If you think that dentists never tire of repeating the importance of preventive examinations and timely treatment of caries and gum inflammation just for the sake of advertising their profession, you are mistaken. Inattention to the health of your own teeth and vain fears of dental treatment can ultimately lead to complications, the treatment of which will be both difficult and expensive. A striking example of such a complication is dental granuloma - a pathological formation that occurs in the root part of the tooth.
In the early stages of its development, granuloma does not show itself with any noticeable symptoms, but as the tumor grows and becomes inflamed, severe pain in the tooth may appear, which cannot be relieved with tablets from the pharmacy. It is possible to remove a granuloma and save a diseased tooth only in dentistry and there is no need to delay contacting a doctor, because an untreated granuloma can lead to the development of serious complications, including osteomyelitis, general infections of the body and even cancer.
In this article we will tell you:
- What causes dental granuloma?
- Symptoms of dental granuloma;
- How is dental granuloma treated?
Also in the article you will find information on the prevention of dental granuloma and prices for treatment/removal of dental granuloma in Moscow.
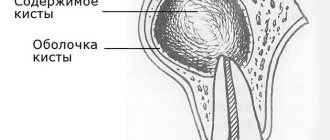
Cyst and granuloma of the tooth
Previously, it was generally accepted that if a neoplasm on the root of a tooth measures up to five millimeters, it is a granuloma, and if it is more than ten millimeters, then it is a dental cyst. Some dentists also distinguish a certain transitional stage - cystogranuloma, but practice shows that there are granulomas reaching even twelve millimeters, so an accurate diagnosis cannot be made only by the size of the formation and its shape. In addition to X-rays, histological examination of tissues is necessary.
The question often arises of how a granuloma differs from a dental cyst. The fact is that a cyst is a bladder filled with fluid or pus, with a shell formed by connective tissue and lined on the inside with endometrium. Secretory fluid is produced by the membrane, and due to this the cyst increases in size. Granuloma grows due to the growth of tissues containing infected cells.
Symptoms and diagnosis of granulomas and dental cysts
Granuloma, as well as cysts, are insidious diseases: the development of these pathologies can occur slowly and asymptomatically, however, under various conditions associated with decreased immunity - colds, flu, hypothermia, etc. – they manifest themselves with unbearable toothache, migraines, dizziness, fever, swelling and darkening of the gums, swelling of the submandibular and mental lymph nodes and general weakness.
The gold standard for diagnosing granulomas and dental cysts is an x-ray examination, which can clearly record dark spots with clear contours, which gives a granuloma cyst in the picture. To confirm the diagnosis, a puncture is performed. For early diagnosis, patients are recommended to periodically take panoramic dental photographs during routine examinations.
Tooth granuloma - symptoms and causes
Is it possible to live with dental granuloma? Yes, but you may not know about its existence for quite a long time: it is often asymptomatic and is detected only on an x-ray, which is performed for a completely different reason. However, it can be assumed if pain occurs when pressing on a tooth or getting into solid food. This condition should not be ignored, as it shows that an inflammatory disease is developing in the oral cavity. It can lead to a decrease in bone volume, resorption of tooth roots and ultimately to tooth loss. The consequences of advanced dental granuloma can be much more serious: perimaxillary abscess, phlegmon, jaw ostiomyelitis.
The hole after tooth extraction is a potential source of infection, which without treatment can lead to the formation of granuloma. Careful treatment of the hole by a doctor and following his recommendations after surgery will protect you from the disease.
Patients often wonder if dental granuloma can go away on its own? The answer to this question is no. It only indicates that an inflammatory process is occurring somewhere nearby, and if you don’t get rid of it, the consequences can be sad. Granuloma under a tooth is tissue saturated with capillaries. It isolates the infection within itself, preventing it from spreading further throughout the body. If the infection is not eliminated, it will continue to grow.
It should be noted that it itself is not a source of infection. This is just the body's reaction to an infection in the tooth. Accordingly, if you get rid of the source of infection, then the granuloma will go away by itself as unnecessary.
