Causes of lymphadenitis
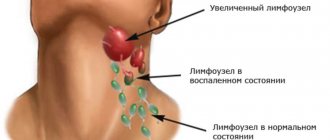
The function of the lymph nodes is to prevent the spread of infectious processes in the body. Any infectious agent that gets into them is destroyed by lymphocytes. When too many foreign microorganisms arrive, lymphocytes cannot cope with so many bacteria, the latter begin to actively multiply. This creates conditions for other types of leukocytes to penetrate into the site of inflammation, which causes an enlargement of the lymph nodes. One or more of them may become inflamed.
Inflammation can be nonspecific and specific. In the first case, the causes of the disease are bacteria and their toxins, viruses, and fungi. Lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes is caused by staphylococci and streptococci; they are pyogenic flora. The primary source of infection in the nonspecific form of the disease are boils, festering wounds, trophic ulcers, caries, erysipelas, and thrombophlebitis. In children, inflammation of the lymph nodes is often a complication of inflammatory processes in the ENT organs (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, influenza), childhood infections (scarlet fever, mumps, diphtheria) and skin diseases (diathesis, pyoderma).
A specific type of disease is triggered by certain types of microorganisms:
- tuberculous mycobacterium;
- plague stick;
- Brucella (the causative agent of brucellosis);
- Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis);
- tularemia bacteria (causing tularemia);
- actinomycete (the causative agent of actinomycosis).
When infected with these types of microorganisms, special symptoms characteristic of a particular disease develop. Lymph nodes undergo specific changes, since infectious agents enter them with the flow of lymph.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
Based on the nature of the inflammatory process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
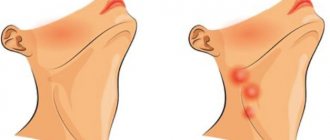
- Acute lymphadenitis. The duration of the course is up to two weeks. Characteristic symptoms: pain and enlargement of regional lymph nodes, fever, headache, general weakness, loss of appetite, swelling and redness of the skin in the area of the affected node.
- Chronic lymphadenitis. The duration of the disease is 1 month or more. Develops with a sluggish infection or after untreated acute lymphadenitis. With this course, the pain syndrome is erased, but the lymph nodes themselves remain enlarged and dense. Lymphatic fluid retention and swelling are noted.
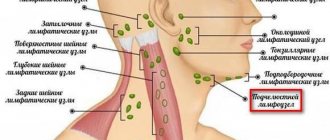
Lymphadenitis is classified according to the location of the inflamed lymph nodes into the submandibular, cervical, axillary and inguinal. All of them are characterized by similar symptoms: enlarged lymph nodes, pain, redness of the skin, intoxication syndrome. The differences are due to the location of the inflammatory focus.
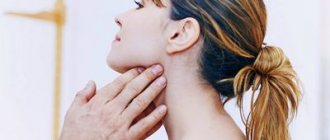
Thus, with cervical lymphadenitis, there is a restriction in head movement; when turning or bending, the patient feels acute severe pain. If the lump is large, it can put pressure on the organs of the neck and cause difficulty breathing, changes in voice, and difficulty swallowing food.
Submandibular lymphadenitis is accompanied by pain in the jaw during talking or eating, but is rarely bothersome at rest. With the axillary type of the disease, hand movement is impaired, swelling of the upper limb on the affected side increases and its sensitivity is impaired.
Inguinal lymphadenitis is characterized by swelling of the legs on the affected side. This manifestation is due to a violation of the outflow of lymph and compression of large vessels in the groin area. If suppuration occurs, the body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, the patient feels weakness and pain in the lower abdomen.
Diagnosis of lymphadenitis
Recognizing acute lymphadenitis is not difficult. To make a diagnosis, anamnesis and a set of symptoms are studied. Difficulty can arise when infection of the lymph nodes is complicated by other concomitant diseases. In all cases, it is first necessary to determine the location of the primary purulent focus. In case of chronic disease, the patient is prescribed a puncture biopsy of the lymph node and histology.
To diagnose lymphadenitis, a general blood test is required. Based on its results, they judge not only the presence of the inflammatory process, but also its scale. Laboratory signs of lymphadenitis will be an increase in the total number of leukocytes and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. With an active purulent process, a decrease in the level of monocytes and eosinophils is detected.
