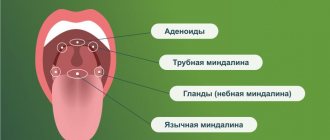
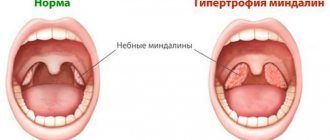
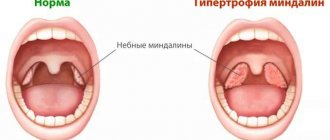
The powerful lymph nodes located around the pharynx cannot cope with the attack of the pathogen, so the body begins to produce antibodies that can find pathogenic bacteria, paralyzing their activity.
As a result, streptococci are defeated, but the child’s body produces so many antibodies that, in addition to foreign cells, the body’s own tissues, primarily the heart and joints, begin to suffer. Therefore, it is always better to entrust the treatment of sore throat in a child to a qualified doctor.
In 10% of cases, sore throat in children can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, rarely pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, chlamydia and fungal flora. Viral pathogens (adenoviruses, herpes virus) more often attack the body of children under 3 years of age.
How and why does infection occur?
Infection occurs by airborne droplets, from a sick person, by using shared utensils and eating contaminated food, as well as by a number of other factors:
- weakened immunity;
- hypothermia or consumption of cold foods and drinks;
- mouth breathing (for chronic adenoiditis, deviated nasal septum);
- irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa with a runny nose;
- recent viral diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis);
- caries and other oral infections.
Secondary tonsillitis in children can occur against the background of scarlet fever, diphtheria, mononucleosis, as well as blood diseases.
In any case, a sore throat develops rapidly, in a matter of hours, and is especially acute in children, accompanied by the main symptoms—a sore throat when swallowing and an increase in body temperature.
Herpetic or aphthous?
It will be somewhat more difficult to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis. The latter got its name from the Greek term “aftha”, which means “ulcer”.
If with herpetic stomatitis there are many ulcers, but they are small, then with aphthous stomatitis there are few of them, and the size can reach 7–8 mm.
The second important distinguishing feature is the absence of swelling of the gums with aphthous stomatitis.
If you are looking for differences between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis, then the third thing you should pay attention to is the localization of the rash. Aphthous is characterized by the appearance of ulcers in the oral cavity, while herpes infection can spread to the border of the lips.
Sore throat in children: forms and clinical manifestations
Depending on the nature of the change and the degree of damage to the tonsils, several forms of angina are distinguished.
Catarrhal sore throat
A mild form, characterized by enlargement and redness of the tonsils, as well as the absence of purulent lesions. The child feels dry mouth, a whitish coating appears on the tongue, and the cervical lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. In addition to a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing, the child feels a sore and burning sensation. The temperature rises to 38 degrees, children complain of weakness and headache.
Follicular tonsillitis
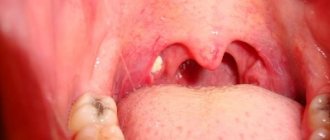
A serious disease in which the tonsils become covered with purulent pinpoint follicles. On days 2-3, the ulcers open, leaving wounds that heal quickly. There is severe pain in the throat, radiating to the ear, making it difficult to swallow, children refuse to eat and drink. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed lightly. Fever and chills are accompanied by a temperature of up to 40 degrees, vomiting, convulsions and fainting are possible.
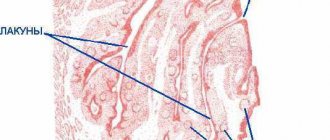
Lacunar tonsillitis
In the lacunae, between the lobes of the tonsils, islands of yellow purulent plaque appear, which tend to unite into wide purulent foci. The symptoms are similar to those of purulent follicular tonsillitis, but are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe intoxication of the body. It hurts the child to turn his head, his mouth opens with difficulty, which makes speech slurred.
Viral (herpetic) sore throat
Most often, the development of the disease is facilitated by vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity. The tonsils become covered with red blisters, which burst, leaving small ulcers in their place. In addition to a sore throat, symptoms are acute respiratory in nature: cough, runny nose, abdominal pain, indigestion, as well as stomatitis and conjunctivitis. Lack of timely treatment of herpetic sore throat in children can lead to serous meningitis.
Fungal tonsillitis
A relatively mild form of sore throat that occurs in children under 3 years of age. It is distinguished by a coating of white, curdled flakes on the tonsils and, with proper treatment, goes away within a week.
What causes the disease
In adults, in most cases (from 50 to 80%) sore throats are caused by viruses. And in children, bacterial sore throats are more common. They are more severe and often lead to complications. It's all about a harmful microorganism called "group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus." When it “sticks” to the tonsils and interacts with the lymphoid tissue, a new substance is formed, the structure of which is similar to our own tissue. The body understands that something foreign has entered it and needs to be dealt with. But in the end, it produces antibodies against its own tissues, which are similar to the structures that appeared as a result of the activity of the microbe. It kind of confuses them. That is why, as a result, not only the throat suffers, but also the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs and systems. Therefore, angina is considered a general disease with a predominant lesion of the palatine tonsils. And if hospitalization is necessary, a patient with a sore throat is sent to the infectious diseases department, not the ENT department of the hospital.
Why is a sore throat dangerous?
