Ear pain is a phenomenon that many people of different ages have experienced. Ear pain is accompanied by discomfort, strong, constant, unpleasant, exhausting sensations, and has a negative impact on sleep patterns and quality of life. For this reason, the question of how to get rid of it comes to the fore.
Practice shows that people experiencing ear pain make many mistakes, which increases the likelihood of complications and negative consequences. In such cases, an ENT doctor is needed. The specialist will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment appropriate for the specific case.
To do this, you can contact our clinic and receive high-quality medical services. Our prices for paid medical services are the most affordable in Rostov-on-Don, and the otolaryngologist provides consultations for both adults and children.
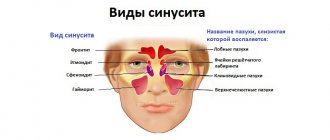
Main types and symptoms of ear diseases
Almost all ear diseases have similar symptoms. Let's look at the most common diseases and their clinical manifestations.
Eustachite
It is infectious in nature. The inflammatory process affects the auditory canal (Eustachian tube), which leads to impaired ventilation in the ear cavity. The result is otitis media. The symptoms are:
- discomfort and pain;
- sensation of fluid;
- hearing impairment;
- crackling or strange noise in the ear;
- an increase in temperature when a purulent process occurs.
All manifestations intensify with movement.
Mastoiditis
Included in the group of inflammatory pathologies of an infectious nature. Affects the inner ear. Often occurs as a complication of the inflammatory process in the middle ear. Characteristic manifestations:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- general weakness, intoxication;
- throbbing pain;
- discharge with pus;
- swelling of the outer ear;
- hearing loss.
One of the main first symptoms is dizziness. It occurs suddenly, without reason.
Meniere's disease
Characterized by increased pressure in the labyrinth of the middle ear. As a result, the blood vessels are affected, and fluid begins to accumulate in the ear cavity. The exact reasons are not clear. Cannot be completely cured. Symptoms:
- attacks of deafness;
- nausea;
- problems with balance, dizziness;
- constant noise in the affected ear.
Discomfort increases with loud sounds.
Acoustic neuritis (cochlear neuritis)
A common disease with a chronic course. Inflammation affects the nerve structures of the inner ear. Patients complain mainly of hearing loss and the appearance of additional sounds. It may be a whistle, a crackling sound, or a rustling sound. Usually occurs in people over 50 years of age. A dangerous complication is necrosis, which leads to complete irreversible deafness.
Otitis and tympanitis
These are inflammatory diseases that affect various parts of the hearing organ. This diagnosis is mainly given to children and the elderly. There are external, middle and internal otitis (labyrinthitis). Manifestations of the disease include:
- severe throbbing pain that worsens with jaw movements;
- temperature increase;
- fatigue, lethargy;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear.
There may be short-term hearing loss. Enlargement of the lymph nodes is often observed. With complications, mesotympanitis (purulent otitis media) and epitympanitis (purulent process affecting the bone) develop.
Otomycosis
The main reason is yeast-like or mold fungi. Pathology can occur in the outer or middle part of the ear. At the initial stage of infection there are no symptoms. The clinical picture is represented by the following manifestations:
- severe itching;
- suppuration;
- presence of ulcers;
- headache from the affected ear;
- ear discharge;
- feeling of stuffiness;
- ear sensitivity.
Often this diagnosis is made to people with chronic metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus), with a persistent decrease in immunity (HIV status) or after chemotherapy.
Otosclerosis
This is a hereditary pathology that affects the bony labyrinth of the inner ear. It occurs more often in women after 45 years. But the first manifestations may appear at a young age. Without appropriate treatment, it often leads to the development of bilateral hearing loss. The disease can be suspected based on the following symptoms:
- gradual deterioration of hearing for no reason;
- strange sound or noise in one or both ears;
- dizziness;
- improved hearing in noisy environments;
- balance disorders.
With such manifestations, you need to contact an otolaryngologist.
Otogenic sepsis
A severe complication that occurs as a result of the spread of purulent inflammation from the middle ear. The infection enters the general bloodstream through the lymphatic tract or through the vessels of the meninges. The diagnosis is typical for young and middle-aged people. Symptoms occur suddenly and include:
- temperature fluctuations;
- chills;
- increased sweating;
- tachycardia;
- refusal to eat;
- deterioration of health;
- shortness of breath.
Surgery is required, so this condition requires immediate hospitalization.
Ear plug
A buildup of earwax that partially or completely blocks the ear canal. A common condition that is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sensation of a foreign object;
- ear congestion and hearing loss;
- coughing may occur;
- yawn;
- slight dizziness, as when motion sickness occurs in transport.
Symptoms often appear after water procedures. A clot of wax swells due to water ingress and completely blocks the passage in the ear.
