Is it possible to swallow phlegm in the throat?
The accumulation of mucus in the throat forces the patient to pay attention to it.
There are only two options: expectoration or swallowing. Both processes are physiological. Swallowing is harmless: sputum passes into the stomach and is broken down into components. Enzymes in the gastric juice transform mucus into water, which returns to the body and brings only benefits. Harmful components are digested and excreted naturally.
The feeling of mucus in the throat due to hypersecretion of the glands of the respiratory system is normal. These nerve endings signal stagnation of phlegm. The main thing is the absence of suffocation, which is a dangerous sign of the development of events: swelling of the larynx with a threat to life.
Sputum in the lungs by composition
What is sputum
© Hank Grebe/Getty Images
Our body produces mucus that coats certain ducts, such as the respiratory and digestive tracts, to protect and maintain certain functions.
This mucus prevents bacteria and viruses from causing infection.
Moreover, our body produces about a liter of phlegm every day.
Most often we don't notice it, but when the mucus becomes thick and takes on an unusual color, such as yellow, green or brown, it can become a problem.
Coughing up white mucus without coughing
Enveloping the larynx with white mucus without a reflexive attempt to remove it is a common reason for patients to see a doctor. Most often, this is pure physiology, not dangerous to health: unfavorable ecology, food irritating the mucous membranes, alcoholic drinks.
If, in addition to sputum, cold symptoms appear: runny nose, headache and fever, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Most likely, acute respiratory infections provoked an exacerbation of a latent process, which is localized in the upper respiratory tract and does not manifest itself in anything other than hypersecretion of mucus. The pathology does not descend into the bronchi, so there is no cough. But such “innocence” may hide tumors of the nasopharynx, so consultation with a specialist is necessary.
For prevention purposes, any expectoration of white mucus without coughing for a couple of days is a reason to visit a therapist.
An examination with special equipment and a series of tests will allow you to determine the true cause of hypersecretion and prescribe therapy or send you to a specialized specialist.
Other reasons
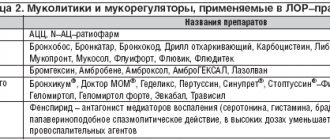
If sputum accumulates in the throat due to allergies, then you should take antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetirizine, Loratadine, Tavegil). Relief should occur within the first day of using them. If the symptom is caused by reflux and reflux of stomach contents, then treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
It will be individual for each patient (with the use of enzymes, anti-inflammatory drugs and dopamine receptor blockers).
You will also be interested in:
- How to treat a dry cough in an adult that lasts for a long time without fever
Causes caused by pathological processes
Green sputum without cough is always the cause of an infectious disease. It can form or accumulate in the throat with the following pathologies:
- pharyngitis (inflammation of the larynx);
- rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa);
- nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nasopharynx);
- bronchial or pulmonary diseases (usually chronic);
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils);
- allergy.
Most often, the feeling of phlegm in the throat occurs in people who suffer from laryngopharyngeal reflux or esophagitis.
Mucus drains from the nose down the back of the throat. Or it is thrown from the lower respiratory tract, esophagus. Irritation that occurs inside the pharynx increases the formation of sputum.
Viral and bacterial diseases that cause excess mucus in the throat are often accompanied by elevated body temperature. When fluid comes back from the esophagus, there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
How to get rid of mucus accumulation in the throat
Fortunately, there are several effective remedies that will help you get rid of excess mucus in your throat at home.
Salt water rinses
© Stockbyte/Getty Images
Gargling with salt or sea water is the easiest and safest way that helps almost immediately get rid of mucus in the throat.
Salt water helps move and remove mucus, but it is important not to overdo the amount of salt, otherwise it can cause even more dryness.
- Dissolve ½ or 1 teaspoon of Himalayan or sea salt in a glass of water.
- Add a pinch of soda.
- Gargle with this solution several times a day.
Breathe the steam
This method helps open the nasal passages and thins mucus in the throat, clearing it.
- Find a large enough bowl or pan and fill it with hot boiled water.
- There is no need to breathe boiling water; the steam temperature should be no higher than 50-70 degrees Celsius to prevent burns.
- To help the steam reach your nasal passages, cover yourself with a towel and lean (but not too close) to the bowl.
- Sit comfortably so that no one or nothing disturbs you.
- You can also add essential oils to the water. eucalyptus, fir, cedar, sage and lavender
, which also purify the air of allergens and prevent colds and respiratory tract infections.
