Many parents have encountered the problem of a red throat in their child, which in most cases indicates inflammation. In this regard, it is very important to correctly determine the cause that caused the pathological process, since the effectiveness and success of treatment directly depends on this. And the first thing the otolaryngologist has to find out is: what is the nature of the disease - viral or bacterial?
We will tell Kaliningraders about all the nuances of the problem: the causes of throat hyperemia, possible diseases, and also how to distinguish a virus from a bacterial infection.
How can you tell if your baby has a sore throat?
First of all, it is necessary to examine the mucous membrane of the larynx. Hyperemia (redness) of the throat is an obvious, but not the only symptom. In addition, other clinical manifestations of inflammation may be present, such as:
- swelling of the tonsils and the presence of plaque on them;
- difficulty and pain when swallowing;
- redness of the visible parts of the throat;
- hoarse voice and sore throat;
- dry, barking cough;
- nasal discharge and nasal congestion;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- loss of appetite and general weakness;
- headache and fever.
If some of the above symptoms occur, then parents should contact an otolaryngologist to find out the true cause of the inflammation. With adequate treatment, the prognosis is usually favorable.
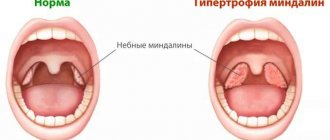
The functions of the tonsils and their appearance are normal
Before diagnosing throat diseases, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with general information about the functions and appearance of the tonsils. These formations are accumulations of lymphoid tissue and are often called tonsils.
- Red throat in a child: how to treat it at home if it constantly hurts and hurts to swallow?
Tonsils perform two main functions: protective and hematopoietic. They produce antibodies that fight pathogenic microorganisms, preventing them from entering the body. The tonsils also form lymphocytes - cells of the immune system.
A healthy person has 4 tonsils: 2 paired and 2 unpaired, they are located at the junction of the nasopharynx and pharynx. Normally, these formations are the size of a walnut and are colored light pink. Also signs of normal tonsils include:
- absence of redness and plaque;
- the mucous membrane is not inflamed, there is no pronounced vascular pattern;
- the tonsils do not come into contact with the palatine arches and do not extend beyond them;
- When pressing on the tonsils with a medical spatula, no pus or mucus is released.
The combination of all these signs indicates a person’s health. However, for some people, increased size of the tonsils is the norm - this is an individual characteristic of the body.
What makes your throat red?
In 80% of cases, the cause of redness of the throat is viruses and bacteria, less often fungal infections. However, it makes sense to voice non-inflammatory causes. These include:
- mechanical microtrauma of the mucous membrane;
- eating hot or coloring foods;
- contact with allergens or smoke;
- prolonged vocal load.
Without a doubt, chronic diseases of the nose and nasopharynx contribute to the spread of infection when inflammation spreads to the throat (the so-called “postnasal drip”). In such cases, it is important to promptly treat rhinitis and sinusitis, preventing the diseases from becoming chronic or protracted.
How to distinguish a viral infection from a bacterial one?
Let's start with the fact that bacterial infection is much less common than viral infection. In such cases, the disease is more complicated than a regular ARVI, and lasts from 5 to 14 days. Typical signs of bacterial attachment include:
- high body temperature;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- thick yellow-green sputum produced when coughing;
- the appearance of white plaque on the pharyngeal tonsils;
- clinical symptoms are expressed locally (ear, throat or nose).
The virus is characterized by:
- hyperemia of the throat is combined with sore throat and runny nose;
- expectorated sputum is clear and flowing;
- the appearance of a rash (with measles, rubella and scarlet fever);
- general weakness and aches throughout the body.
There are also significant differences regarding the treatment regimen. If the inflammation is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are indicated; only they can solve the problem. Accordingly, with viruses, antibacterial drugs will be useless; in such cases, it is necessary to take antiviral drugs. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor who will identify the true cause of the red throat and prescribe the right solution.
Causes of a red throat
| CAUSES | A COMMENT | ||
| causes: | Infectious causes | a comment: |
|
| causes: | Non-infectious causes | a comment: |
|
In 70% of cases, inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa is caused by ARVI viruses (rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, influenza and parainfluenza viruses), as well as other viruses (enterovirus, herpes virus, Epstein-Barr virus for infectious mononucleosis, and others).
