In what cases may the bone fail to take root?
The bone may not take root in cases where it becomes infected, including when the patient violated the schedule for taking antibiotics or did not follow the doctor’s orders.
Much attention is paid to food intake: the patient can simply, out of forgetfulness, bite into something hard, and his stitches will come apart, and the material and bone graft will become infected through the open wound.
The above accounts for 90 percent of cases
when the bone may not take root.
Are there any contraindications to bone grafting?
Of course, there are contraindications to bone grafting. These include
:
- various chronic diseases, incl. diabetes mellitus with high sugar levels,
- the period when the patient takes a number of drugs, including chemotherapy,
- in the period after chemotherapy, when the bone cannot be “touched” at all.
Features of hygiene after bone grafting
After bone grafting it is recommended
:
- use of special surgical toothbrushes,
- the use of toothpaste should be limited, and even better, use special toothpastes for post-surgical interventions,
The main thing when carrying out hygiene is NOT TO INJURY
area of bone grafting! You should try to eliminate contact with this area or reduce it to a minimum.
When can you do without bone grafting?
You can always do without bone grafting when you can install an implant of the required diameter and required length into the remaining bone.
And, in fact, you shouldn’t do bone grafting just to assert yourself. Some doctors suffer from this, trying to prove to themselves or someone else how they can do bone grafting.
But, as they say, the best bone grafting is the one we don’t do: if the patient can be rehabilitated without bone grafting, then it’s better to do just that. Since volume can be added with soft tissues, connective tissue can be transplanted - a graft, or drugs can be added to replace the volume of soft tissues - and achieve an excellent result!
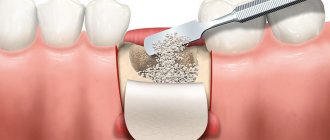
What is Guided Bone Regeneration
Guided bone regeneration is an operation to compensate for the lack of bone tissue with a substitute, which is secured with a barrier membrane. After the procedure, a framework is formed around the transplant (it is formed by vessels and osteocyte cells that produce new tissue). Natural bone is gradually replacing artificial material.
Extensions using the NDT method are carried out according to classical parameters:
- thickness of the vestibular bone wall (at the cheek) - up to 2-2.5 mm;
- bone thickness between the implant and the root of the adjacent unit - up to 2.5-3 mm;
- The thickness of the bone wall between two titanium roots is up to 3 mm.
What implants are used after bone grafting?
Are there “special implants” that are recommended in cases of bone grafting? Both with bone grafting and without bone grafting, it is necessary to use implants only from good, proven manufacturers, those that have a good clinical base. For example – Straumann, Nobel, Ankylos, Xive, Astra Tech.
There are a number of other implant systems that give good results. But at the German Implant Center we use only the best implant systems, only premium ones.
Indications
The operation allows you to increase the “necessary” volume for high-quality classical implantation, helps restore the functions of the jaw, and returns the gums to an attractive appearance.
The bone is built up “with reserve”, since after the operation the surface layers will be supplied with a small amount of oxygen due to their lower blood circulation. Therefore, the volume of inevitable tissue resorption is calculated.
In addition to implantation, indications for NRC are:
- rapid restoration of physiological parameters after tooth extraction;
- congenital or acquired defects of the bone around the teeth;
- prevention of tooth displacement, loosening, and loss due to periodontal tissue diseases.
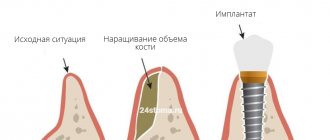
Why does atrophy occur?
How is implantation performed during bone grafting?
Implantation during bone grafting can be carried out either simultaneously with bone grafting, or delayed - when the implants are installed in the new “grown” bone.
As an experienced implant surgeon, in my practice, in 80-90 percent of cases I perform bone grafting at the same time
with implantation.
I will explain why I perform plastic surgery with implantation at the same time, and what is the advantage of this approach. Bone grafting itself requires a long healing period, from 4 to 9 months. And if we maintain this period and then do implantation, then we have to wait another 4 months. That is, the time frame in this case increases significantly.
And if I do implantation along with bone grafting, then the implant takes root along with the bone. A good implant has an excellent osteogenerating surface, and when fused, an excellent result
.
This reduces the patient’s rehabilitation time. And most importantly, the patient DOES NOT NEED
second surgery. We understand that a large number of surgical interventions do not improve trophism, mucous membranes, or bone tissue.
Everything we do at the German Implant Center, from tooth extraction to implantation, is carried out as atraumatically as possible for the patient.
How many implants are placed during a total restoration?
