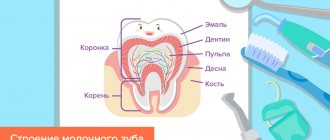
Temporary teeth
Timing of teething
Dental buds are formed during the period of intrauterine development. The eruption of the first teeth begins at the twenty-fifth week of the baby’s life. The lower incisors appear first, followed by the upper ones by eight months. The age at which baby teeth, called premolars, erupt varies from one to two years. The last to appear are the canines and second premolars, which occurs from sixteen to thirty months.
This teething schedule is optimal, but it is impossible to determine the exact timing. The process depends on the characteristics of the child’s body, the health of the mother during pregnancy and genetic factors.
Timing of teething in children in the table
| Type of tooth | Lower jaw | Upper jaw |
| Medial incisor | 6 – 10 months | 7 – 12 months |
| Lateral incisor | 7 – 16 months | 9 – 13 months |
| Fang | 16 – 23 months | 16 – 22 months |
| First premolar (baby molar) | 12 – 18 months | 13 – 19 months |
| Second premolar (baby molar) | 20 – 31 months | 25 – 33 months |
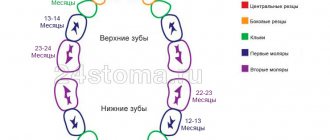
The order of teething in children
The teeth follow the principle of pairing, for example, if one fang appears, a second one should be expected soon. The sequence of teething is determined by nature based on the practical significance of dental units for survival.
The front teeth of the lower row grow first, then the upper ones come. The lateral incisors disrupt the order of teeth eruption; their appearance begins with the upper jaw. Then comes the eruption of chewing teeth - the first premolars. The last to emerge are the canines and molars. The process of teething in children is completed by the age of 2-3 years.
Diagram of baby teeth eruption in children
How many teeth should a child have at 3 years old?
All twenty baby teeth appear by about 2-2.5 years. It includes eight incisors and molars, as well as four canines. By this time, they are erupting, including in the wrong direction, but by the age of three, in most cases they occupy a normal position, since the child is actively chewing food.
If by the age of three a boy or girl does not have a full set, do not panic. This may be an individual characteristic of the child. To be sure, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician and dentist to clarify the cause of the delay and rule out rickets, metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases.
Permanent teeth
Timing of teething in children
The first permanent teeth appear several months before the baby teeth fall out—the molars, or “sixes,” erupt. This occurs at the age of six. By the age of eight or nine years, it is the turn of the incisors. When a child is ten to twelve years old, premolars and canines erupt. Next come the second molars, the eruption of molars is completed by adulthood.
Important!
Wisdom teeth appear much later, after twenty years. However, their complete absence is also the norm.
Timing of teething in the table
| Name | Lower jaw - time of eruption | Upper jaw - eruption time |
| Medial incisor | 6 - 7 years | 7 - 8 years |
| Lateral incisor | 7 - 8 years | 8 - 9 years |
| Fang | 9 - 10 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First premolar | 10 - 12 years | 10 - 11 years |
| Second premolar | 11 - 12 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First molar | 6 - 7 years | 6 - 7 years |
| Second molar | 11 – 13 years | 12 - 13 years old |
| Third molar | 17 – 21 years old | 17 – 21 years old |
Teething order
The pairing principle also applies to permanent dental units. The correct sequence of teething is important for the formation of the bite; it is necessary to carefully monitor the time of loss of baby teeth and the order of growth of molars.
The lower molars appear first, then the upper ones. Next, the temporary teeth of the lower jaw fall out, the permanent teeth erupt, and only then the upper dental units are replaced.
This schedule for teething in children is not universal, but if there are significant deviations, you should consult a specialist.
What teeth appear first in children?
The rudiments of baby teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development, so modern diagnostic technologies make it possible to track this process and prevent some deviations. After birth, the first teeth usually begin to erupt when the baby reaches six months of age. This means he will soon be ready to eat more solid foods. In the vast majority of cases, the incisors appear first: as a rule, the lower central incisor becomes the “pioneer”.
Signs of teething
Symptoms of teething in infants
The appearance of baby teeth is a little more difficult than that of permanent teeth, since the baby has not yet encountered pain and cannot understand what is happening to him. Teething in children under one year of age is accompanied by the following signs.
- The most common symptom of teething is fever. An increase to 38 degrees within three days is normal.
