Pulpitis in pregnant women
A pregnant woman's teeth are especially susceptible to the negative effects of pathogenic bacteria. This contributes to the more frequent development of caries and pulpitis. There are several reasons why a pregnant woman's teeth are more susceptible to disease:
- The development of pulpitis is promoted by saliva, the composition of which is influenced by changes in hormonal levels.
- Contact with enamel of vomit during toxicosis. They have a low level of acidity, which leads to thinning of tooth enamel.
- Supplying gums with plenty of blood. The gums become loose and susceptible to the negative influence of bacteria. As a result of inflammation, caries appears, developing into pulpitis.
- A large amount of calcium is required for normal fetal development. The lack of this element in the body of the expectant mother leads to tooth decay.
If pain occurs, you should consult a specialist. The method of treating the disease is determined by the dentist. Delaying treatment can lead to complications and the development of other diseases.
Characteristics of the pathology
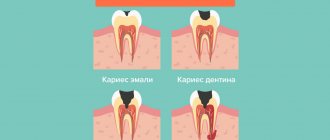
This disease is an inflammatory process in the dental pulp. Inflammation can develop if caries treatment is not carried out in a timely manner. The disease begins to progress and eventually affects internal tissues.
In pregnant women, the situation is complicated by hormonal imbalances and a constant lack of minerals and trace elements in the body. The main role here is played by a lack of calcium, due to which the skeletal system is formed and maintained. In this case, not only the pain syndrome, which significantly complicates the life of the expectant mother, is important, but also the detrimental effect of the inflammatory process on the child in the womb.
It is possible and even necessary to treat the pulp in this condition. If the situation is left to chance, a progressive infection can cause significant harm, and only timely intervention by a dentist will help avoid serious problems and numerous complications.
Remember, a pregnant woman should take any medications (analgesics) only after consulting a doctor.
The need for treatment of pulpitis
Some women do not know whether they should have dental treatment during pregnancy, or whether the procedure should be postponed until postpartum. Pulpitis must be treated when it appears. Several reasons requiring immediate treatment of the disease:
- Pulpitis is inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Untimely treatment leads to the absorption of bacteria into the blood of the expectant mother. This can lead to fetal developmental disorders.
- Presence of acute throbbing pain. Promotes the production of large amounts of hormones. This negatively affects the development of the child. Severe toothache can lead to uterine contractions and premature birth.
- Infection in the gastrointestinal tract. Infections that enter the gastrointestinal tract from the tooth can lead to late toxicosis.
Taking into account the above factors, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a dentist if symptoms of pulpitis appear.
Symptoms
The inflammatory process develops quickly, leading to a rapid deterioration in well-being. Its pronounced manifestations are:
- severe pain, most often manifested at night;
- high tooth sensitivity when eating cold or hot food;
- increased body temperature, which in some cases can reach 38°C.
Experiencing unremitting pain, the expectant mother is in a constant state of stress. At the same time, the body releases hormonal substances, which is very unsafe for the baby in the womb.
How long does it take to treat pulpitis?
Treatment of pulp inflammation has features depending on the stage of pregnancy. The expectant mother needs to inform the dentist about her situation and the stage of pregnancy. The specialist will select medications that will not harm the baby’s health for a certain period of time.
First trimester (from the moment of conception to the 12th week inclusive)
Treatment of pulpitis in pregnant women in the first trimester is not recommended. During this period, the fetus experiences increased sensitivity to toxins. The use of even the safest anesthesia can provoke developmental disorders.
The need for treatment is determined by the dentist. Treatment of chronic pulpitis is postponed to a later date. In the first trimester, the disease is treated during exacerbation.
Second trimester (from week 13 to week 28 inclusive)
At this time, the likelihood of harm to the fetus during dental treatment is reduced. The second trimester is the most favorable period for the treatment of pulpitis during pregnancy. The doctor performs the treatment under local anesthesia. Drugs are used that have a minimal amount of vasoconstrictor substances and do not penetrate the placenta. Such medications do not harm the baby.
