How dangerous is this?
A tooth is not a completely foreign body. This is a part of the victim’s body, which is also small and does not have serious dangerous properties such as toxicity. No human tooth is large enough to cause significant problems if it enters the stomach and esophagus.
It is very difficult to swallow the entire jaw
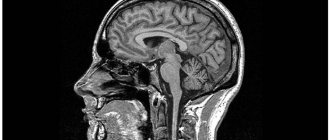
If you swallowed a tooth, you know about it, but you don’t feel it anywhere above the stomach, then there is nothing to worry about - it has already reached the center of the digestive system and will eventually come out naturally. The danger arises when a tooth gets stuck in the esophagus. It doesn’t matter whether it’s a solid tooth or a splinter, there is a high probability that it will have sharp edges. They are too small to seriously damage the mucous membrane of the throat, but they can cause panic and suffocation in sensitive people. It is not easy to push a tooth further out of the esophagus if it is stuck - those who have experienced such trouble associate their sensations with a fish bone stuck in the throat, only smaller.
The most dangerous situation is a tooth getting into the windpipe. This rarely happens, but it is necessary to act quickly and clearly. No fatal cases have been recorded, but the victim may even lose consciousness due to lack of oxygen and a panic attack.
What to do when a filling falls out
Further treatment tactics depend on the patient’s behavior after the temporary filling falls out. If you do not take any action and wait for your appointment, then most likely the doctor will have to re-clean the tooth cavity or even carry out additional procedures to eliminate pathological processes that have arisen due to external factors. An open tooth is accessible to all infections and is highly undesirable at any stage of treatment.
If the filling falls out on the day of installation
In cases where the temporary filling falls out after 2 hours or approximately this time, you must immediately contact a specialist for re-filling.
What should you do if a temporary filling falls out in the evening, when you can no longer visit the dentist? In such a situation, it is necessary to close the cavity. For this, for example, you can purchase a special dentin paste or its analogues at the pharmacy. You should try to remove the remains of the filling, but without using sharp objects, so as not to damage the internal tissues and channels. After this, the cavity is filled with paste, and the next day they are sent to the attending physician.
If it is not possible to purchase such a paste, it is recommended to minimize food intake and constantly rinse your mouth with mouthwash or other antiseptic agents. Rinsing is necessary after each meal to flush out food particles from the exposed tooth that may get into the cavity.
Loss of filling in sealed and unsealed canals
The greatest risk occurs when a temporary filling falls out and the canals are not sealed. Due to the high probability of contamination of the dental canals, the patient should also “seal” the tooth with paste, or rinse the tooth regularly. You can also use a soda solution for rinsing. On the same day or the next day, the patient must go to the clinic to take measures to close the cavity in the crown.
If a temporary filling falls out, but the canals are sealed, what should I do? In such patients, the likelihood of complications is minimal, since neither infection nor foreign particles can penetrate into the canals themselves. But it is still impossible to leave the cavity open, since the crown is weakened and its internal tissues are not protected from mechanical stress. Patients are also advised to rinse as a preventative measure and to see a dentist again, who may even install a permanent filling right away.
What can be done and what should not be done?
It is difficult for the victim himself to assess how deeply the tooth has sunk. Independent attempts to remove it from the esophagus will lead to a gag reflex and, possibly, new damage to the oral cavity.
What not to do:
- Trying to reach the tooth with your fingers and especially with foreign objects
- Panic and try to “cough up” the interfering object
- Do nothing and hush up the problem, expecting it to go away on its own
Examine the gums if possible. If a tooth has fallen out or crumbled, then you should know what condition it was in in the near future. A small analysis will help you understand how big the chip is now in your throat; careful palpation of the gums from below will help you determine whether the root remains inside.
If there is no sensation of pain in the larynx or esophagus, then the natural way of exiting the swallowed tooth is most likely and there is no reason for concern
With all this information, go to your dentist or immediately to a traumatologist if you have difficulty breathing. The specialist will tell you what to do now, and at the same time will diagnose other teeth, warning of possible danger.
If a crown or filling is swallowed
Fillings with sharp edges carry the same potential danger to the esophageal mucosa as teeth, but they are much smaller in volume. Fillings may also not fall off completely, but rather break off into small fragments that pose almost no danger.
Important! If a fresh filling is swallowed, immediately contact the dentist who placed it. It was either placed incorrectly or fell out due to its unreliability. An infection should not get into a hole recently filled with a filling - the chance of infection and inflammation is very high.
A swallowed crown will not cause any harm in itself, but you should visit the dentist as soon as possible to protect the remaining tooth without a crown.
The crowns are also small in size and if they get into the esophagus and further, they will not cause harm (except for possible micro-scratches). If a filling or crown falls out, you need to immediately fix this problem by installing a new one, even if the tooth does not hurt or bother you in any way. Open dental canals and healthy parts of the tooth will begin to deteriorate after a few weeks from eating food or hot liquids. Due to delay, there may be a need to completely re-treat the tooth.