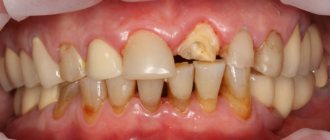
Symptoms of granuloma
Often the chronic granulomatous form of periodontitis is asymptomatic; sometimes patients complain of minor pain when biting and discomfort in the area of the diseased tooth. When granuloma grows, the following symptoms occur:
- swelling and redness of the gums:
- darkening of the affected tooth;
- increased toothache, its bursting nature;
- sharp sharp pain in the tooth in the morning, immediately after waking up;
- discharge of pus from the subgingival space;
- development of periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum (patients call it gumboil): the gums swell greatly, the swelling spreads to the lips and cheek; toothache radiates to the ear, temporal region, eye; a fistula tract may appear through which pus is released;
- increase in body temperature to 38°C and above;
- headache;
- feeling that the tooth has grown and become taller when biting;
- general weakness.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease:
- a sharp change in climatic conditions (weather change, moving to an area with a different climate);
- stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- previous colds;
- physical stress.
Treatment of dental granuloma: what to do?
Today, therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma is successfully carried out; in some cases, dental granuloma is treated with a laser, which does not require tooth extraction. As a rule, it is necessary to carry out high-quality endodontic treatment of the canals: cleaning, rinsing with an antiseptic and filling. They must be carefully sealed so that infection cannot enter from the oral cavity. Subsequently, the dentist monitors the condition of the tooth and the tissues around it. After five to six months, an x-ray should be taken, and if the tumor decreases in size or disappears, the therapy is considered successful. If it continues to grow, this makes it possible to diagnose not a granuloma under the tooth crown, but a dental cyst and re-treatment, which is carried out by a surgeon.
What is a dental cyst?
The inflammatory process - a dental cyst (from the Greek “kystis” - bubble) - is formed in the form of a small inflammatory ball that swells as part of a response to injury or infection. The inflamed area looks like a pus-filled bubble, sometimes reaching several centimeters in size. The body’s active work to restore order and remove slagged cells occurs constantly. At some point, a lot of them accumulate, and our excretory system selects the weakest area of the body through which they can be removed. In this case, the soft tissue around the tooth becomes the target, where a purulent neoplasm appears. An emerging problem can be diagnosed in the early stages using an orthopantomogram.
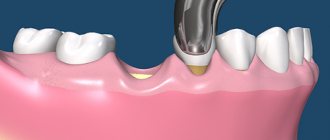
Removal of tooth granuloma
If therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma does not help, surgical intervention is used. From the outside, through the bone, access is made to the tooth root, the granuloma is scraped out, the place of its attachment is carefully processed, and the mucous membrane is sutured. In some cases, the infected root tip of the tooth is excised. Subsequently, the bone is restored, and the tooth continues to serve for a long time. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire root. This is also a common operation today. In this case, the desired root is excised along with the coronal part, and if the remaining roots are able to withstand the required load, a prosthesis is installed in this place.
If a tooth granuloma has been removed, but pain or inflammation remains, and it is painful to press on the tooth, you should contact a dentist in Moscow again. The situation when a tooth hurts after treatment or removal of a granuloma is common. The pain may persist for a long time, but you should make sure that there is no inflammation and that this pain is truly residual and not an indicator of another problem.
Traditional methods and treatment at home
The use of traditional methods in the treatment of granuloma can lead to complications and irreparable consequences.
Under no circumstances should hot compresses be applied to the cheek on the side of the inflammation: this will accelerate the spread of pus. Even if you know the names of antibiotics used in the treatment of tooth root granuloma, you should not take them yourself. Treatment methods should only be chosen by a doctor.
The only thing that can be done while it is not possible to get an appointment with a doctor (for example, symptoms appeared late in the evening) is to take a Nurofen or Ketanov tablet to eliminate the pain.
You need to understand that the development of inflammation occurs inside the root canals and in the jaw, which cannot be reached by any folk remedies, and only the help of a specialist will help save the tooth.
Treatment of dental granuloma with antibiotics and physiotherapy
Dentists often suggest treating dental granuloma with antibiotics. As a rule, this is only a temporary solution to the problem, since it does not eliminate the source of inflammation, and after some time the disease will return. Dentists successfully use physiotherapeutic treatment methods. For example, depophoresis works great for curved or complex tooth canals. Its action consists in the effect of a weak electric current on a suspension with copper hydroxide, which relieves inflammation, penetrating into all corners of the tooth.
Laser treatment
A promising method of treating tooth root granuloma is laser therapy. The advantages of this method with timely initiation of treatment:
- non-contact impact on the source of inflammation;
- the laser ensures the sterility of the procedure;
- absence of stress and pain for the patient;
- short recovery period after treatment.