Ear injuries
With sudden changes in pressure (at great depths in water or in air), injury to the eardrum occurs. Damage is also possible when exposed to loud sound vibrations. This condition is characterized by pain and bleeding. In case of mechanical damage from various objects, bruises or blows, dizziness and severe ringing in the ears are noted. Characterized by temporary deafness.
It is also possible for various tumors to form in the ear. The tumor usually forms inside or near the ear. It is extremely rare that it affects the middle section. They are characterized by slow growth and the absence of painful symptoms.
Causes of ear diseases
Diseases can occur for various reasons. The main ones include:
- Improper hygiene or using inappropriate items.
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of other chronic foci of inflammation in the body. Infectious diseases of the nasopharynx are especially dangerous.
- Injuries.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Heredity.
- Excessive production of ear secretions.
- Professional activities associated with constant noise.
In children, ear diseases are diagnosed more often due to the physiological structure of the child’s ear. Also, their local and general immunity has not yet been fully formed. In adults, the causes are usually associated with other chronic pathologies or injuries.
Diagnosis of ear diseases and consultation with a doctor
If you experience ear pain, or your hearing begins to decrease for no apparent reason, you should definitely contact an otolaryngologist. Depending on the symptoms, you may need to consult an audiologist - a doctor who deals with hearing disorders.
Diagnostic methods
The patient’s complaints, as well as the study of family history, play a major role in making a diagnosis. The doctor performs an external examination of the auricle. If this is not enough to determine the disease, then they resort to hardware methods.
- Otoscopy is a painless method of examining the outer ear using an otoscope. This is a tool that looks like a lighted tube. Helps to identify hidden infections, injuries, and also detect a foreign body.
- Tympanometry is an acoustic method for studying the functionality of the auditory tube and the mobility of the ossicles in the middle ear.
- Audiometry is a test to study hearing acuity. Conducted by an audiologist on a computer.
- X-ray of the ear and temporal bone - recommended for inflammatory pathologies. Helps identify pathological changes in parts of the inner ear.
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan.
In case of discharge and suspicion of a bacterial infection, bacterial culture is carried out. It reveals the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, which allows you to choose the optimal therapy. For chronic ear infections, a general blood test is prescribed.
Types of ear pain
Pain in the ears can manifest itself in different ways. The specificity of pain acts as one of the guidelines in determining pathology.
Nature and intensity of ear pain:
- Sudden pain. Accompanied by acute pain, it can be caused by injury or a foreign object;
- Progressive pain. It occurs against the background of pathologies with moderate dynamics of development. May indicate wax plug, inflammation in the ear canal;
- Severe pain in the ear, accompanied by throbbing. Character for boil, OVSU, injury;
- Stitching, sharp. The pain occurs periodically, bringing with it discomfort. The main reason is neuralgia;
- Blunt pain. Manifests against the background of diffuse otitis, may indicate the presence of sulfur plugs, inflammation of the middle section in a chronic form;
- Itchy pain. Relevant for those cases when we are talking about damage to the external part. May be caused by otitis media, disruption of the integrity of the ear canal, eczema;
- Intermittent. This kind of sensation is characteristic of radiating pain;
- When swallowing. Causes: OVSU, malignant tumors of the oral cavity and larynx, pharyngitis, tonsillitis.
Possible complications of ear diseases
If the spread of infection is not stopped in time, it can enter the lymph and also the brain tissue. In these cases, death is possible. Thus, complications of ear diseases can be:
- meningitis;
- abscess development;
- bacterial sepsis;
- facial paralysis;
- neoplasms, including cancer.
Advanced inflammation can destroy the integrity of the eardrum. This can lead to hearing loss or deafness. It can be partial or complete, affecting one ear or both. But the most important thing is that in some cases deafness becomes irreversible.
Treatment of ear diseases
The treatment regimen is selected only by the doctor after conducting the necessary research methods. You should not self-medicate. Treatment in most cases is complex. The main goal is to eliminate the inflammatory process and reduce pain. For chronic pathologies, therapy is aimed at prolonging the period of remission. For ear diseases, the following groups of medications are used:
- Antibiotics in the form of tablets or drops (if a bacterial infection is detected).
- Analgesics.
- Antiseptic solutions for washing the affected ear.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments that are placed in the ear canal using turundas.
- Vasoconstrictor drops for the nasopharynx.
- Hormonal drugs (for medical reasons).
Physiotherapeutic methods give good results. But they are prescribed after the acute period has passed and only by a doctor. For mycoses and other fungal infections, physiotherapy and heating are prohibited. For sulfur plugs, special means are used to soften it.
In case of purulent pathologies and the occurrence of an abscess, surgical intervention is performed. If hearing loss or partial deafness occurs, the doctor may recommend tympanoplasty. This is a microsurgical operation that is aimed at improving sound conductivity. In severe cases of hearing loss, prosthetics are performed.
What to do if your earlobe becomes inflamed from an earring?