Third trimester (from 29 weeks until birth)
The presence of acute toothache in a pregnant woman in the later stages can lead to premature birth. In the third trimester, treatment of pulpitis is necessary. Before visiting the dentist, you should consult with a gynecologist accompanying your pregnancy.
Therapy
| Service | price, rub. |
| Primary consultation and examination with a doctor | For free |
| Initial consultation with an implantologist, orthodontist, orthopedist (orthopantomogram is required) | For free |
| Repeated examination without prescribing treatment | For free |
| Examination by a doctor with prescription of medication | 500 |
| Help for antenatal clinics, hospitals, sanatoriums | 500 |
| TREATMENT OF CARIES | |
| Treatment of caries “without drilling” ICON technology – 1 tooth | 3000 |
| Treatment of caries (filling, anesthesia, lining) | 2700 — 4200 |
| Treatment of deep caries (filling, anesthesia, x-ray, lining) | 3800 — 5100 |
| Artistic tooth restoration (frontal group of teeth) | 4800 — 6700 |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth (filling, gasket, anesthesia, x-ray, pin) | 3600 — 4600 |
| NERVE REMOVAL – CANAL TREATMENT (depulpation) is carried out in two visits, payment in stages, includes x-rays, anesthesia, canal treatment, temporary filling | |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 1-canal tooth, without the cost of a filling | 4400 — 5500 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 2-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 6500 — 7600 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 3-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 8600 — 9700 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 4-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 10700 — 11800 |
| Installing a seal | 3200 — 3600 |
Consultation is free.
Our teeth consist of hard tissues (dentin and cement) and enamel covering them. Any tooth has a cavity from which the entrances to the canals open, which are located inside the tooth root. The neurovascular bundle passes through the canal. Doctors call it pulp. Patients often use the expression “dental nerve.”
When the neurovascular bundle becomes inflamed, an acute disease develops - pulpitis, which is usually accompanied by pain. The pain can be of varying intensity; usually the tooth reacts to cold and hot and hurts at night.
Any pain in the body is a signal to the owner that something has happened. Pain cannot be tolerated: such “heroism” and self-medication can lead to the development of more serious diseases and complications.
So, is it possible to treat pulpitis during pregnancy and what will happen if it is postponed until the postpartum period?
Stages of treatment
Treatment of pulpitis is carried out in one or several visits to the doctor. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Diagnostics. The doctor conducts a survey and examination of the pregnant woman’s oral cavity.
- Introduction of anesthesia. The drugs used are safe for the fetus.
- Removal of the part of the tooth affected by caries.
- Pulp removal. A pulp extractor is used - a rod with spikes that engage the tissue.
- Cleaning of channels and their mechanical treatment.
- Installation of a seal. The root canals and crown part of the tooth are filled.
- Checking the filling of the canals using radiography.
In some cases, treatment is carried out in 2–3 visits to the doctor. For the period between appointments, the doctor installs a temporary filling. It protects the tooth cavity from food and pathogenic bacteria.
How to avoid pulpitis during pregnancy
To reduce the likelihood of developing the disease during pregnancy, you need to:
- Get examined at your dentist's office while preparing for pregnancy and in the first weeks after conception.
- Visit the dentist promptly as prescribed by the gynecologist.
- Eat right, eat less sweets.
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene.
- Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables. They contribute to the natural cleansing of dental crowns from soft plaque.
- Use high-quality toothpaste and brush.
- Take prenatal vitamins prescribed by your gynecologist.
Use of radiography
Treatment of pulpitis involves the use of x-rays. They are necessary for the dentist for diagnostics, high-quality cleaning of root canals from inflamed pulp and control over the quality of the work performed.
The dentist must take into account the individual characteristics of each patient’s teeth. To determine the depth, location and curvature of the root canals, the specialist needs to send the expectant mother for an x-ray. This will allow him to get a more detailed picture and correctly treat pulpitis.