You can breathe in the warm steam while taking a hot bath or using an inhaler.
Rinse your nose
Use a special teapot, a syringe without a needle and fill it with saline solution or use a ready-made spray that is sold at the pharmacy.
- To prepare a homemade solution, dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt and dissolve in a glass of distilled water (240 ml).
- Over the sink, tilt your head to one side and place the spout of the teapot in one nostril, gradually pouring the solution so that it comes out of the lower nostril.
- Repeat on the other side.
Ginger
© baibaz/Getty Images
Ginger is known for its anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. It is also a natural decongestant that has been used since ancient times to prevent colds and flu.
Study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology
showed that hot ginger tea effectively combats upper respiratory tract infections.
- Grate a small piece of fresh ginger (about 3 cm) and pour boiling water over it. Cover with a lid and leave to steep for 10-15 minutes.
- Drink ginger tea 2-3 times a day, adding lemon or honey to taste.
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound that has antiseptic and healing properties. It helps reduce mucus by killing bacteria that cause excess mucus production.
You will need:
- 1 teaspoon turmeric
- ¼ teaspoon salt
- 1 glass of warm water
- Add 1 teaspoon of turmeric to a glass of warm water.
- Add a pinch of salt (about ¼ teaspoon).
- Mix well and gargle 3-4 times a day to thin the phlegm in the throat.
Honey with lemon
Natural raw honey has natural antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties, and has a soothing effect on the throat.
Canadian researchers have found that even one serving of honey helps reduce mucus and cough. Moreover, honey was found to be more effective than cough suppressants in reducing the frequency of these symptoms.
Lemon is rich in vitamin C, strengthens the immune system and relieves congestion.
- Add 1 tablespoon of honey and 2 tablespoons of lemon juice to a glass of water.
- Drink this drink several times a day to relieve congestion.
- You can also take a tablespoon of natural honey 2-3 times a day until you get rid of the constant urge to clear your throat.
A little spicy
© claudiodivizia
Hot pepper, horseradish, mustard and wasabi help to get rid of congestion almost instantly.
If you tolerate spicy foods well, this is a natural way to relieve inflammation and prevent excess mucus from building up.
Capsaicin Research
and
allyl mustard oil
have shown that both of these substances, found in spicy foods, reduce phlegm production and inflammation.
Apple vinegar
Apple cider vinegar helps restore the alkaline balance in the body, preventing the production of large amounts of mucus.
- Add 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to a glass of water and stir well.
- Drink this drink 2-3 times a day until you get rid of excess phlegm.
- You can also gargle with this solution.
Drink more water
It is important to drink enough fluids to thin mucus and prevent it from building up in the throat.
- Aim to drink 2 liters of fluid per day, including water, tea, soups and other drinks.
- Choose herbal drinks that help relieve excess phlegm, such as chamomile or turmeric tea.
Possible causes of sputum without cough and additional symptoms
Sputum is mucus that is secreted by glandular cells of the trachea, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and bronchi. Normally, no more than 100 ml of mucus accumulates in the tracheobronchial tree per day. It has bactericidal properties and is involved in the removal from the respiratory tract:
- dust;
- allergens;
- pathogenic agents.
When the mucous membrane is irritated, the activity of glandular cells increases 10 times or more.
Therefore, in case of illness, up to 4 liters of pathological sputum are produced per day. Expectoration of mucus without coughing is a nonspecific symptom that accompanies pathologies of various systems:
- respiratory;
- digestive;
- endocrine;
- nervous.
To find out the cause of the condition, you need to determine:
- the nature of sputum - elasticity, transparency, color, smell;
- associated symptoms – chest pain, sore throat, burning sensation in the nose;
- factors that provoke exacerbation are strong odors, physical activity, drinking hot drinks, etc.
Expectoration of mucus without coughing in half of the cases indicates damage to the nasopharynx or bronchopulmonary system.
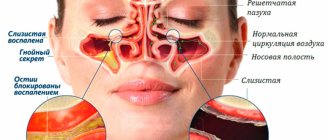
Sinusitis and rhinitis
Thick mucus is released without coughing in case of inflammation of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. Copious sputum is expectorated in the following diseases:
- The best cough syrup for children from all types
- Rhinitis (runny nose). Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is accompanied by the secretion of viscous mucus. Its transparency and elasticity depend on the form of the disease. An infectious runny nose produces yellow or green mucus. In people with insufficient tone of blood vessels, vasomotor rhinitis occurs, in which a transparent secretion is formed. With atrophic rhinitis, foul-smelling green sputum occurs.
