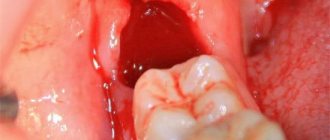
How long does it take for flux to last after tooth extraction?
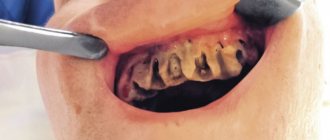
Swelling of the gums after tooth extraction continues for varying periods of time. The duration depends on the chosen method of surgery, the condition of the oral cavity and the immune abilities of the patient’s body. On average, swelling subsides in 3-4 days, sometimes lasting up to 7 days. Complications are indicated by persistence of flux for more than a week. Swelling appears 2-3 hours after the operation; along with it, the anesthesia wears off and pain may occur. Sometimes the cessation of anesthesia is accompanied by a slight increase in temperature. Therefore, the dentists at Dr. Fedorov’s clinic prescribe painkillers.
Maximum swelling is observed on the third or fourth day. By the seventh day it should completely go away. It's not just the gums that can become swollen. If your cheek is inflamed after tooth extraction, most likely the process began to develop before the operation.
How does tooth inflammation manifest?
The first signs of acute inflammation are:
- Redness of the gums around the tooth.
- Swelling.
- Pain when biting, pressing, and later without it.
- Sensitivity to temperature changes, sour, sweet.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
- Bleeding gums.
If the inflammation has progressed to a chronic stage, the patient may observe:
- Increase in temperature (local or general).
- Weakness.
- Intense pain.
- Inflammation is manifested in the results of clinical tests.
PROMOTION Hygienic teeth cleaning 2000 rub.
What to do if your gums are swollen after tooth extraction
Monitor your body's condition throughout the week. It is recommended to make an appointment with a doctor if:
- On the fourth day after surgery, the swelling did not decrease, but rather increased.
- A sharp throbbing pain occurs in the jaw, gum or cheek area - not to be confused with the aching pain that appears after the anesthesia wears off.
- The temperature rose to 38℃ and did not subside throughout the day.
- There is a feeling of persistent weakness and general malaise of the body.
- There is pain in the throat when swallowing.
If your gums are simply swollen after tooth extraction and there are no complications listed above, follow the recommendations received from your dentist. The swelling will completely go away within a week.
On the second day after tooth extraction, my cheek became swollen
The cheek does not always swell immediately after the patient’s gum is cut. Swelling may occur the next day - this is also natural. There may be no swelling of the cheek at all; often only the gums suffer. Moreover, everything is normal if postoperative recovery proceeds with the following introductory notes:
- body temperature on the second day is normal - not elevated;
- no sharp, throbbing pain in the gums;
- a day after the onset of swelling began to gradually decrease.
What will they do in the hospital: diagnosis, treatment
First of all, the doctor needs to determine the diagnosis and cause of the inflammation. To do this, radiography is performed to determine what stage the process is at.
The main factors leading to inflammation are:
- Advanced caries, due to which an infection has entered the tooth.
- Incorrect treatment (poor canal filling, bad filling), which also leads to infection.
- Injuries, root fracture, etc.
- Insufficient hygiene.
If the situation is neglected, there is a possibility of immediate removal of the diseased element.
If treatment is possible, first of all, the diseased tooth is cleaned of damaged tissue. The procedure requires the administration of anesthesia. The doctor will clean the canals, expand them if necessary, and disinfect them. If necessary, the patient takes a course of antibiotics, rinses with disinfectant solutions, and physiotherapy. A special substance may be placed into the tooth as a temporary filling. After there is no inflammation or pus left in the tooth, it can be sealed with a permanent filling.
Reasons why the cheek swells after tooth extraction
Swelling appears due to the inflammatory process occurring in the mucosa and pulp after surgery. This is a non-infectious inflammation. If operations are carried out correctly and the surgeon’s instructions are followed, the swelling goes away painlessly and without the need to take antibiotics. The integrity of the oral mucosa is disrupted during doctor intervention. The more swollen the gums are after tooth extraction, the more the integrity of the mucous membrane is damaged.
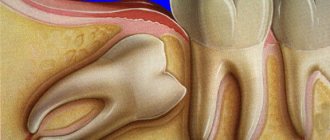
Severe swelling most often appears in patients who have had their wisdom teeth extracted - they generally have large, intertwined roots that complicate the process. The same applies to situations where inflammation began before surgery.
Cheek swelling during wisdom tooth removal
Working with outer teeth is a complex operation. Therefore, swelling always occurs after wisdom teeth removal. Doctors often resort to cutting the gums, after which they apply stitches.
For two to three days after surgery, the temperature may remain above 37℃, and opening the mouth, talking and swallowing may be accompanied by pain. The risk of infection and serious inflammation is higher than with other tooth extractions. The surgeon must prescribe baths with an antiseptic solution and antibiotics. Additionally, it is recommended to eat soft, pureed foods at room temperature, and refrain from sweets, alcohol and smoking.