Radiography during dental treatment does not harm the health of the fetus. The rays pass through the tissue in the tooth area. A specialized apron that does not transmit x-ray radiation is put on a pregnant woman's stomach. This makes the procedure safe for the baby.
Treatment of pulpitis during pregnancy is necessary. The presence of the disease can negatively affect the fetus. A timely visit to the dentist will help avoid complications and the development of other diseases.
What is pregnancy characterized by - a dentist's point of view
During pregnancy, the body undergoes a large-scale restructuring - hormones and glands begin to work differently. There may be a deficiency of key micro- and macroelements, and the calcium-magnesium balance, which is especially important during this period, is disrupted. During pregnancy, the composition of saliva changes - it is more viscous, its PH is shifted to acidic, and its mineralizing ability decreases. This increases the risk of bone damage, gum problems and tooth decay.
Extraction, dental prosthetics and surgery during pregnancy
Pregnancy is accompanied by increased emotional and psychological stress, and even the thought of dental surgery provokes serious stress. Therefore, doctors try to replace it with treatment as much as possible, but in some situations this is impossible. These include:
- fractures of the roots and crowns of teeth;
- deep caries with purulent foci;
- cysts larger than 1 cm and other dental problems that cannot be solved with conservative methods.
Wisdom teeth are not removed without special indications to avoid alveolitis and other complications. To eliminate them, antibiotics are needed that are not compatible with pregnancy. If the case is obvious, and saving the tooth is dangerous due to focal infection or inflammation, surgery must be performed. It is performed under local anesthesia, but after its effect you need to be prepared for unpleasant sensations. Drugs approved during pregnancy, such as paracetmol, will help reduce them. In some cases, antibiotic therapy is also needed - the dentist will select safe medications.
Prosthetics, unlike implantation, is allowed during pregnancy, although the format of interventions is “cut down”. Teeth can be fitted with crowns and bridges, ground down, sanitized and prepared for procedures. However, if the case is not urgent, it is better to postpone prosthetics until after pregnancy.
Family Dentist Clinic: dental care for pregnant women
In our clinic, dentistry for pregnant women is well developed:
- We use a safe local anesthetic - Ultracaine with an adrenaline concentration of 1:200,000. The active substance articaine penetrates the placenta in minimal quantities, provides a reliable analgesic effect, does not increase heart rate, and is quickly eliminated from the body.
- If there is an urgent need for examination, we take a dental photograph with a digital radiovisiograph and additionally protect the abdomen with an apron. The beam of the device is directed only at the tooth, the radiation dose is low, comparable to a walk in the summer sun.
- An ergonomic chair ensures optimal position of the spine without muscle strain.
- Patient and attentive doctors help relieve anxiety and nervous tension, answer all questions in detail, and give recommendations on taking vitamins and oral hygiene.
- Materials for filling, aesthetic composites are non-toxic, blend with the shade of tooth enamel. The restorations look as natural as possible.
The importance of dental hygiene - preventive measures during pregnancy
Pregnancy worsens the condition of teeth; large-scale interventions during pregnancy are often dangerous. At this time, preventive and hygiene measures are more important than ever. Preventing disease during pregnancy is much easier than sanitizing affected teeth. It is required to include in your child planning activities a dental examination and all necessary sanitation and preventive cleaning. It is also carried out during pregnancy - the schedule is drawn up by the dentist. To preserve your teeth and prevent them from deteriorating, you need to:
- thoroughly brush your teeth with a paste without lauryl sulfates (or with its minimum concentration);
- use remineralizing compounds that reduce the sensitivity of enamel and stabilize caries in the form of spots;
- eat right and take vitamins, paying attention to the sufficiency of calcium and magnesium in the diet.
All dental care necessary during pregnancy can be obtained at the Moscow clinic "Mazot".
Experienced doctors will select safe medications and methods of dental sanitation; the atmosphere will help you relax and avoid stress. The clinic performs all types of preventive, therapeutic and surgical interventions. After the procedures, the expectant mother will leave the office in a good mood, having solved the problem and maintained her health without harm to herself and the fetus. Make an appointment