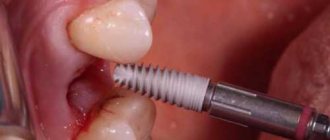
Before the procedure, the tooth cavity is opened and the root canals are cleaned. A laser light guide is inserted into the prepared channel and the granuloma is treated with laser radiation. Under its action, the granuloma evaporates, and at the same time, nearby tissues are disinfected.
Is it possible to put a crown on a granuloma on the root of a tooth?
Dental prosthetics imposes special requirements on the doctor and the patient. If we are talking about installing a crown on a tooth of which no more than 1/3 remains, that is, only the root, then it must be carefully prepared: the canals are sealed, the infection is eliminated. A granuloma under a tooth is an indicator that an inflammatory process is occurring in the tooth, and before dental prosthetics it is necessary to get rid of it, or sooner or later the granuloma will still have to be treated, since it can become inflamed under the crown. So why not do this right away, before installing a denture?
Why does a dental cyst appear?
What is the prerequisite for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease - dental cyst:
- physical trauma;
- periodontitis, peritonitis, pulpitis - inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth;
- residual effects after diseases of the nasopharynx - ARVI, complications after influenza;
- decreased immunity;
- advanced caries process;
- poor oral hygiene;
- development of infection in the root canal;
- poorly placed crown, poor quality filling;
- the appearance of problems with the wisdom tooth.
Tooth granuloma and folk remedies: will there be any benefit?
As we have already found out, granuloma occurs as the body’s response to inflammation that occurs in the tooth canals or periodontal tissues: a kind of tubercle of tissue appears under the tooth, absorbing and processing microbes. Is it possible to cure dental granuloma without seeing a doctor? At home, treating granuloma on the root of a tooth with folk remedies can be a dangerous undertaking. It is unlikely that with the help of herbal decoctions you will be able to get rid of infection in the dental canals. You can alleviate the condition by rinsing with tinctures based on calamus and propolis. Sage, chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, oak bark have an antiseptic and antibacterial effect, and rinsing with decoctions of these herbs can alleviate the symptoms of the disease, but this is a temporary measure, since dental granuloma cannot be cured in this way. All this should be used in complex treatment after consultation with a dentist-therapist.
Diagnosis of granuloma
During a routine examination, there are no signs of granuloma development. The affected tooth may not have a cavity or may have been treated previously, but without signs of any abnormalities. When tapping on the tooth, patients do not feel anything; slight sensitivity is possible; The doctor may be alerted by a painful bulge on the gum along the projection of the granuloma. In this case, the patient must be referred for an X-ray examination.
Granuloma is often discovered accidentally when taking x-rays during treatment of caries and root canals in adjacent teeth. In the photograph, an apical granuloma appears as a dark spot at the tip of the tooth root.
Urgent dental care for the development of purulent inflammation
We already wrote above that dental granuloma develops asymptomatically for a long time and this form is called chronic. But if a person experiences severe stress, catches a cold, a malfunction occurs in the immune system of his body - the granuloma will turn into an acute form, in which purulent inflammation can begin to actively develop. Its signs are excruciating pain that does not subside after taking pharmaceutical painkillers, swelling of the gums and cheeks, and increased body temperature.
Naturally, with such symptoms, you need to urgently contact the dentist to get emergency help. Treatment will depend on where the pus is located and accumulates:
- If the pus is in the granuloma itself, then assistance to the patient will consist of opening the tooth to ensure the outflow of pus through the root canals;
- If there is swelling on the gum and cheek, this indicates that the pus could go into the mucous membrane or periosteum and then the doctor will have to make an incision in the gum to drain it.
If you go to the dentist with a granuloma of a tooth that is completely destroyed, it would be advisable to remove such a tooth. But at the same time, it is important that the tooth extraction procedure is carried out efficiently and not only the tooth is extracted, but also the granuloma. If the tumor remains in the socket, alveolitis may develop - a rather serious and unpleasant complication.
If you have had a tooth with a granuloma removed, you must properly care for your teeth and oral cavity after this operation. You should:
- Temporarily stop drinking too hot food/drinks, alcohol, smoking;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia of the body and for this purpose do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, be sure to dress according to the weather;
- Eliminate stress and physical activity;
- Eat soft and warm foods for a week, trying not to chew on the side of the jaw on which the extracted tooth was located.
Be sure to take all medications and carry out all procedures prescribed by your doctor! If, within 3-4 days after the removal of a tooth with a granuloma, pain and swelling do not go away, contact the clinic immediately. The persistence of pain and swelling may indicate that the inflammatory process continues for some reason.