Why does cheek swelling occur?
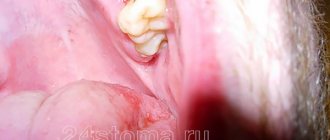
A common cause of edema is odontogenic periostitis, or gumboil. The inflammatory process of the periosteum is accompanied by the formation of purulent contents at the base of the root. The causes of gumboil are the spread of infection from a diseased tooth - carious or pulpy. In this case, only surgical treatment of periostitis, an incision in the gum and cleaning out the pus will help relieve swelling.
Another cause of cheek swelling is gingival cysts. If the cystic formation is localized not strictly under the root, but on the side, the gums and along with it the patient’s cheek swell. Getting rid of cysts involves performing tooth-preserving operations or, in advanced cases, tooth extraction. Often the cyst itself does not cause swelling, but after surgery to resect it, the patient receives swelling, which goes away within 2-3 days.
Patients with impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth often suffer from swelling during periods when the tooth is actively trying to erupt.
Other causes of cheek swelling
If you have a tooth removed and your gums are swollen, the cause does not necessarily lie in soft tissue damage. Swelling is possible due to the following:
- performing an operation if the patient has a flux;
- complex course of the operation - due to tooth growth in the wrong direction, strong inclination, removal of large teeth with large, intertwined roots;
- inflammation and infection of soft tissues or tooth roots before surgery;
- allergies or other forms of individual intolerance to anesthesia and medications used during removal - therefore it is important to know exactly what components you are allergic to before removal;
- poor antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and mistakes made by the doctor during tooth extraction;
- chronic diseases leading to complicated recovery - neuralgia, hypertension, as well as a general decline in the body’s immune functions;
- ignoring prescriptions received from the dentist - for example, independently adjusting the dosage or deciding not to take antibiotics.
Most often, patients' swelling does not subside after tooth extraction due to lack of normal care - skipping medications, complete absence or insufficiently frequent disinfection treatment.
Possible complications
Patients face complications due to incorrect care, complex or incorrect removal. Dentistry distinguishes 5 types of complications:
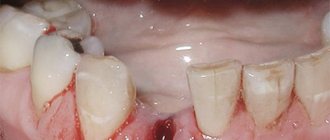
- Alveolitis - to put it simply, this is dryness of the socket. A blood clot always forms in the latter. It does not need to be removed, since the clot protects soft tissues from the penetration of bacteria and infection. If it is accidentally removed, the mucous membrane becomes susceptible to the pathogenic influence of bacteria, and suppuration may develop. Sometimes the inflammation shifts and spreads - a large area of the jaw, cheekbones and eyes become inflamed.
- Osteomyelitis is bone inflammation. With osteomyelitis, acute pain is felt in the upper and lower jaw, and swelling only increases.
- An abscess is suppuration inside the gum. Can move, leading to loosening of the tooth root.
- Flux is a severe inflammation of the jaw, in which the temperature rises and acute pain appears in the area of the jaw and temples.
- Neuritis is an inflammation in which the motor activity of the facial nerve is disrupted. Neuritis is indicated by swelling of the cheek, palate, tongue and larynx.
How dangerous is tooth inflammation?
Inflammation, especially if left untreated, affects not only the tooth itself, but also the tissue around it. Lack of treatment is dangerous for many reasons:
- The patient may lose a tooth.
- Inflammation negatively affects the entire body, adversely affecting the functioning of the kidneys, heart and other systems.
- The infection that caused the inflammation will spread, causing flux, bone inflammation, purulent abscesses, osteomyelitis, and sepsis.
- The disease can spread, affecting adjacent teeth and periosteum.
How to eliminate cheek swelling
It is impossible to get rid of edema 100% before the inflammatory process stops. To reduce discomfort and pain, you can apply cooling compresses for 7-10 minutes with a break of 30-40 minutes. Taking painkillers, baths and rinsing with soothing solutions at room temperature helps.
How to remove cheek swelling after tooth extraction at home
- Avoid contact with the hole. It should not be touched with the tongue, brushed, or allowed to get in contact with food.
- Adhere to dietary restrictions. You should not eat or drink for 4 hours after removal. In the next week, food should be soft, at room temperature, not hot or spicy. Eating sweets is not advisable.
- In the first 3-4 hours after removal, apply cooling compresses to the cheek. It is optimal to keep the compress for 3-5 minutes, maximum – 10-15. The compress can only be done on the first day.
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. The main thing is to follow all the dentist’s instructions.
Is it possible to do without going to the dentist?
A visit to the dental clinic is the only way to get rid of inflammation and, if possible, save the tooth. The sooner the drugs are taken, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. Otherwise, the patient risks getting the complications described above, among which tooth loss is not the most unpleasant outcome.