We specialize very broadly in total implant rehabilitation. In the upper jaw, 6-8 implants are recommended according to our protocol; in the lower jaw, 6 implants are sufficient for total rehabilitation.
Often, implantation occurs simultaneously with the installation of temporary teeth, that is, the patient leaves the clinic “with teeth”, and not on the second or third day, but on the same day when implantation is done:
Preliminary implantation planning is carried out using CBCT, the implants are placed in the required positions.
After this, a surgical template is made, according to which the implants are installed. And based on the same computed tomography (CBCT) and images, a temporary structure is made that will be attached to the implants installed for the patient.
And it turns out the so-called “full case” is when the patient comes, if necessary, if circumstances require it, teeth are removed (or they have already been removed/lost earlier), implants are placed on the patient and an orthopedic structure is fixed - his new teeth.
Balloon sinus lift
Balloon sinus lift is used for those patients whose bone height is 3-4 mm. The advantage of this method is that the implant is installed immediately after the sinus lift is completed.
The essence of this method is very similar to the technology of closed sinus lift. Raising the floor of the maxillary sinus and filling the space with synthetic dental tissue is done in the same way as with a closed sinus lift. The same surgical instruments are used.
The difference is that a thin catheter with a balloon is inserted under the mucous membrane, into which a special radiopaque liquid is then injected. The balloon begins to expand and thereby delicately peel off the mucous membrane. This method allows the implant to be implanted immediately after the sinus lift is completed.
On which jaw does tooth bone resorption occur faster?
How quickly does a deficiency of bone and bone tissue occur in the absence of a tooth?
In fact, tooth bone tissue decreases faster in the upper jaw, since the upper jaw is softer and more porous. In the lower jaw, the bone also disappears quite quickly, since the vestibular plate near the teeth is quite thin. Six months after tooth loss, quite severe atrophy of bone tissue occurs, and the atrophy progresses. And therefore, in order to avoid atrophy, it is advisable to do implantation simultaneously immediately after tooth extraction.
This format is the regular, daily work of the specialists of the German Implantology Center. For example, a patient comes with a crack in the root of a tooth - the tooth must be removed. We can go with two options:
Option 1.
We can remove the tooth and 3 months later implant the tooth into the patient.
But during these three months, shrinkage of the bone tissue still occurs, since - I said earlier - the vestibular bone plate is very thin. And in this case, the patient undergoes 2 surgical interventions
: the first is tooth extraction, the second surgical intervention is the installation of a dental implant.
Option 2.
In our practice, we recommend and practice the second option. This is a one-step implantation, when the patient has a tooth removed, an implant is installed, and in order to avoid collapse of the bone tissue in the places where the roots of the tooth used to be, these places are filled with a bone graft. Due to graft filling, we do not have tissue “collapse”; the contour of both the gums and the jaw bone tissue is preserved. Which, in turn, is very difficult to achieve with delayed, delayed implantation.
Who can undergo bone grafting?
Who are potential patients for bone grafting, and what are the age restrictions for it?
This is a bit of a tricky question :). The oldest patient I have performed bone grafting on is a 75-year-old patient, a wonderful, purposeful woman. She had bilateral terminal defects on her lower jaw. She really wanted implantation and refused a removable structure.
I performed bone grafting on this woman at the same time as implantation. And literally 6 months later she was fitted with prosthetics. And everything went great.
In the case of the patient’s age, the main thing is that he has no contraindications. Perhaps there are age restrictions, but they are not so pronounced, because, although trophism deteriorates with age, regenerative abilities decrease, but the main thing is the presence of contraindications. You need to look at the tests, and if the patient is healthy at 75 years old, then why not?
Possible postoperative complications
After a sinus lift, the following problems may arise:
- acute chronic sinusitis;
- swelling of the palate;
- sinusitis;
- increased body temperature;
- rupture of the mucous membrane inside the maxillary sinus or its perforation;
- chronic runny nose;
- bleeding from the nose and at the operation site.
All these troubles can occur due to insufficient qualifications of the doctor and the use of low-quality materials and instruments.
How to do without bone grafting
Is it possible to do without bone grafting and sinus lift?
Yes, in some cases you can do without bone grafting. But you need to understand that if the patient does not have bone tissue, and we install an implant, the crown will hang over the gum, and something from food will constantly get clogged there. That is, it is aesthetically unsightly, and all the food will be stuffed there, the patient will always have a “pocket of food supplies” from yesterday and the day before yesterday.