- Swelling of the gums. Often, when children are teething, their gums swell, their sockets itch, and they have a desire to chew hard objects. It is important to prevent the child from damaging the mucous membrane; it is better to buy a special teether to relieve discomfort.
- Decreased appetite. Children refuse to eat due to stress or itchy gums.
- Teething syndrome. Neurosis, tearfulness, anxiety, poor sleep and whims may indicate the imminent appearance of the first tooth, even if the child does not experience pain, fever or swelling of the gums.
Important!
An increase in white blood cell levels during teething should not be a cause for alarm. This is a common occurrence associated with a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of eruption of permanent teeth
A change in temporary bite is accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. The process has the following characteristics.
- Root resorption and loss of baby teeth. A sure signal of the appearance of a new tooth in the coming months.
- Increase in jaw bone size. Permanent teeth are larger than baby teeth, the jaw grows, creating conditions for a change in bite.
- Pain in the gums. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane are a reaction to teething.
Important!
Body temperature above 38 degrees, cramps, refusal to eat and difficulty breathing are not symptoms of the appearance of milk and permanent teeth. These are signs of an infectious disease. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
Causes and consequences of dental pathology
Abnormal two-row growth is possible for many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic colds and decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of soft foods and purees;
- lack of vitamins and useful elements;
- premature removal of milk units;
- disturbance in the location of tooth germs.
With timely treatment, the orthodontist will easily straighten the bite and place each tooth in its proper place. If you delay visiting a doctor, the consequences can be serious:
- malocclusion;
- problems with hygiene and the development of caries;
- facial deformation due to jaw imbalances;
- ugly smile.
A sign of a potential shark jaw is the absence of gaps between the teeth in a 4-6 year old child. Insufficient space is the first prerequisite for the appearance of a second row of teeth in children and a signal for an attentive parent.
It is easy to see an incorrectly growing tooth, especially in the lower jaw. During the period of change in bite, dentists recommend monitoring the process - periodically conducting home or professional examinations and listening carefully to the baby. Complaints of discomfort in the mouth, inconvenience of chewing and pain indicate the need to visit a dentist to assess the condition of the oral cavity.
Painful teething: advice for parents
When faced with teething in children, many parents are at a loss. First of all, you need to call an ambulance and determine the reason for the baby’s poor health. If symptoms are confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medications for teething - antipyretics and painkillers.
You can treat your gums yourself with an anesthetic gel with a cooling effect to reduce itching and swelling of the mucous membrane. Ice will also help. To reduce gum irritation, there are special silicone fingertips made of hypoallergenic material.
Folk remedies for teething will effectively relieve painful sensations - a decoction of chamomile, sage, tincture of valerian and honey will soothe inflamed tissues.
Painkillers for teething are contraindicated in children; this can worsen their health.
Important!
Without a doctor's recommendation, antibiotics and other strong teething medications can cause an allergic reaction.
Features and anomalies during the eruption of baby teeth. Why and what to do?
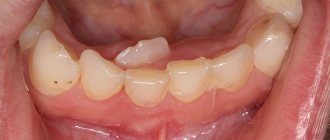
The period of teething is one of the most difficult in infancy. Especially if the baby has problems. In this article we are not talking about fever, cough, runny nose and diarrhea during teething. We will focus on more serious troubles. And they, lately, are becoming more common and different. And the most harmless of them is that the child’s teeth grow crookedly. This happens often in children. Now we will only talk about baby teeth! Permanent teeth are a separate matter.
Milk teeth rarely grow crooked. More often, parents are concerned about the spaces and gaps between their baby teeth. In both cases, it’s okay. The fact is that the rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the first months of pregnancy. On a small jaw, the teeth are located close to each other. As the jaw grows, the teeth move away from each other and uniform gaps form between them. If the gaps are uneven - very large (three), this may indicate the absence of individual teeth or uneven growth of the jaws - contact your dentist.
If a child has a crooked tooth growing, or baby teeth are growing very crowded, there may be several reasons:
- poor nutrition of the mother during pregnancy, when tooth buds were forming;
- lack of calcium, microelements, vitamins in the child’s diet (with a monotonous diet);
- insufficient load on the baby's teeth - when feeding only liquid, ground food after 8-10 months. It is imperative to let your child chew apples, carrots, peels, and dried fruits on his own;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx: runny nose, tonsillitis, adenoids, which provokes constant mouth breathing;
- bad habits: pacifier, finger sucking, sleeping with a pacifier in the mouth, bottle feeding after a year. It is necessary to teach your baby to drink from a cup, eat with a spoon, and chew age-appropriate food sooner.