Diagnostic examination involves instrumental methods - ultrasound. With its help, you can determine the shape and size of the lymph nodes, their connection with surrounding tissues, and the presence of an abscess. If necessary, computed or magnetic resonance imaging and x-ray contrast lymphography are used.
Nonspecific lymphadenitis should be differentiated from other diseases, such as lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, chronic granulomatous disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as metastases from malignant tumors.
What situations can lead to a reaction of the inguinal lymph nodes? First of all, these are various inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (mainly the reproductive and urinary systems), external genitalia, perineum and thighs. This may be infection of skin lesions, local inflammation in the form of a boil or carbuncle, erysipelas of the lower extremities, fungal infection, syphilis or herpetic infection, bacterial or viral disease of the genitourinary tract - chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, tuberculosis and others, primary damage to the lymph nodes with tularemia, plague, as well as generalized infections – HIV infection, tick-borne rickettsiosis and others.
There are other inflammatory diseases that lead to enlargement of the lymph nodes, but they are all accompanied by a different clinical picture, where inguinal lymphadenopathy is far from the first place. Palpable lymph nodes should always alert the doctor, because often malignant tumors metastasize to the lymph nodes, and generalized blood tumors (leukemia) and local tumors of the lymphatic system (lymphomas and lymphogranulomatosis) are always accompanied by damage to the lymph nodes. Metastases to the inguinal lymph nodes can give rise to tumors of the external and internal genital organs: uterus, ovaries, prostate, bladder; the skin itself (melanoma), rectum. The main manifestation, as the name suggests, is enlarged lymph nodes. However, it is especially important to identify additional symptoms, which can provide necessary information for further diagnosis. Detection of visible inflammatory changes in the skin or external genitalia, urination disorders, and pathological discharge from the urinary or genital tract most likely indicate an infectious etiology. Frequent changes of sexual partners and neglect of barrier methods of contraception indicate the possibility of contracting sexually transmitted infections (syphilis, HIV, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea).
A tumor etiology can be suspected in the presence of symptoms of chronic intoxication - prolonged low-grade fever, sweating, weight loss, weakness, coagulation disorders with multiple hemorrhages and many others, as well as most often dense, painless lymph nodes. Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory diseases associated with inguinal lymphadenitis in men is carried out by a urologist and andrologist, and in women by a gynecologist and urologist, and for specific infections, consultation with an infectious disease specialist may be indicated. Suspicion of tumor processes requires a consultation with an oncologist.
For diagnosis, it is especially important to identify additional symptoms during a conversation and physical examination. Additional methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics include a general analysis of urine, blood, biochemical blood test, taking samples for testing for bacterial, viral and fungal infections, cystoscopy (examination of the bladder cavity), vaginal examination in women, rectal examination, ultrasound, MRI , CT and other imaging methods of the pelvic organs and other areas to search for the primary tumor, the use of cytological and histological (biopsy) methods to verify the diagnosis (if a tumor is suspected).
Treatment of inguinal lymphadenitis itself is possible when the nature of the underlying disease is established. For inflammatory diseases, most often this is drug therapy - antibacterial drugs, antiviral and antifungicidal drugs are used to treat inflammation. The prognosis for inguinal lymphadenitis is favorable in most cases.
Treatment of lymphadenitis
Treatment of inflamed lymph nodes is carried out in two directions:
- determining the source of the inflammatory process and eliminating it;
- relief of chronic and acute inflammatory process in the lymph node.
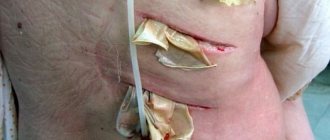
First of all, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the underlying disease that led to infection of the lymph nodes. If purulent inflammation develops, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital, where the abscess is surgically opened.
Treatment of axillary lymphadenitis
Treatment tactics for axillary lymphadenitis depend on the form and cause of the disease. In most cases, lymphadenitis does not require special therapy and goes away on its own after the underlying disease is eliminated. If the process is complicated by suppuration, then the treatment tactics completely change.