Option with a smaller diameter implant
You can place an implant of a smaller diameter, and at the same time we can carry out soft tissue regeneration - replant the mucous membrane (this can be connective tissue from the palate, from the tubercle of the upper jaw). And thus we achieve replenishment of the volume of soft tissues. Due to this, aesthetics are visually improved and hygiene problems are eliminated.
Whenever it is possible to avoid various surgical procedures, but not at the expense of quality, then they should be avoided.
That is, surgery for the sake of surgery - it is not needed
.
Materials for bone tissue building in dentistry
Bone augmentation before dental implantation involves the use of different types of osteoplastic materials. Osteoplasty can be synthetic or natural; each type has its own characteristics and characteristics; the price of bone tissue augmentation and recovery time after surgery depend on the type of osteoplastic material. What types of osteoplasty for building up gum bone tissue during implantation can be offered to you in modern dentistry?
Autogenous osteoplasty for augmentation
This is the name given to bone material of biological origin, which is obtained directly from the patient. Donor osteoplasty is taken from certain areas of the jaw or chin. The process of obtaining donor bone is painful and traumatic, but the biomaterial quickly takes root, and its use does not cause complications or negative reactions of the immune system.
Allogeneic materials
The bone donor for dental bone tissue augmentation is another person, and not the patient himself. This type of osteoplasty is taken from deceased or deceased donors, subjected to specialized and complex processing and placed in donor tissue banks. To some, this method of obtaining bone material may seem unethical, however, the use of allogeneic osteoplasty reduces the risk of bone rejection, eliminates the need to collect material directly from the patient, and therefore reduces the traumatic nature of the operation as a whole.
Xenogeneic osteoplasty for building bone tissue on teeth
This type of osteoplastic material is obtained from porcine or bovine bone. It is available in the form of blocks or granules. Xenogeneic osteoplastics take root quite well, but still worse than allogeneic and autogenous materials.
Alloplastic osteoplasties
Granular synthetic osteomaterial made from calcium phosphate.
Its main advantage is its affordable price, which reduces the cost of bone tissue augmentation. A separate type of osteoplastics used in bone tissue augmentation are collagen membranes, which isolate the bone defect and activate the processes of growth of natural jaw bone.
Donor materials
The following can be used as donor materials:
- Protein molecules that are similar in structure to the original bone. They are responsible for starting the process of cell regeneration.
- Membranes made of collagen and impregnated with a regenerating composition.
- Hydroxyapatite compounds, membrane barriers and bone granules.
- Biologically active compounds together with a variety of distracting drugs.
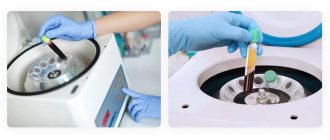
The best solution seems to be the combination of several materials when performing guided bone regeneration. Not only bone tissue is suitable for this, but also blood cells, synthetic fibers, and so on. If you add the patient's blood to crushed bone granules, regeneration will be more active and survival rate will improve.
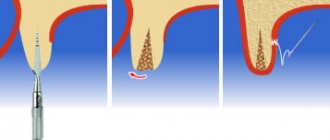
Stages of guided bone regeneration surgery
Guided regeneration around implants is performed in several stages:
- Using a scalpel, the doctor removes the periosteal flap. During tissue incision, the point is taken into account that in the future the membrane installed in the sinus should not touch the root system. The distance should be about 4 mm, otherwise the proliferation of bacteria and the development of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity cannot be avoided.
- The optimal size of the implanted plate for a particular case is selected, with an emphasis on the specifics of soft tissues and parameters of bone restoration.
- Decortication of the surface of the hole is carried out. For this purpose, spherical burs and fissures of compact sizes are used. In some cases, the doctor uses thin drills. Provides access to the drugs necessary for the rapid restoration of the affected area and to activate blood circulation in the jaw.
- The membrane is installed. Titanium feints are used, the attachment location is chosen in an inconspicuous area. After installing the first side, regenerating drugs are administered, only after that the doctor begins to fix the second side. It is important to achieve maximum fit, otherwise soft tissue will grow into the formed folds, which will negatively affect the result of the dental operation.
- The flaps are sutured over the membrane. It is important that the surgeon uses the thinnest threads. It is also necessary to match the boundaries of the incisions as accurately as possible - in this case, healing is accelerated and the risk of inflammation is eliminated when food debris enters the sinuses.
- At the final stage, the doctor disinfects the suture. The implant is installed after final bone regeneration.
If you are interested in restoring your teeth using soft tissue grafting, start with a consultation. Visit the official website of the medical center - make an appointment with a doctor online. During the initial examination, the doctor will diagnose existing diseases, if any, and prescribe treatment.