Timely detection of the disease is the key to success. Don't rely on home treatment. Without the intervention of a dentist, tooth inflammation can only progress, causing more and more dangerous consequences over time.
Prevention of dental diseases
Prevention is the easiest way to keep your teeth healthy. The basic principles are simple and easy to implement:
- Oral hygiene, regular brushing using a quality brush and toothpaste. The paste should not be too aggressive; it is better to avoid highly abrasive products.
- The toothbrush must be replaced with a new one in a timely manner (every 3-4 months).
- Rinsing will help remove food debris and keep your gums healthy.
- Soft tissues play an important role in maintaining dental health by fitting tightly and keeping bacteria away from the vulnerable cervical area. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the health of your gums.
- You need to visit the dentist's office every six months, regardless of whether there are any complaints.
Inflammation rarely begins immediately in the pulp or roots. Often it can be identified and eliminated at the very beginning and thereby prevent complications.
What to do if a tooth breaks off What to do if part of a tooth breaks off and scratches the gum
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur after various dental prosthetics and depend on many reasons. This problem is most typical for patients with complete edentia after the installation of removable structures. It may be accompanied by redness, pain, unpleasant odor, or bleeding. But even after fixing crowns or bridges, similar symptoms can occur if hygiene rules are not followed or the prosthesis is not made correctly. In any case, the patient should contact the dental clinic for advice.
Rest after surgery
The first few hours after drainage installation are the most critical. During the procedure, the dental surgeon needs to administer anesthesia, cut the gum, pump out the pus, and perform an antiseptic treatment of the cavity. The patient is weakened by the infectious process and the operation itself. Therefore, upon returning home, it is recommended:
- sleep for a couple of hours;
- take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs after the anesthesia wears off - Nimesil, Nise, Nurofen, Ketanol;
- do not drink or eat for several hours.
What if the tube falls out?
If the drain falls out, the patient should immediately consult a dentist.
Returning the drainage system to the gum on its own can lead to wound infection and serious complications. The doctor will examine the oral cavity and assess the situation. The absence of swelling after the drainage system falls out indicates the end of the process of outflow of pus - in this case, its re-installation is not required. If the swelling does not subside, the dentist will install the system into the gum again. Reasons that can cause a drainage tube to fall out include:
- improper brushing technique;
- excessive number or intensity of rinses;
- errors in the process of fixing the tube.
To maintain the drainage tube throughout the required period, the patient must adhere to certain rules. These include:
- intake of liquid and pureed food;
- drinking clean water;
- rest on the cheek opposite the affected area;
- exclusion of solid foods and sweets from the diet.
Avoid gum damage
If you handle cutlery, hygiene products carelessly, or get bumped or dropped, the drainage will not be level, will move, or will fall out prematurely. This is extremely undesirable, since the outflow of pus stops, and the edges of the wound begin to shrink.
The drainage is usually removed after 3 to 5 days by the doctor or patient. If it fell out earlier, you need to go to the clinic. The dentist will assess the patient's condition. In the absence of severe swelling or exudate, the doctor will recommend only drug treatment. When the inflammatory process does not subside, re-installation of the elastic tube will be required.
Improvement after installation of drainage should occur within the first day. If the tumor increases, the pain intensifies, and the temperature does not subside, you must tell your dentist.
Causes of inflammation
An allergic reaction to the materials from which the prosthesis is made. This can include a plastic base (residual monomer in its composition), dyes, metal alloys, etc.
The uncomfortable base of the removable structure, resting on the mucous membrane, can rub or press unnecessarily, causing redness, pain and discomfort, especially when chewing.
incorrectly made crown that goes deep into the periodontal sulcus will injure the gums, also causing inflammation - gingivitis. Destruction of the circular ligament leads to free penetration of microflora into the marginal periodontal area, which causes the development of periodontitis.
incorrectly made bridge , due to the supports, can have the same traumatic effect as a crown. Also, the intermediate (washing) part of the bridge resting on the mucous membrane leads to the accumulation of food debris, complicates hygiene, and sometimes causes the formation of ulcers and welts under the structure.
What is an apexectomy
Stages of tooth root resection
This is a surgical procedure that allows you to get rid of the source of infection located inside the gums without removing the tooth unit. Otherwise called resection of the apex of the tooth root. Often, infectious foci form in the area of the tooth root, and apexectomy allows you to cut out and remove the affected part of the root without affecting healthy tissue. This treatment method is considered the best for granuloma, periodontitis and similar serious pathologies, in which the affected teeth were removed in the past.
Avoid physical activity
The patient is prohibited from doing anything that provokes bleeding:
- engage in any sport;
- lift weights;
- do difficult homework;
- to take a bath;
- go to the sauna and solarium;
- travel for a long time in vehicles or fly on airplanes.
Read also: What antibiotics to take for tooth flux
Important! If you do not follow these recommendations, the wound will bleed, heal for a long time, and pus may spread into nearby tissues.