How to behave immediately after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is prescribed only in exceptional cases when it is no longer possible to do anything conservatively. Indications for extraction are gumboil, phlegmon, advanced periodontitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw, severe malocclusion, cyst, complete destruction due to injury, inflammation of impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth, tumor formations. Usually the operation is performed planned on an outpatient basis, sometimes urgent removal with inpatient recovery is required.
There is no need to be afraid of the removal procedure. Thanks to modern technologies and anesthesia, it is quick and almost painless. But it is very important to behave correctly immediately after the operation and maintain a gentle lifestyle and diet for some time.
During tooth extraction, tissue and blood vessels are inevitably injured. This leads to bleeding, which can be either minor or severe. First of all, to stop the bleeding, the doctor places a gauze swab into the hole. It should stop in 15-20 minutes, and the patient can go home. If the wound is serious or there are problems with blood clotting, local hemostatic agents will be needed.
Even if the bleeding stops quickly, it can start again. At home, you also need to apply sterile gauze swabs. In addition, in case of severe pain, it is allowed to take painkillers - Ketanov, Nimesil. Continued pain may indicate the development of inflammation - in this case, you should urgently consult a doctor. You may have to take antibacterial agents (antibiotics).
After surgery, swelling of the gums and cheeks often appears. To relieve hyperemia, cold is applied, for example an ice pack. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 10-15 minutes, otherwise the dental nerve may get cold. Under no circumstances should you apply warm compresses - this will lead to inflammation and bleeding.
Oral hygiene should be canceled on the day of tooth extraction. Starting from the second day, you can brush your teeth very carefully with a soft brush. In this case, the wound must be avoided. Hygienic procedures help cleanse the gums and speed up healing. Rinsing your mouth with alcohol and rinses is prohibited. You can make non-hot baths with herbs (sage, chamomile) at the rate of 1 tablespoon of dry mixture per glass of boiling water.
These simple rules must be followed so that the wound heals quickly and an implant can be placed.
Is it possible to do without visiting a doctor?
It is possible if no discomfort is felt. Tooth enamel and the “body” of the tooth do not pose any threat even if they are damaged by caries. The body will easily tolerate this and “pass” a foreign object through the gastrointestinal tract without damage.
The closest analogy is to imagine that you swallowed a cherry pit.
A swallowed crown or filling is still worth a visit to the doctor in any case. This way you can prevent further destruction and not endanger neighboring healthy teeth.
Causes of food getting stuck between teeth
The main reason for food getting between the teeth is a violation of the density of their contact with each other (in dentistry this concept is referred to as a “contact point”), which can be caused by:
- low-quality fillings (prostheses). An incorrectly placed filling may not exactly follow the topography of the tooth and may have an overhanging edge. A sign of poor quality fillings can be either stuck food or breaks in the dental floss during its use;
- natural structure of the dentition. This may be curvature of the teeth, diastema (gaps between the lower or upper central teeth), trema (gaps between the lateral teeth);
- deformation of the dentition due to injury, tooth extraction, and various diseases of the oral cavity.
- Unprofessional prosthetics. There may be a gap between the crown and the tooth; the denture design does not correspond to the anatomical shape.
- There is no papilla between the tooth and gum. It fills the interdental space, and in the absence of such a papilla, the problem of food getting stuck appears.
- Crevices. May appear as a result of injuries or diastema. As a result, pieces of hard food constantly get stuck in the cracks, which have to be removed with thread or a toothpick.
- Loss of teeth. As a result, the integrity of the dentition is compromised, which provokes the occurrence of the problem in question;
- Caries. As a result of carious lesions, the enamel is destroyed and a cavity is formed. Residues of food accumulate here, which can only be removed purposefully: ordinary rinsing and salivation will not cope with this task.
Binge eating
This mistake is made by people who are not familiar with the structure of the digestive system. The only option when this solution can be partially correct is that the tooth is stuck at the end of the esophagus and you feel it somewhere above the stomach.
You can eat a small piece of black bread (white is more sticky), fruit or vegetable (preferably with a dense consistency). If after this the sensations do not change in any way, try again in half an hour. You can drink water.
Important! Feelings can be distorted by worry and anxiety - there have been cases when people, frightened by far-fetched threats, feel pressure and scratches from within that are not there. You can check your condition with a moderate sip of water.
In addition, a swallowed crown or other metal element of dental corrective structures will not be visible on an x-ray due to the large amount of food in the stomach and waste in the intestines.
Prevention
- A healthy lifestyle and daily oral care using personal hygiene products will help prevent the development of gumboil. For cleaning, use a medium-hard brush.
- After each meal, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a special mouthwash or use dental floss. Instead of a pharmaceutical composition, it is allowed to use an aqueous solution of food salt, sea salt or an alcoholic tincture of propolis.
- Do not use non-sterile objects as toothpicks. Such actions lead to mechanical injuries and infection.
- Periodic professional dental cleaning helps remove stone, which provokes the development of inflammation of the gums with pus.
- The daily diet must be supplemented with fresh vegetables and fruits. Apples, carrots and other solid plant foods cleanse plaque from enamel and strengthen teeth.
It is also important to treat dental defects immediately and undergo regular clinical examinations at least twice a year. It is much easier to prevent dental disease than to treat its negative consequences. You should be attentive to your health and not ignore the warning signals that your body gives.