- Sinusitis. When the maxillary sinuses become inflamed, sinusitis occurs, the ethmoid sinuses - ethmoiditis, the sphenoid sinuses - sphenoiditis, and the frontal sinuses - frontal sinusitis. If you cough up white, thick mucus without coughing, the cause of the illness is a viral infection or allergy. With bacterial and fungal inflammation, it acquires a yellow or green tint and an unpleasant odor.
Expectoration of mucus without coughing occurs mainly in the morning, as during the night it flows down the back wall of the throat into the hypopharynx.
Pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis
Phlegm in the throat without cough in children and adults occurs due to inflammation:
- palatine tonsils – tonsillitis;
- pharynx – pharyngitis;
- larynx - laryngitis.
If the secretion is transparent, this indicates the onset of the disease or the attenuation of inflammation. In the absence of complications, the cough does not bother you, and small amounts of sputum are expectorated. If it becomes thick and green, purulent inflammation is possible.
The release of viscous mucus without coughing after laryngitis is a sign that the inflammation has become chronic.
Reflux esophagitis
If there is no cough, but there is sputum in an adult, the cause may be the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus - gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, which irritates the mucous membrane and provokes the production of mucus.
GERD manifests itself:
- heartburn;
- sour taste in the mouth;
- swallowing disorder;
- hoarseness of voice;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating.
GERD is characterized by insufficiency of the esophageal sphincter.
The contents of the stomach enter the esophagus when the body is tilted or in a supine position. Therefore, clear mucus is coughed up after waking up. If you accidentally inhale gastric juice, a spasmodic cough occurs, accompanied by a burning sensation in the laryngopharynx.
Tuberculosis and other lung infections
Viscous mucus accumulates in the respiratory tract during infectious inflammation of the bronchi and lungs. Green sputum occurs when the ENT organs are damaged:
- Koch's bacillus;
- adenovirus;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- pneumococcus;
- coronavirus;
- measles virus;
- peptostreptococcus;
- pyogenic streptococcus;
- corynebacterium.
Pathogenic microorganisms produce toxins, so signs of intoxication (poisoning) come to the fore:
- weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- sweating
With viral inflammation, the sputum is clear, with bacterial inflammation it is yellow, and with purulent inflammation it is green.
If there is no cough and mucus accumulates in the bronchi, breathing becomes harsh. When listening with a stethoscope, moist rales are heard in the lungs.
Allergy
Sputum production without coughing is one of the signs of a respiratory allergy. Irritants (allergens) are:
- medicines;
- plant pollen;
- Food;
- fumes from household chemicals;
- dust mites.
Manifestations of respiratory allergies:
- Night cough in children and adults - causes of dry and wet cough, diagnosis and treatment methods
- labored breathing;
- redness of the throat mucosa;
- nasal congestion;
- lacrimation (with hay fever);
- pain when swallowing;
- hoarseness of voice.
Depending on the location of the inflammation, the allergy occurs with or without a cough.
Patients complain of expectoration of clear, viscous sputum, which sometimes becomes glassy. In the absence of treatment, the clinical picture is supplemented by new symptoms - spasmodic cough, shortness of breath, swelling of the mucous membranes.
Bronchitis
With inflammation of the bronchi, the production of bronchial secretions increases 5-7 times. At the initial stage, the cough appears and then disappears. When accumulated mucus irritates the receptors, coughing attacks occur. Without taking mucolytics, she does not expectorate, so wheezing appears in the lungs.
Symptoms of bronchitis:
- malaise;
- hard breathing;
- chest discomfort;
- nasal congestion;
- moderate increase in temperature.
After 2-3 days, the mucus begins to come out abundantly, so a productive cough occurs. It intensifies at night or in the morning, with a sharp change in temperature.
Sjögren's syndrome
Sputum without fever and cough is one of the signs of Sjögren's disease. It is characterized by damage to connective tissue and exocrine glands. Accompanied by sinusitis and tracheobronchitis, separation of rusty sputum.
Symptoms of Sjögren's disease:
- muscle and joint pain;
- dry eyes;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- violation of the act of swallowing;
- prostration;
- dry tongue;
- formation of crusts in the nose;
- enlargement of the parotid glands.
The mucous membrane of the throat dries out and acquires a bright red tint.
If the glands are insufficient, the saliva becomes viscous. Due to dysphagia (impaired swallowing), the patient cannot swallow it. Therefore, there is a feeling of mucus accumulation in the throat.