The cause of inflammation can be bacteria:
- group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS)
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenza
It should be remembered that a red throat can be a manifestation of infectious diseases such as measles, scarlet fever, and rubella. In some cases, differential diagnosis with other infectious diseases is required.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostics consists of examining the patient, collecting anamnesis and a comprehensive examination, including:
- pharyngoscopy - visual examination of the pharynx;
- mirror laryngoscopy – examination of the larynx using a laryngeal mirror;
- endoscopic method - examination of the larynx using an endoscope;
- clinical blood test;
- bacteriological method (culture of mucus from the oropharynx will help determine the causative agent of the disease).
When examining a small patient, the doctor assesses:
- general view of the mouth, throat and larynx;
- color of mucous membranes and presence of swelling;
- size and color of tonsils;
- condition of the submandibular lymph nodes.
As soon as the causative agent of the disease is known (virus, bacteria, fungus or allergen), the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. If necessary, the otolaryngologist will refer the child to a specialized specialist.
External signs of a sore throat
The condition of the oral cavity is influenced by the environment, past diseases, and inhaled microbes, so an absolutely healthy pharynx is rare. According to statistics, by the age of seven, almost every child suffers from various chronic throat diseases. You can determine whether the throat is affected or not by the following signs:
- The tonsils become red and increase in size, swollen follicles are clearly visible on them, which are sometimes filled with pus, and there is a white, yellowish or gray coating. With herpetic tissue damage, blisters and small ulcers form.
- The soft palate becomes inflamed and a rash may appear on it.
- The back wall of the pharynx looks swollen, loose, the follicles are enlarged. Upon examination, a pronounced network of small vessels can be detected. The presence of ulcers indicates infection with the herpes virus (see also: symptoms of herpes on the tonsils in a child). The tongue is hyperemic.
- The tongue is coated. If it has a brown or gray tint, affecting the tongue and teeth, this may indicate chronic pharyngitis.
Methods for treating throat diseases
Therapeutic measures, as in the treatment of any other diseases, involve solving two main problems:
- Elimination of intoxication and local syndromes.
- Prevention of the development of complications from other organs and systems.
As a rule, when treating red throat, drug treatment is used, taking into account the age of the child and the severity of the pathology. Depending on the etiology of the identified disease, the following drugs can be used:
- antiviral;
- antibacterial;
- antifungal;
- antiseptic;
- antihistamines;
- antipyretics and painkillers;
- immunomodulators and vitamins.
Treatment can be effectively complemented by physiotherapy: UV and UHF therapy, quartz, electrophoresis. Note that in 90% of cases, infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract have a viral etiology, so antibiotic therapy is indicated only if a bacterial infection is detected. Only a doctor can determine it. We remind parents once again that it is categorically unacceptable to prescribe antibiotics on their own.
We care about your health
Pharyngitis is an inflammation that is localized on the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx. Since this disease is usually of infectious origin, it is usually accompanied by symptoms of upper respiratory tract dysfunction. If signs of illness occur, it is recommended to immediately contact an experienced ENT specialist. Thanks to this, you will be able to prevent the development of complications.
Pharyngitis (acute, chronic) - symptoms in adults and children
Pharyngitis is accompanied by severe inflammation in the pharynx area, which is associated with increased activity of pathogenic microorganisms. The development of the disease can be caused by cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus, which are viable at low temperatures.
Infection of the pharynx by these microorganisms usually occurs as complications of diseases of the ENT organs. Acute inflammation often spreads to the tonsils, creating a large lesion.
If treatment for this disease is not started in a timely manner, it will become chronic. In such cases, coping with pharyngitis can be quite difficult.
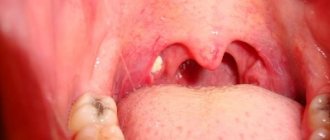
Pharyngitis - photo of the throat with disease
Photograph of the throat with acute pharyngitis
Photograph of acute infectious pharyngitis
Causes of pharyngitis
The development of pharyngitis can be caused by inhalation of cold air, as well as exposure to various irritants - alcoholic beverages, cigarettes. The infectious form of the disease is a consequence of infection with various microbes - staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci. Pharyngitis can also develop when infected with various viruses and fungal infections.