After tooth extraction during the treatment of granulomas, prosthetics and dental implantation are carried out no earlier than six months later. Such a pause in treatment is necessary for the complete restoration of all tissues in the area of tooth extraction.
Symptoms of a dental cyst
It is practically impossible to recognize the disease at the stage of its inception. The epicenter of development is located deep in the tissues, so it is quite difficult to immediately make a diagnosis. The inflammatory process makes itself felt when external signs or pain symptoms appear:
- darkening of the enamel, redness of the gums;
- pain when biting, pressing;
- itching sensation near the gums;
- discomfort when chewing;
- the appearance of a tugging, sharp piercing pain in the area of the tumor.
During this period of time it is difficult to determine what is happening where. It seems to the patient that this or that tooth hurts - he may mistakenly indicate a healthy one, but in fact, “dead” cells accumulate, and the inflammatory process enters the next stage of development. A purulent formation is formed: the skin is stretched under the pressure of an enlarged, rapidly growing bladder. As the amount of pus increases, the blister grows in size, exceeding 1 cm in diameter. At this stage, the patient’s sensations and appearance make it possible to visually diagnose a dental cyst:
- swelling of the gums, face;
- severe aching pain;
- elevated temperature;
- lack of appetite, malaise;
- statement of the fact of pain in the lymph nodes, their enlargement;
- headache if a cyst appears in the maxillary sinus.
The problem cannot be ignored. The formation of a purulent capsule does not go unnoticed. The process must be kept under control to avoid side effects. We recommend that you consult a specialist when the first, even the slightest, signs of the disease appear. Timely medical care from a dentist helps save the tooth; its results have a positive effect and cause a cosmetic effect.
Types of dental cysts
A molar cyst is distinguished by several characteristics:
- depending on the reasons for the appearance;
- according to location.
Distributing according to the reasons that provoke the appearance of a dental cyst, the following varieties are distinguished:
- A keratocyst appears on the lower jaw. Older people are susceptible to the disease. It can turn into a malignant form - it grows deeply into the body and destroys the bone.
- Odontogenic or radicular dental cyst is the most common type. After periapical inflammation and necrosis of the pulp, a granuloma of the dental root is formed in the upper part. The size of the purulent focus ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm. The process does not affect bone tissue and does not provoke tooth displacement.
- A cyst that forms at the site of teething is a retention cyst. It appears during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. A purulent fistula with bloody contents looks like a dark blue abscess. Education is formed if the process of eruption is slow. The purulent contents of the abscess should be opened and cleaned out.
- A calcifying odontogenic tumor occurs in the area of the support of the lower jaw. Experts do not have a consensus on the reasons for its formation - they have not yet been fully studied.
- A residual formation with pus occurs after tooth extraction as a result of careless work by the doctor. If a piece of root or a fragment of a tooth remains in the wound, a granuloma forms.
- A follicular cyst forms in place of soft tissues that resist the eruption of a new tooth. A cyst grows around a tooth hidden by the gum, enlarges and can spread to other teeth. The result of the development of a cyst can be tilting, tooth displacement or root resorption.
- A lateral periodontal cyst looks like a small formation, most often found on the lateral part of the root.
Depending on the location of the purulent tumor, there are:
- A cyst is formed on a tooth root. Three location options: basal, inter-root or peri-root zones. When a purulent capsule forms, the disease manifests itself well.
- The purulent focus is located in the maxillary sinus. Making a diagnosis is extremely complicated - you cannot do without an image of a certain area. In the advanced phase, the cyst provokes the appearance of sinusitis.
- At the initial stage, a cyst on the gum is asymptomatic. At the moment of filling with purulent contents, the bubble begins to grow rapidly. In treatment, medications are used, and they are also fought by puncturing the capsule, treating with saline solution and cleaning until complete healing.
- The formation of a cyst under the tooth crown occurs after unsuccessful disinfection during its installation after treatment. As a result of a loose fit, food debris gets under the crown, rots and creates a favorable environment for cyst growth. To treat it, you need to remove the crown.
- A cyst on the front teeth has practically no room for development and localization. It comes out at the initial stage of development.
- A wisdom tooth cyst forms at the site of a long-erupting “figure eight.” As a treatment for this category of teeth, a proven effective method is recommended - removal of the cyst and wisdom tooth together.