As a rule, inflammation of already healed punctures is associated either with trauma or with the qualities of decoration that we discussed above. Exacerbations of systemic diseases cannot be discounted - they can also cause atypical reactions.
It’s not just that the ear gets inflamed from an earring: you should find out the reasons for this phenomenon in order to avoid them in the future. As sad as it may be, sometimes you have to completely abandon such decorations. Nothing critical - there are a great many cool clips on sale.
If a hole in your earlobe becomes inflamed from an earring, you should at least temporarily stop wearing the corresponding jewelry. Wait until traces of the inflammatory process have completely passed. Recommendations on how to care for your ears during this period are below.
Total redness of the ear, accompanied by the discharge of pus from the puncture, is a good reason to consult a surgeon. And if the temperature rises, you should not go to the doctor, but run!
Inflammation after puncture
Most often, inflammatory reactions occur after unprofessional punctures made on a whim: there are hands, ears and a sewing needle - why not? The inflammatory response is the lesser evil of such rash decisions.
Gold earrings with topaz in the Sunlight catalog
In salons, ears are pierced with special guns, which immediately and almost painlessly insert the earrings, or with piercing needles. Although it is impossible to completely sterilize a special gun, the risk of infection tends to zero. An even better option is a disposable catheter needle: it is guaranteed to be sterile.
Redness of the earlobe and the appearance of crusts are a normal reaction of the body in the first couple of weeks after surgery. But if the lobe becomes purple, a “tugging pain” appears, and pus literally flows from the puncture, adequate measures need to be taken.
Medical steel, from which primary stud earrings are made, promotes rapid healing of wounds. Implantation titanium demonstrates even better qualities.
Prevention of ear diseases
Ear pain is no less painful than toothache. But there is a real risk of losing your hearing. To avoid this, do not delay going to the otolaryngologist at the slightest unpleasant symptoms. If you follow the basic rules, you can completely avoid ear diseases:
- Do not let infectious diseases of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract take their course. They require full treatment and bed rest.
- Do not clean the ear canal with foreign objects, especially sharp objects. Do not let children clean their ears themselves.
- Protect your ears from exposure to loud sounds and cold. When working in a noisy industry, use protective equipment (earplugs).
- When swimming in ponds or pools, use a cap and earplugs to prevent water from entering your ear.
- Using headphones for long periods of time also negatively affects your hearing.
- Strengthen your immune system.
If you are prone to otitis media and other inflammatory processes in the ears, visit an ENT doctor for preventative measures annually. It is also recommended to visit an otolaryngologist after 40 years of age if one of your relatives has been diagnosed with hearing loss or progressive deafness.
Why do earrings hurt my ears?
There are several basic reasons why earrings hurt your ears:
- Problematic puncture. Ears should only be pierced in professional salons where specialists work and strict rules for sterilizing instruments have been established. But even with a professional approach, the choice of puncture point may not be entirely correct - human anatomy sometimes presents incredible surprises.
- Incorrect care. Most often, the ear hurts from the earring due to improper care. A person treats wounds irregularly, uses inappropriate means, and touches his ears with dirty hands. Here we can also mention the excessive haste in replacing primary stud earrings with other jewelry.
- Traumatization. In the first days, wounds are especially painful and vulnerable. You can injure the puncture site even when combing your hair or changing clothes. In the future, the main risk factor is wearing very massive and voluminous jewelry (for example, gypsy rings or long pendants), especially during active sports and physical labor.
- Diseases. Some diseases are absolute contraindications to ear piercing. Among the most common are diabetes mellitus, various blood diseases, a tendency to tumors and the formation of rough scars.
- Allergic reactions. Believe it or not, there are rare cases of allergies even to medical steel, which is used to pierce the ears with a gun! What can we say about other metals, even noble ones? If your ear hurts from a gold earring, most likely the alloy contains ligatures that provoke allergic reactions.
- Wrong selection of earrings. Earrings that are too massive always carry some risk (the holes are stretched and more often injured), so it is not recommended to wear them every day - only on special occasions. Problems can also arise if you choose the wrong lock: for example, an English clasp requires selection according to the parameters of the eyelet.
Under no circumstances should you pierce the ears of friends and relatives without special knowledge and skills. Who can guarantee that the needle is absolutely sterile and the puncture will not be in the problem area of the lobe?
What to do if earrings hurt your ears?
The first thing to do is take off the earrings, without hoping that everything will return to normal on its own. If your earlobe hurts from an earring, but the wound has healed a long time ago and there are no signs of inflammation, the reason may lie directly in the jewelry. Most often, such reactions are provoked by jewelry.
Noble metals (silver, gold, platinum) are inert and cannot cause allergic reactions, but they are not used in their pure form to make jewelry (too soft). All kinds of alloys are added to them: copper, nickel and other metals. This is what causes similar reactions in some people.
If after removing the earrings the pain and redness go away, then you just need to choose another piece of jewelry. Otherwise, you must first take measures to eliminate inflammation (more on them below).