General recommendations: maintain rest, immobilize the affected area (do not rub or injure the affected lymph nodes), proper nutrition, take painkillers, anti-inflammatory medications. Therapy for acute axillary lymphadenitis depends entirely on the stage of the disease. Conservative treatment is used for the initial stages: UHF therapy, sanitation of the source of infection (opening of abscesses, leaks, cellulitis, drainage of the abscess), antibiotic therapy taking into account the sensitivity of the microbial flora in the main focus.
Surgical intervention is necessary for purulent axillary lymphadenitis: adenophlegmon, abscesses are opened, pus is removed, and the wound is drained. It happens that a biopsy confirms the presence of a tumor process - benign or malignant. Treatment may include radiation and chemotherapy. In the case of lymphadenitis, as in the presence of any other diseases, it is extremely dangerous to self-medicate.
Back to articles
Drug treatment: drugs most often prescribed
Treatment is complex and includes the use of various groups of medications. It is customary to use the following drugs for lymphadenitis:
- Antibiotics. To eliminate the source of infection (Amoxicillin, Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, Vancomycin, Lincomycin).
- Analgesics. To eliminate pain syndrome (Tramadol, Trimeperidine).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects (“Ketoprofen”, “Ibuprofen”, “Paracetamol”).
- Antihistamines. Helps relieve the inflammatory process (Cetirizine).
- Antiseptics for topical use (Vishnevsky ointment).
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy methods are used - UHF. Ultrahigh-frequency therapy accelerates the elimination of the inflammatory process and enhances local tissue immunity. This method of treatment is contraindicated when the patient has a persistent increase in body temperature, has a tumor process, tachycardia, or muscle pain.
Frequently asked questions about lymphadenitis
What is submandibular lymphadenitis?
This is an inflammation of the lymph nodes that are located under the lower jaw. This form of the disease develops in the presence of an infectious focus in the oral cavity. This could be caries, periodontitis, gum disease, tonsillitis. It is accompanied by symptoms such as pain at the location of the node and redness of the skin above it, increased body temperature, pain during eating and during conversation, general malaise, and headache.
How long does it take to treat lymphadenitis?
The duration of treatment for the disease depends on a number of factors: the form of the disease; the presence of a purulent process; causative agent of lymph node inflammation. To completely eliminate the inflammatory process and eliminate pathogenic microbes in uncomplicated lymphadenitis, the course of treatment will be about two weeks. In the chronic form of the disease, therapy is long-term.
Is it possible to warm a lymph node?
Thermal effects on the inflamed lymph node are allowed when the inflammatory process has not yet been complicated by the formation of pus. It is believed that warming compresses with camphor oil or infusion of medicinal herbs help relieve pain and inflammation. However, you should consult your doctor before undertaking warming procedures, as such actions may worsen the infection. If the skin over the inflamed lymph node is red, then warming it is contraindicated, as this is a sign of suppuration.
How to recognize lymphadenitis?
The inflammation initially develops asymptomatically. But soon, characteristic signs of lymphadenitis appear:
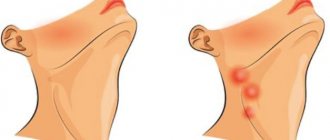
- enlarged lymph nodes under the lower jaw, pain when touched;
- redness of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- swelling;
- attacks of throbbing pain;
- insomnia;
- difficulty swallowing;
- heat;
- weakness;
- increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood.
Of course, these symptoms do not appear in 1 day. And many people ignore the appearance of mild pain. But if you do not consult a doctor at this time, the picture of the disease will become obvious in just 3 days. The lymph nodes will become inflamed, swollen, and the edema will gradually cover the entire submandibular surface. Patients become lethargic, complain of fatigue, weakness, and high fever. They cannot eat because the inflammation prevents them from opening their mouth normally and sleeping due to pain and fever.
If you continue to ignore the symptoms and postpone a visit to the doctor, the inflammation will become purulent, which will result in blue swelling and increased pain. To prevent this from happening, you should contact a dental surgeon at the DaVinci aesthetic dentistry studio.
The sooner the patient contacts the dentist, the easier it is to eliminate the infection. But many people themselves try to diagnose themselves and choose treatment, which leads to the spread of inflammation and aggravation of the above symptoms. Treating the disease in advanced stages is more difficult and takes longer.