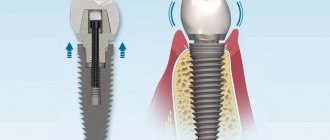
A tooth on an artificial root has a multicomponent structure. The supporting part in the form of a cylindrical or conical rod sits tightly in the jaw bone. An abutment imitating a tooth stump is fixed on top of the root substitute. And the prosthesis is already attached to it. Normally, all elements of the system are fixedly connected to each other, so if the crown on the implant is loose, it needs to be sorted out. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon, which is the task of the dentist to establish.
What symptoms accompany implant mobility?
There are two possible scenarios:
- there is no inflammation of the tissue around the implant, and it just wobbles, but does not hurt,
- the implant wobbles due to inflammation and pain in the jaw.
Of the possible complications, the first “scenario” is the least dangerous condition, which is most often caused by errors of the specialist installing the structure, and a number of diseases that affect the rate of osseointegration (diabetes mellitus, for example). In this case, the patient simply feels the mobility of the metal rod 2–3 weeks after the operation, the implant wobbles a little. The soft tissues around retain their former natural appearance, there is no pain or change in condition in the oral cavity. This is the most favorable outcome, allowing you to correct the situation with the least damage to your health and wallet.
However, the implant can also wobble due to poor-quality installation, as well as complete failure to engraft into the bone. This situation is not favorable - most likely, the product will have to be removed.
In the second case, mobility against the background of inflammation is a serious symptom that indicates rejection of the structure. And the instability of the structure, as a rule, occurs after the long-term existence of other signs of inflammation:
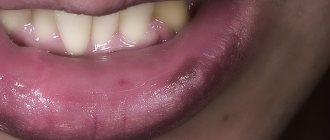
- the gums around the implant have changed color, become bright red, bluish, unevenly colored,
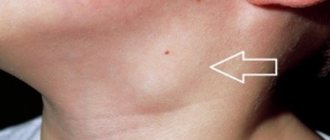
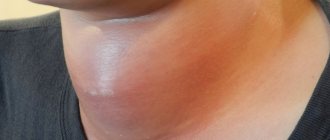
- there was slight swelling,
- the mucous membrane does not adhere tightly to the artificial structure, partially detaches from its surface,
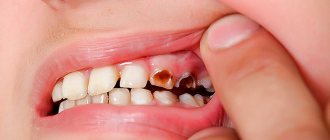
- when chewing, pain occurs, as well as when touching the gums,
- bleeding gums around the implant,
- the appearance of a putrid odor from the area of the installed implant,
- discharge of pus from under the gums,
- body temperature remains elevated to 39°,
- there is a general malaise.
All these symptoms indicate developing mucositis or peri-implantitis - first superficial, and later deep inflammation of soft and bone tissues.
In both cases, you should not wait for the situation to improve; you should immediately seek professional help. Read more about the unfavorable outcome of implantation in the material “Dental implant rejection.”
How to recognize rejection?
If the implant is rejected, then mobility is not the only and most often not the first symptom. You should worry if:
- Painful sensations arose in the implant area after they subsided in the first 3 days after the operation.
- Swelling or hyperemia has appeared.
- The bleeding, even minor, does not stop for a long time.
- There is pus draining around the implant.
- A putrid smell appeared in the mouth.
If you notice one of these symptoms or, naturally, regarding a dental implant, then try to see your implantologist as soon as possible. He will examine the implant area and prescribe treatment to relieve inflammation. If the treatment process begins on time, as soon as you notice that the tooth-implant is swaying, then rejection can be avoided.
Consequences of implant mobility
A loose dental implant is only a symptom; other problems may arise in the future:
- If you never see your doctor, the entire implant may fall out.
- If peri-implantitis begins, the bacterial infection can spread to other areas and even threaten life.
- If you wait, the bone around the inflamed implant will dissolve, and then it will be very difficult to restore the required height in order to be able to install the implant again.
When it is not the implant that is loose, but the crown on it
How to determine whether an implant or crown is loose? The entire structure, which completely replaces the tooth, consists of several elements - an artificial root, an abutment and a crown that replicates the outer visible part of the tooth. Depending on the type of structure and the method of fastening the crown, the connection of the parts to each other may be different.
Read more about fixing crowns to an implant in the material “How to choose a crown for an implant and which ones are better? Review of modern single prostheses and methods of their fastening.”
It is possible that the screw fastening between the crown and the abutment may loosen or the properties of the cement composition may be lost for a number of reasons. But the implant itself can also become loose. However, at home it is difficult to reliably determine which element has weakened the fixation; this requires assessment and diagnosis by a specialist.
If it turns out that the crown is indeed weakened, then you can return it to its place in the clinic where the implantation was performed. Such cases occur more often with temporary crowns. The doctor will tighten the screw with a special tool and secure it to the implant. When the elements are cemented together, the crown “sits” again after cleaning.
What is the difference between a custom abutment and a standard one?
In general, as the name implies, in the first case the abutment is produced individually in a single copy and has a form strictly necessary for a particular case. In the second case, we are dealing with a factory stamped product.
A standard titanium abutment is installed in the oral cavity. Such a standard “cylinder” does not follow the shape of a real tooth and does not maintain the correct shape of the gums. In addition, when fixing the crown to such an abutment, excess cement can easily penetrate deep into the gap between it and the gum.
An individual zirconium abutment is made strictly according to the desired shape, which is usually what a central incisor should have. The gums are well supported. There is no space for cement to “drip” deep under the gum.
The left crown is made on an individual abutment , the right - on a standard one . The difference in shape is obvious. The first has a more regular, natural profile.
