Nature has provided for everything
Losing baby teeth is a natural and inevitable process that everyone goes through in childhood. Most often it begins at 5-6 years of age and passes painlessly. Sometimes the replacement of temporary teeth may begin earlier or, conversely, late. Some deviations from the usual indicators are not always considered a violation, since much depends on the health and physiological state of the child. When he begins to change his teeth, we recommend making an appointment with the dentist, as this is a very important period for the formation of your baby’s bite.
What to do if a child has a dental injury
- If the injury is combined with a fall or a strong blow, you should immediately visit the emergency room and make sure that the child does not have a concussion or fractures, including facial bones - jaw, nose, etc.
- If other injuries are excluded or you are sure that it was the tooth that was damaged, you can immediately go to an urgent appointment with the dentist. If you have a tooth injury, we will see you immediately, since the speed of action often determines whether the tooth can be saved.
- The dentist numbs the area of the injury, determines the type of injury and prescribes treatment. In some cases it starts immediately, sometimes you need to wait a little. Treatment of a tooth injury can last up to a month.
It is important to correctly diagnose and treat an injured tooth to prevent complications. Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
What you should pay attention to
The child’s body prepares in advance for the period of teeth change. Here are the main signs of the changes taking place:
- mobility and loosening of primary teeth
- redness and swelling of the gums
- the appearance of interdental spaces due to jaw growth
- the rudiments of a permanent tooth become visible
When a baby tooth is replaced with a permanent one, the root gradually dissolves. The process is helped by a new tooth pushing out the temporary one from below.
Usually children and their parents remove the loose tooth themselves. But we recommend contacting a specialist who will provide professional assistance.
A baby tooth falls out, why and how it happens
Changing a child's baby (temporary) teeth to permanent ones is a natural process. It occurs as the jaw bones grow and develop. The task of parents, when baby teeth fall out, is to treat this with increased attention. There are often cases of malocclusion in children, which subsequently have to be corrected for a long time and then treated. One of the main reasons for this is a violation of the sequence of loss of primary teeth.
In what order do teeth fall out?
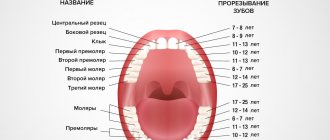
The loss of baby teeth occurs in the same order in which they first erupted. First, the child loses the lower and upper incisors, then the lateral molars, and lastly the canines. The replacement of baby teeth with permanent teeth begins at the age of 5.5 years and ends at the age of 13. At the same time, instead of 20 dairy ones, 28 permanent ones grow. There is room for eight new chewing teeth due to the expansion of the jaws. By the way, wisdom teeth most often erupt in adulthood, and for some they do not grow at all.
Sequence and estimated dates
Parents should know which baby teeth fall out first in children, as well as the sequence. Doctors adhere to the following scheme:
- Central incisors - 5-7 years;
- Lateral incisors - 7-8 years;
- Molars (1st upper jaw, 2nd lower jaw) - 9-11 years;
- Fangs - 9-12 years;
- Molars (2nd upper jaw, 1st lower jaw) - 10-13 years.
It is important to take into account that here is a generally accepted scheme and approximate dates when baby teeth fall out and permanent ones begin to appear, but depending on many factors there may be some changes that can be considered normal. However, if significant deviations are noticed, you should not delay your visit to the doctor.
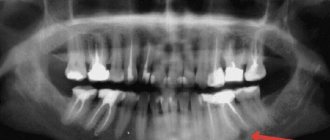
What to do if a tooth does not fall out in time
According to statistics, in 20-30% of cases, children experience a “shark smile” when the permanent tooth has already erupted and is growing, but the milk tooth has not yet fallen out. Clinical studies have proven that in such a situation, parents should not hesitate to go to pediatric dentistry. The doctor will carefully examine your child's mouth and remove the temporary tooth. If you do not contact the dentist in a timely manner, double dentition can lead to improper formation of the bite, impaired diction and the functioning of the digestive system. In addition, with a “shark smile” it is difficult for a baby to bite and chew food, particles of which remain between the teeth and under the gum. As a result, inflammatory processes and caries occur. All this can be avoided by making an appointment with a specialist.
Features of baby teeth
Now I will answer another very popular question: “how do baby teeth differ from molars?”
These are the baby's very first teeth. They appear before the age of three, and begin to erupt until there are 20 teeth. See the photo above for the cutting diagram.
They do not have such deep roots as permanent teeth, have a more rounded shape and smaller size, and are white in color, while permanent teeth have a yellowish tint. By location, they are directed vertically, and the radicals are slightly outward.
Wisdom teeth cannot be milk teeth, because they grow into deep roots only by the age of 18-20, and sometimes later.
Orthodontic treatment – caring for the future
Some parents do not attach importance to the fact that the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the permanent one is already emerging. Or, on the contrary, the temporary one is lost early, and the tooth that replaces it does not grow. If you notice deviations, we recommend that you contact an orthodontist as soon as possible, who will provide effective treatment.