As practice shows, only in half of the cases are enlarged tonsils and sore throat caused by purulent sore throat. Many diseases, such as diphtheria or Epstein-Barr virus, have symptoms similar to sore throat. Therefore, only a qualified doctor with modern diagnostic equipment and a well-equipped laboratory can accurately determine the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Each causative agent of sore throat is sensitive to a certain type of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor depending on the diagnosis.
Remember!
Incorrect or untimely treatment of sore throat in children, as well as relying on folk remedies for “red throat” can lead to serious complications and irreversible consequences.
Delay in diagnosis and prolonged treatment provoke the development of rheumatoid arthritis, vascular diseases, heart diseases (including rheumatic endocarditis), renal failure and many chronic diseases leading to disability.
Diagnostics
A consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist begins with collecting the patient’s medical history and complaints. The ENT doctor finds out how long the symptoms of inflammation have been appearing and whether any treatment has already been carried out. Direct examination includes palpation of the neck, parotid and occipital areas. Then the ENT doctor examines the oral cavity and pharynx. If necessary, an endoscopic examination of the pharynx is performed. He assesses the condition of the mucous membranes, palatine tonsils (their size, the presence of plaque on them or purulent plugs in them).
The patient may also be prescribed laboratory tests: a general blood test, a throat smear. If complications are suspected, serological blood tests, X-rays, electrocardiography, etc. are additionally performed.
After suffering a sore throat, a child may be diagnosed with myocarditis, arrhythmia, heart murmurs, pyelonephritis, renal failure, and rheumatism. If an infection from the tonsils enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body, sepsis may develop.
Causes of disease development
Acute and chronic throat diseases can occur for various reasons, among the most common are:
- microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- allergens;
- adverse environmental impacts;
- voice overstrain;
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- general decrease in immunity;
- smoking.
A combination of several reasons is possible. Their identification and elimination is an integral part of treatment.
Bacterial or viral?
In addition to viral origin, the disease can be caused by bacteria: streptococci and staphylococci are normally present in the microflora of the oral cavity and begin to multiply uncontrollably during the inflammatory process. The latter may be caused by caries or periodontitis (read more about the disease in the article).
How to distinguish viral stomatitis from bacterial one? It is extremely difficult to do this at home, so it is better to consult a doctor. The main differential feature is the localization of the rash. With viral herpetic stomatitis, vesicles with transparent contents first appear on the tongue (its tip, along the side surfaces and under it), and then can even spread to the pharynx and tonsils.
For bacterial stomatitis, the location of the rash on the gums and those areas where the skin borders the mucous membrane (for example, on the red border of the lips) is more common. Also, with a disease caused by streptococci, “jams” are often observed - pustules on the corners of the mouth, which quickly begin to bleed, become covered with a crust, crack and cause constant discomfort while eating and talking.
Types of diagnostics
An experienced doctor can identify herpetic stomatitis in adults during an initial examination, relying on only two methods.
- Clinical picture.
Based on the totality of the patient’s specific complaints and distinctive external signs, the dentist will not only assess the severity of the disease, but also differentiate it from ordinary stomatitis, candidiasis, etc. - Immunofluorescence.
Express microscopy method, the most accurate for diagnosing acute herpetic stomatitis.
Treatment of viral sore throat
Before treatment, it is necessary to diagnose and identify the pathogen. If the viral nature of the occurrence is confirmed, then, as a rule, the treatment regimen is as follows:
- Taking antiviral drugs. They speed up the fight against viruses and reduce recovery time. Basically, the ENT doctor prescribes tablet forms of drugs, but in severe cases injections are used.
- Taking antihistamines. They reduce the severity of intoxication and reduce swelling of the throat.
- Use of painkillers, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs.
- Taking antipyretics based on ibuprofen or paracetamol. Recommended only when the temperature rises above 38°C.
- Taking immunostimulants. To strengthen and restore the patient's immune system, immunostimulating agents are prescribed. In addition, they enhance the effect of antiviral drugs. Children are prescribed in the form of drops or suspensions.
- Gargling. Gargling with herbs, antiseptics, and ready-made preparations reduces pain in the throat and eliminates inflammation.
The otorhinolaryngologist recommends drinking as much water, fruit drinks, warm tea, juices, and herbal infusions as possible, since the disease causes dehydration. The liquid removes toxins and viruses from the body.
Throughout the illness, you should stick to bed rest and not have a sore throat on your legs. If you follow bed rest for 2-3 days, the recovery time is significantly reduced, and improvement in well-being occurs on the second day.
The air must be humidified and the room ventilated. It is imperative to adjust your diet, namely to exclude smoked foods, spicy foods, too hot or cold foods, which will irritate the inflamed tonsils.
Usually the disease goes away completely within 6-7 days.
Causes of viral sore throat
As a rule, the virus enters the body when the body’s protective functions are reduced. Immunity may decrease after recently suffering from influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, as well as nutritional disorders (exhaustion). The following factors reduce the body's resistance to viruses:
- Poor nutrition and ignoring vegetables and fruits.
- Staying in an unventilated area. It is for this reason that preschoolers get sick.
- Stress.
The virus can enter by airborne droplets, contact, household and waterborne routes. Children often become infected with viral sore throat when visiting a swimming pool, kindergarten, or school. In close contact with a sick person, the likelihood of getting sick doubles.