Inflammation of the adenoids
Sputum without cough in a child appears against the background of adenoiditis. This is the name for inflammation of an enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsil. The adenoids block the nasal passages, so viscous secretions accumulate in the nasal cavity. During sleep, it flows into the throat through the back wall of the pharynx.
Manifestations of adenoiditis:
- night snoring;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- coughing up yellow mucus;
- restless sleep;
- headache;
- elevated temperature.
There is no cough while awake. It occurs in the morning or immediately after waking up due to irritation of the throat by nasal secretions. If left untreated, the Eustachian tube becomes inflamed (eustachitis), so the child complains of decreased hearing acuity and ear pain.
Esophageal diverticulum
An esophageal diverticulum is a saccular bulge in the wall of the esophagus. It manifests itself as dysphagia, bad breath, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. Many people experience hypersalivation - excessive production of saliva, so they complain of copious sputum discharge without coughing attacks.
Associated symptoms depend on the location of the diverticulum. The most striking clinical picture when a protrusion forms in the clavicle area:
- change in voice timbre;
- nausea;
- scratching in the throat;
- expectoration of thin sputum;
- regurgitation of food;
- backflow of mucus from the esophagus into the throat.
Large diverticula put pressure on the respiratory system, causing coughing. It is combined with chest pain and dizziness.
Consequences of smoking
Non-infectious bronchitis is a problem faced by smokers with more than 7 years of experience. Systematic damage to the bronchi by tobacco smoke leads to irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane, which increases the activity of glandular cells.
Symptoms of smoker's bronchitis:
- rawness in the throat;
- occasional cough;
- mucus department;
- dyspnea;
- hard breathing;
- tachycardia (against the background of coughing attacks).
During the day, sputum passes without coughing. But during sleep, it accumulates in the throat, so in the morning coughing attacks occur, during which clots of transparent mucus are released.
Worm infestation
If a child or adult does not cough up clear or white sputum, the cause may be helminthiasis. In the acute phase, parasite larvae circulate in the blood and enter the bronchi. They irritate the mucous membrane, causing a productive cough. A person complains about:
- chest pain;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- shortness of breath;
- nausea.
When the mucus is swallowed, the worms enter the intestines, where they develop into adults. In the later stages, helminthiasis manifests itself:
- abdominal pain;
- unstable stool;
- weakness;
- sleep disturbance;
- elevated temperature;
- convulsions.
With a chronic disease, immunity decreases, so rhinitis, tracheitis, and influenza often recur.
Other reasons
Foul-smelling mucus without coughing is a dangerous symptom that occurs against the background of purulent inflammation of the ENT organs. Without treatment, complications are possible - abscess and gangrene of the lung, sepsis (blood poisoning).
Possible causes of expectoration:
- lungs' cancer;
- pulmonary syphilis, disintegration of syphilitic gum;
- bronchopulmonary carcinoma;
- cystic fibrosis;
- pulmonary mycosis;
- actinomycosis;
- bullous disease;
- pleural empyema;
- COPD
Yellow sputum without cough is a sign of bacterial diseases of the nasopharynx. If clots of dried blood are found in it, this indicates mucopurulent inflammation. Brown sputum in the morning without cough occurs with bronchiectasis and cardiac pathologies.
Treatment of snot in the throat in an adult
Postnasal drip syndrome affects people of all ages. To find out how to get rid of snot in the throat, an adult patient also needs to consult an ENT doctor. The specialist will prescribe a set of examinations to identify the cause of the pathology and appropriate treatment.
What to do if the snot in the throat does not go away after taking medications? This situation may be caused by incorrectly selected therapy or structural abnormalities of the intranasal structures and paranasal sinuses. In this case, the doctor may choose a different conservative therapy regimen or recommend surgical treatment.
Patients with a deviated nasal septum undergo septoplasty. This is an endoscopic operation that is aimed at eliminating deformation of the nasal septum without changing the shape of the external nose. Thanks to this procedure, nasal breathing is restored and one of the main causes of rhinitis and sinusitis, which provoke postnasal drip, is eliminated.
If there are indications, the patient may undergo surgery to resect concha bullosa or remove a Thornwaldt cyst, a cyst-like formation in the nasopharynx. It causes postnasal drip, which is difficult to respond to conservative therapy. After the operation, the patient's condition usually returns to normal.
Without an examination, it is impossible to say how to treat snot in the throat, so this situation requires mandatory attention from specialists.