Often the disease becomes a consequence of infection from other organs adjacent to the pharynx. Very often the inflammatory process is the result of rhinitis, sinusitis or caries.
Provoking factors include the following:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- weakening of the immune system;
- prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane;
- infectious processes in the body;
- eating cold foods.
People of any age are at risk, but pharyngitis is most often diagnosed in children and patients with weak immune systems. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, a chronic form of the disease may develop.
Symptoms of pharyngitis in adults and children
The general condition of people suffering from pharyngitis usually remains normal. Sometimes the temperature rises, increased drowsiness or slight malaise appears. Local symptoms include discomfort in the throat, dryness, soreness, and the sensation of a foreign object in the throat. Subsequently, pain of moderate intensity occurs.
If there is pronounced swelling in the throat area, the pain syndrome spreads to the ears, which provokes a feeling of stuffiness. Also, against the background of a sore throat, a dry cough may appear. As the pathology develops, it acquires a productive character.
Since pharyngitis is an inflammatory process, a reaction from the lymphatic system may occur. As a result, there is a slight increase in the anterior cervical lymph nodes and slight pain when palpating them.
With a severe viral infection, a person may have more pronounced signs of intoxication of the body. In addition to pharyngitis, symptoms of dysfunction of other organs often appear - for example, laryngitis or tracheitis.
With an exacerbation of the chronic form of pharyngitis, the patient’s well-being remains normal. In this state there are no symptoms of intoxication, in addition, the temperature usually remains normal. The chronic disease is accompanied by increased dryness and a feeling of a lump in the throat. Sometimes there is a slight cough.
What does Pharyngitis look like?
Pharyngitis - what does the throat look like when it’s sick?
Photo of pharyngitis
Treatment methods for pharyngitis - acute and chronic
For therapy to be truly effective, an accurate diagnosis must be made in time. To do this, you should consult with an ENT doctor who will examine the oral cavity. To determine the type of pathogen, a specialist will take a swab from the throat.
If the patient's general condition remains normal, treatment of pharyngitis should be symptomatic.
It usually includes the following components:
- gentle diet;
- compresses on the neck;
- gargling;
- inhalation;
- hot drink;
- warm foot baths.
Mild forms of the disease do not require the use of antibiotics. In this case, local antimicrobial therapy is indicated. The doctor may also prescribe antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
To determine the treatment method and select the right drug, the ENT specialist must focus on the following criteria:
- wide spectrum of action of the drug;
- low degree of absorption of the active substance from the mucous membrane;
- low allergenicity;
- no irritation to the throat;
- no toxic effect.
ENT clinic Medkvadrat is an effective treatment for pharyngitis in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki. We will quickly and effectively cure pharyngitis. Make an appointment with an ENT specialist.
Prevention of pharyngitis
To prevent the development of acute pharyngitis, it is necessary to exclude hypothermia. It is also very important to avoid irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa with agents of nutritional origin. To prevent this disease, general hardening of the body with cold should be carried out, timely sanitation of the oral cavity should be ensured, and inflammation of the nasopharynx should be treated in time.
To prevent the occurrence of chronic pharyngitis, it is necessary to exclude exposure to negative factors on the body. These include smoking, eating irritating foods, and air pollution. Adequate treatment of pathologies of internal organs and metabolic disorders in the body is of no small importance.
Pharyngitis is a fairly common disease that is accompanied by inflammation in the pharynx and causes unpleasant symptoms. To prevent negative health consequences, you need to prevent this disease. If symptoms do appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
You can make an appointment at a convenient time by phone. + 7
Overview video of the Medkvadrat ENT center in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki:
Recovery criteria
The following signs indicate successful treatment and speedy recovery:
- normalization of temperature;
- absence of signs of intoxication and asthenic syndrome;
- redness and swelling of the oropharynx disappeared;
- the size of the lymph nodes decreased.
Note that it is equally important during the treatment process to strictly follow medical recommendations, which consist of following bed rest, a gentle diet and drinking plenty of fluids.
We remind Kaliningrad residents that you can make an appointment with a pediatric otolaryngologist by filling out a preliminary application on our website or by calling: +7 (4012) 357-773 or +7 (4012) 973-100.