the child has a red throat.
Remember, it is very important to always take into account, in addition to the fact that we see a red throat, also general clinical symptoms: are there any other symptoms of disease, how disturbed is the child’s general condition, is there an increase in temperature? And only in this case it is necessary to somehow deal with this problem.
On the other hand, a red throat may be a symptom of some chronic disease in the pharynx, the most common of which are chronic tonsillitis or chronic pharyngitis, which can exist as independent diseases or, in the case of chronic pharyngitis, as a symptom of some disease in the underlying parts of either the gastrointestinal tract or lower respiratory tract. Therefore, if you often observe a red throat in your child, then in this case you need to consult a pediatrician, or better yet, an otolaryngologist, because it is with him that you can clearly determine what this pathology is associated with. An otolaryngologist will be able to teach you to differentiate a mild disease such as acute pharyngitis, which is a symptom of a respiratory infection, from a more severe condition, and also to rule out a chronic disease in the tonsils of the back of the pharynx.
A visit to an otolaryngologist is the ideal solution
I repeat once again, what would be the most logical solution if you often observe a red throat in your child? This problem should be discussed with an otolaryngologist, who will analyze the diseases that the child suffered from, analyze the objective picture, and, if necessary, can examine the microflora in the oral cavity, on the back wall of the pharynx, in the lagoons of the tonsils. And only then will it be possible to come to some correct conclusion, on the basis of which treatment will be selected or the dynamics of observations will be selected, i.e. a certain concept will be formulated according to which this child will be observed or treated.
Is the red throat effect related to respiratory function?
How can a red throat and respiratory dysfunction be connected? In general, these are two rather related problems, if only because when a child’s breathing function is impaired, the child switches to mouth breathing. Breathing through the mouth is not physiological: the child breathes through the mouth, while the inhaled air is insufficiently warmed and moistened, and in any case this will lead to certain changes, and then inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, primarily the back wall of the pharynx. This will manifest itself in the form of hyperemia or redness of the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx.
If we talk about how quickly this problem can be dealt with, then it is impossible to answer this question unequivocally; a lot here depends on the reason why the red throat appeared. Therefore, it is quite difficult to give any recommendations here; it all depends on the condition that led to the redness of the throat.
Teething symptoms
There is an opinion that the appearance of the first teeth is accompanied by the development of a whole complex of pathological processes (fever, the appearance of a rash, abnormal stool, vomiting, convulsions, etc.). In fact, the formation of a temporary bite is a natural process that is not characterized by the symptoms described above. Pathologies detected during the teething period are most often manifestations of infectious diseases or a consequence of changes in diet.
In particular, factors that can lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms include:
- introduction of artificial complementary foods;
- hypovitaminosis;
- acute viral infections;
- stomatitis;
- tonsillitis;
- runny nose;
- otitis;
- vaccination, etc.
The true symptoms of teething are:
- hyperemia and gradual swelling of the gums;
- the appearance of a small bluish hematoma on the gum tissue;
- slight bleeding from the gums;
- wet cough;
- mild itching caused by mechanical irritation of sensitive nerve fibers in the gum tissue;
- increased salivation;
- various somnological disorders;
- sharp deterioration in appetite;
- tearfulness, capriciousness.
The danger of redness of the throat during this period
During teething, the baby's body weakens and becomes vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria or colds.
When a baby is teething, the child endlessly puts various objects into his mouth, which are not always sterilely clean. It introduces an infection and hyperemia of the tonsils occurs (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sore throat occur), this is a very dangerous disease for such young children.
If some symptoms intensify and last more than 2-3 days (fever, red sore throat, runny nose with yellow or green discharge, cough or wheezing in the chest), you should consult a pediatrician.
Redness in the throat of a baby may be a sign of diseases:
- mechanical, thermal damage;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- allergic reaction;
- ARVI;
- acute respiratory infections;
- diseases of the stomach, esophagus;
- problems with the nasopharynx.
First aid for teething
When baby teeth appear, the baby may require not only parental care, but also medical attention. The dentist may recommend that parents use anesthetic dental gels and treat the affected areas of the gums with decoctions of sage, oak bark or soda solution. If the pain is severe, the baby may be prescribed paracetamol, ibuprofen and other systemic painkillers.
To ease the discomfort that a child experiences when teething, it is necessary to use teethers - specialized devices made of rubber or plastic that the baby can bite and gnaw on without risking damage to the soft gum tissue. In addition, it is advisable to regularly massage the child’s gums with a finger wrapped in a clean, damp bandage.
The order of changing baby teeth in children by age
After the age of 3 years, parents can take a little break from the changes. And then, at about 5 years of age, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. The process begins with the lower incisors. Then, after about a year, chewing “sixes” are cut, which parents may mistakenly mistake for milk ones. After another year, the upper incisors are replaced.
To go through this journey with your child without problems and pain, visit the dentist regularly. Children may experience pain simply from jaw expansion. Your doctor can easily tell you the cause of the discomfort. The age of 6–7 years shows the prospect of bite formation. Here you can quickly correct problems that arise so that by adolescence your child has a smooth, beautiful smile.
Next, the procedure for replacing baby teeth continues with the upper lateral incisors by the age of 8 years. At the age of 9–10 years, the molar first premolars appear, followed by the second premolars a year later. 12–13 years is the age when canines appear, and at 14 years the last second molars are cut.
The procedure for replacing baby teeth ends with the complete formation of a bite of 24 teeth.
Caring for emerging teeth
Teething is an absolute reason for making the first visit to the pediatric dentist. During the consultation, the doctor identifies all deviations in the structure of the child’s dental apparatus, assesses the condition of the frenulum of his lips and tongue, draws up a dental care plan and a plan for preventive visits to the dental clinic.
It is advisable to brush emerging teeth twice a day. Initially, you should use a baby silicone brush or a small piece of gauze without toothpaste for cleaning. A regular toothbrush can be used when the child is one year old, and toothpaste when he reaches two years of age. In addition, it is important to pay attention to the process of enamel mineralization. In particular, it is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets and include foods enriched with calcium, phosphorus and ascorbic acid in the baby’s diet.
What to do when the temperature rises
Often parents, even with a slight fever, begin to actively treat the child with antiviral, antipyretic and antibacterial drugs. Even if this symptom is due to the appearance of the first teeth. Most pediatricians (including Dr. Komarovsky) are against such radical methods. Why shouldn't you do this?
A temperature of 37 degrees and above is a kind of protective reaction of the body and helps it more actively produce antibodies against viruses and bacteria. Low body temperature does not allow you to effectively fight infection. Therefore, sometimes it is worth not interfering with natural processes and immediately suppressing even minor signs of fever.
But you shouldn’t fall into inaction either. If the fever reaches significant numbers (38 degrees or higher) and is accompanied by a change in the general condition of the child, then prescribing antipyretic drugs for high fever is a primary measure.
If the rise in temperature is not controlled by conventional medications, then it is possible to scrub the child with cool water or an vinegar-alcohol mixture.
If the fever does not subside within 3 days, then you must definitely visit your treating pediatrician to decide on further examination and the possibility of prescribing antibiotics or other medications.
Some parents prefer homeopathy in such cases. Such drugs do not effectively reduce the temperature, but they can alleviate the baby’s general condition and speed up the recovery process. A prerequisite before taking homeopathic medicines is to consult a specialist.