For example, with the premature loss of a baby tooth, the free space is very quickly taken up by neighboring teeth. There is not enough space for a permanent one. Therefore, it is very important when forming a temporary occlusion to fill such gaps, preventing the occurrence of an occlusion anomaly. To hold space for a permanent tooth, orthodontics uses a plate with artificial teeth. For single defects, a non-removable “ring-loop” design is most often used. The device does not cause discomfort, and the child wears it until the permanent tooth erupts.
The product manufacturing process is standard: impressions are taken, models are made, and the design is created in the laboratory within two weeks. Its fixation takes 15-20 minutes. After installing the device, you do not need to drink or eat for 2 hours. It is better to limit the consumption of “pulling” foods - toffees, chewing gum, etc.
How to behave if your child’s first tooth falls out?
The first baby tooth that falls out is another step towards growing up. So why not mark this event with some interesting ritual for the child, so that further loss will be easier for the baby and bring more joy.
Tooth Fairy
Give your baby a little magic. Let the good sorceress take the first tooth from under the pillow while he sleeps, and in return leave a small gift: candy, a coin or a toy. The next baby tooth that falls out will bring joy to the baby.
Mouse
Another tradition that children really like is to give a lost tooth to a mouse. The mouse will chew the old tooth, and a new one will appear in its place.
Together with your baby, you need to find a secluded corner in the house and put the fallen tooth there. At night, a mouse will run into the corner and take it away.
We hope that falling out baby teeth and emerging permanent teeth will not cause trouble for either children or parents. And to make the first molars give the baby even more joy, we have developed a special Asepta Teens toothpaste to protect and strengthen the enamel of permanent teeth in children over 8 years old. The paste increases the resistance of enamel to bacteria and acids, helps saturate teeth with calcium and phosphorus, and provides effective protection against caries and gum inflammation. And the rich taste of apricot, peach and cream will turn brushing your teeth into a real treat.
Doctors are our pride
We did the research and found out why they trust us. In reviews
On our website, parents note the highly qualified doctors who have knowledge of several related areas and have extensive experience
working with children
. This allows you to see the clinical picture as a whole and plan treatment correctly.
In 2022, family dentistry "DOMOSTOM" in Domodedovo entered the TOP 100 private children's dental clinics in Russia according to the rating of the expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile with the support of Kommersant Publishing House.
Our clinic’s team of professionals knows how to help your child. Sign up for a consultation with us. Attentive doctors will tell you in detail about the condition of the baby’s oral cavity and answer all questions.
Anatomical differences between primary and permanent teeth
As we said above, temporary teeth differ from permanent teeth in a smaller number, as well as in significantly smaller sizes (they are 2 times smaller than permanent teeth).
At the same time, the shape of the crowns of primary teeth is always more spherical, and in the area of the neck of the primary tooth there will always be a noticeably more pronounced narrowing. In addition, temporary teeth are whiter than permanent teeth and often have a bluish tint. Differences between temporary and permanent teeth (description below) –
Anatomical differences:
- Tooth enamel – the enamel of temporary teeth is much less mineralized (saturated with minerals, primarily calcium and phosphates). Therefore, with insufficient oral hygiene, children develop caries almost instantly. In addition, the thickness of the enamel of temporary teeth is approximately 2 times less than that of permanent teeth - this circumstance leads to a very rapid transition of caries to pulpitis. There are also many microcracks and pores on the surface of the enamel of temporary teeth.
- Dentin of the tooth - the dentin layer is located under the layer of tooth enamel, and its thickness is also 2 times less (than that of permanent teeth). The dentin of temporary teeth is lighter, it is less mineralized, softer, and therefore it is much easier to prepare with a drill than the dentin of permanent teeth. Due to the fact that dentin is less mineralized and softer, the carious process in dentin spreads deeper faster, which leads to the rapid development of pulpitis in baby teeth.
- Pulp (neurovascular bundle) - some parents ask: “Are there nerves in baby teeth?” Of course, they exist, but due to the thinner layers of enamel and dentin, the pulp in baby teeth is located much closer to the surface of the tooth. The pulp chamber (tooth cavity), in which the pulp is located, is always larger in primary teeth, and therefore the pulp occupies a relatively large volume in the tooth. And besides, in baby teeth the “pulp horns” (processes) are more pronounced, which creates an additional danger of injury to the pulp during the treatment of caries.
- Roots of teeth – some parents ask: “Do baby teeth have roots?” Of course, they have roots, but they are thinner and widely spaced (at the same time, the root canals and apical openings in baby teeth are wider than in permanent teeth). But the development and growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth leads to the formation of constant pressure on the roots of primary teeth, which leads to their gradual resorption and loss. We hope that our article: Scheme of loss of baby teeth in children was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dentist, 3. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (EU), 4. National Library of Medicine (USA), 5. “Pediatric therapeutic dentistry. National leadership" (Leontyev).