Inducing vomiting
Inducing vomiting is a very bad idea. If a tooth is stuck in the esophagus, this may not help, and getting it out of the stomach at the cost of dehydration and possible digestive upset is too costly in terms of the resources of the human body. It should be remembered that vomiting is an emergency defense mechanism, and not a normal state of the body. To cause it yourself means to consciously undermine your health.
Even if the tooth really got stuck on the way from the esophagus to the stomach, a sharp influx of semi-digested food from below will push it with enough force for the sharp edges to leave a scratch on the mucous membrane.
Are there medications that will improve the situation?
There are no solutions aimed at solving this specific problem. Such medications are not sold because the problem is not significant and will soon resolve itself or with minimal help from doctors.
Under no circumstances should you use drugs that artificially speed up digestion - this will cause no less harm to the body than vomiting.
Dehydration, stopping the healthy digestive process, pain, loss of appetite - all these symptoms can appear if you take the drug without appropriate indications.
If the tooth is severely stuck and scratched, no medications will help - go to the emergency room, where foreign objects are pulled out of the esophagus every day. This can only be done by a professional physician who knows how the esophagus works and will not damage it. If you don’t want to wait in line at the clinic and search for the right office, you can find a private dental office - usually there is at least one of these in every area.
The child swallowed a foreign body
- “This won’t happen to me! I'm an attentive mom! All small toys are put away in cabinets without handles, I’m ready for the baby to crawl soon and my house is safe for him!”
I would like to say so, BUT... So we came to visit my grandmother, and she had a cube on the sofa - the older grandchildren did not put away the game - they were walking with them... And I noticed this cube when my son already had it in his mouth. And at this moment the main thing is really not to panic! Because if you say sharply and loudly to a child “spit it out” or “what do you have there?!”, while exuding fear with your whole appearance, you can get a swallowed toy.
I smiled at my child and asked him to show me what he had found, and luckily for me, the toy was in my hands. Was I scared? - VERY!
So what to do if the situation is out of your control?
So, if your baby has swallowed or inhaled a foreign body - a toy, a button from the carpet or some other trifle: ⠀ 1. The first rule is DON’T PANIC!
The most critical situation is that a foreign body has entered the respiratory tract.
A) If an object is stuck in the nasal passages (children often try to push cherry seeds there because they are curious - what will happen?), then in no case try to get the object yourself, do not use tweezers or other devices, as this will only make the situation worse by pushing the object even deeper! If your child knows how to blow his nose, then close the “healthy” nostril and ask him to exhale through his nose. If ineffective or at an early age, you should consult a doctor!
C) If a foreign body gets into the respiratory tract, DO NOT knock on the child’s back or shake under any circumstances! Your task is to turn the baby upside down by the leg or throwing him over the knee, then try to remove the object using tapping and pushing movements. If these measures are ineffective, then in the same diagonal position (head below the butt) you need to take the child to the doctor URGENTLY!
If your baby swallows an object and it gets into the stomach, it means that the foreign body has passed through the esophagus - the narrowest opening of the digestive tract. Otherwise, such striking symptoms as coughing, vomiting and pain while drinking and eating would occur. These manifestations indicate that the object remains in the esophagus - see a doctor URGENTLY!
If, fortunately, there are no these symptoms, a foreign object can be expected in the pot after 2-4 days. On this day, an examination by a pediatrician is required. And if the doctor, after a thorough examination of the baby, concludes that the child’s health is not in danger, the object will come out naturally, but the contents of the diaper will have to be monitored. If the item has not come out by the end of 4 days, contact a doctor.
WHAT NOT TO DO if you swallow a foreign body? Feed the baby intensively and thoroughly - bread, thick cereals; try to induce vomiting (by pressing on the root of the tongue or drinking plenty of water); give enemas and laxatives.
All these procedures can harm the child even more, especially if the swallowed object is large or has a non-round, complex structure.
Sorbents can be used, but there will be no benefit or harm from them.
⠀IF VOMITING STARTS: clean the child’s mouth, turn his head to the side so that the airways are clear.
Don't wait until everything goes away on its own - CALL A DOCTOR IMMEDIATELY IF your baby swallows:
- Toxic item or substance (soap, powder, alcohol, plasticine, glue)
- Sharp object
- Large item
- “active” item (batteries, magnet, coin)
Who can we contact:
- surgeon
- pediatrician
- toxicologist (in case of poisoning or ingestion of a toxic substance).
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist of the DIALINE network of multidisciplinary clinics Oksana Vladimirovna Bolshakova
Make an appointment
What to do if a child swallows a tooth?
Children are the ones who swallow teeth most often - they chew faster, are in a hurry and know little about handling sick and weak teeth. A parent may not know for a long time that a child’s molar is weak or crumbling; children often hide such information in order to delay a visit to the dentist.
Young children lose their baby teeth, which they often accidentally swallow.
It is better to explain to the child in advance that there will be many more teeth that fall out and you should handle them more carefully. A tooth scratching the throat will cause a baby much more anxiety than an adult - he may start crying, unable to get rid of the irritant.