All these factors, as well as heredity, can cause improper growth of baby teeth. Crooked baby teeth can only be treated by a pediatric dentist, who can assess the complexity of the problem, because often the teeth straighten on their own as the baby grows. But there is no need to rely on this, because you may miss more serious problems. After all, crooked baby teeth in children - photo can cause improper growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth, and therefore their curvature, loss from the dentition, etc.
There are other features of the growth of baby teeth. The most common:
- increasing the spaces between teeth. The large gap between the upper frontal incisors is a consequence of the deep location of the maxillary frenulum. Consult an orthodontist at the Utkinzub clinic;
- the black edging of the cervical zone of the teeth is a violation of the absorption of iron, which provokes increased proliferation of leptotrichia bacteria. Treatment by a dentist and treatment of the cause by a pediatrician;
- yellow-brown teeth already when teething ( the child grows dark teeth ) is the result of the mother’s treatment with tetracycline antibiotics during pregnancy (tetracycline teeth);
- greenish staining of baby teeth – metabolic disorders, in particular bilirubin. Also observed in hemolytic diseases associated with the destruction of red blood cells. A complete medical examination is indicated;
- Red baby teeth occur with the disease “porphyria” and appear as a result of a violation of the metabolism of porphyrin - a red pigment. A complete medical examination is indicated.
- gray, soft teeth – lack of enamel coating, hypoplasia. Appears when the mother has a malnutrition during pregnancy or as a result of metabolic disorders in the child. Contact your dentist.
Other developmental anomalies of the dental system may be associated with genetic diseases, constitutional causes, congenital developmental anomalies, and tumors. (“Absence of milk teeth – adentia. Second row of teeth”) All the above-described cases of abnormal development, including crooked teeth in children , are a reason to contact a pediatrician and pediatric dentist as soon as possible. The sooner the cause of the anomaly is identified, the greater the chances of quickly and effectively correcting the situation and guaranteeing the child a full, healthy life.
Deviations in teething
Minor changes in the timing and sequence of dental growth should not cause alarm. However, significant deviations from the norm in teething are a cause for concern.
- The tooth does not appear for a long time. Reason: genetic predisposition to long eruption or lack of rudiments.
- Too early appearance of teeth. Caused by disruption of the endocrine system.
- Black or brown enamel surface color. Indicates high iron levels, poor salivation, or chronic inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
- Incorrect row position. Bite pathologies indicate a hereditary factor or deformation of the maxillofacial bone.
Tooth growth abnormalities in children
Unfortunately, the development and growth of teeth in children does not always occur as expected: there are a number of anomalies of various types that in one way or another affect the aesthetics and/or functionality of the teeth.
Causes of impaired growth and development of teeth:
- bad heredity;
- fetal injury during pregnancy or birth; intrauterine growth retardation, infections and so on;
- disruption of the endocrine system, thyroid dysfunction;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries to teeth;
- bad habits in children that can affect the formation of teeth;
- lack of proper hygiene and poor diet.
Below is a table that describes the most common types of dental anomalies in children.
| Anomaly class | Description |
| Size of teeth | There are microdentia (too small teeth) and macrodentia (too large teeth). The anomaly can affect one or several teeth (and even the entire dentition). |
| Number of teeth | There is partial (lack of several teeth) and complete (absence of all teeth) adentia. Hyperdentia is a supernumerary set of teeth (usually in the second row). |
| Shape of teeth | Cone-shaped, barrel-shaped (Hutchinson's teeth), Pflueger's teeth (the neck is more developed than the coronal part). |
| Anomalies in the structure of enamel and dentin | Hypoplasia (spots and grooves on the body of the tooth), hyperplasia (tubercles, enamel drops, etc.), dentinogenesis imperfecta (violation of the structure and color of dentin). |
| Color irregularities | Enamel pigmentation (gray, black, amber enamel color). Most often it is caused by a disruption of the immune system during the prenatal stage of development. |
| Malocclusion | All types of dental malocclusions: mesial, cross, open, deep and so on. |
Despite the fact that some dental anomalies in children are quite serious, a timely visit to the dentist will help you avoid problems and maintain the health and beauty of your smile. If you let the situation take its course, unpleasant consequences will not keep you waiting.