Which is better and is there a difference for the patient? Imagine that you come to a shoe store and find a model you like. Everything would be fine, but fashionable boots are produced only in certain sizes, say, 37, 39, 41 and 43. And as luck would have it, yours is 40. Well, at the very least, you can take the 41st and wear your favorite stilettos with a woolen sock. Yes, it’s unaesthetic... but they don’t die from it, do they?! But what if you ate a lot of Rastishka as a child and your feet grew exactly 50?
No extra socks will help here. And this is just a rough comparison. After all, your size may luckily be exactly 39. And so, it looks like the shoes are on, but you still don’t feel comfortable... the foot feels tight in width, but in the instep, on the contrary, everything somehow dangles... In general, it seems to fit, but it’s uncomfortable. Now, in contrast to this, imagine that your shoes will be made to order specifically for your foot, taking into account all its features. In such shoes, even with a 10-centimeter heel, you will feel like you are wearing house slippers. Almost the same can be said about the differences between standard and individual abutments. For work that does not claim to be high-class, especially in terms of aesthetics, in austerity mode, you can get by with standard ones. Well, for example, on chewing teeth. If we are talking about maximum aesthetics and service life, then custom ones are the best choice. It must be said that at the dawn of implantology, the difference in price between factory-made and individually made abutments was significant. Today, with the advent of more and more CAD/CAM* systems, the cost of producing individual abutments from all materials (primarily titanium and zirconium) has actually become equal to the cost of standard factory ones.
What causes implant loosening - the main reasons
If a tooth implant begins to wobble, then the reasons for this must be sought in one of three directions. Among them:
- physician errors: rejection due to specialist errors is noted at the initial stage of implantation of the structure (in the first 3–4 weeks) and indicates a poorly performed operation. We will look at possible errors in more detail below.
- systemic diseases and conditions of the patient: they affect the rate of osseointegration or affect the implant that has already taken root. If the cause is disease (periodontitis, hormonal changes during menopause or menstruation in women), then part of the reason for rejection can be considered the shortcomings of the preparatory period on the part of the doctor, who did not take their presence into account. Also, a patient can hide his illnesses from the doctor and, at his own peril and risk, decide to have an operation, the result of which will be rejection. Mobility may occur 5 years or more after implantation due to the appearance or development of systemic diseases, the occurrence of which is difficult to predict,
- patient errors: they are mainly related to the care of installed structures and prevention. By maintaining a level of hygiene for implants and prostheses, the patient creates conditions for their long-term service. Ignoring the requirements can also lead to such unpleasant consequences as inflammation of the tissues around the implants, which, as it progresses, leads first to mobility and then to rejection of the structure.
We must not forget that we are considering exceptional cases of implant mobility and rejection. In general, clinical practice and statistics[1] indicate 2–5% of such cases.
Rejection of titanium dental implants after healing: when does it happen?
The main causes of delayed rejection and instability of implants:
- Peri-implantitis. This inflammation of the surrounding tissues may be a consequence of non-compliance with the protocol or the development of initially undetected weak infectious processes, caries, or the initial stage of periodontal disease.
- Features of bone structure. A small amount of tissue will not hold the embedded pin.
- Pathologies during osseointegration. When choosing a cheap implant from the “no name” series, the pin does not integrate; only scar tissue grows. Fibrosis begins and the structure falls out.
Sometimes the cause of trouble is the treatment of emerging oncological diseases, the use of potent drugs that affect the regeneration of tissue cells.
Implant mobility caused by erroneous actions of the doctor
If the implant begins to wobble during the healing period, for example, a month after installation, then the problem most often lies in the incorrect actions of the doctor while preparing the patient for implantation and directly during the installation operation. Since implantation is a complex undertaking, the doctor may make mistakes at different stages, both at the beginning and directly during the surgical intervention.
During preparation
Receiving false information about the condition of the bone where implants will be implanted. This is possible with insufficient and uninformative diagnosis, when other methods are used instead of computed tomography - orthopantomogram (OPTG) or radiography.
Incomplete preliminary examination (or complete refusal of it) of the patient to determine if he has relative and absolute contraindications that make implantation difficult or impossible. It is also possible that the doctor will not take into account the special hormonal status of women (menopause, postpartum or menstrual period) and will allow surgery during this period without taking into account the condition.
During the preparation of the treatment plan
Incorrect assessment of the place for the implant in the bone, the location of the artificial structure is too close to the roots of living teeth, with insufficient bone tissue.
Directly during surgery
There is a wide scope for incorrect actions: violation of the sterility of instruments and equipment, bacteria entering the prepared hole along with saliva, or when the edge of the implant touches any surface. The use of improperly sized implants, the use of structures for a different surgical protocol, overheating of the bone tissue when forming a bed for the implant, installation of the rod at the wrong angle, excessive deepening of the rod, etc.
For prosthetics
During the manufacture of the prosthesis, violations may occur, resulting in incorrect distribution of the chewing load, inconsistency of the prosthesis with the implants, penetration of the cement composition into the socket, prosthetics of only one row without taking into account the load on the second, and others.
In order not to encounter unpleasant consequences of implantation, a specialist must be chosen carefully, based on many indicators of his work. How not to make a mistake with your choice, read the material “How to choose a doctor and clinic?”
What to do if the implant has already fallen out
When an unpleasant situation with a rod arises, in most cases radical measures are needed. As a rule, cleaning of the hole and antibacterial treatment are required. After the inflammation has subsided, after a month or a month and a half, tests are taken and examinations are prescribed if necessary. If the tissue volume is small, osteoplasty is performed to obtain the required dimensions to hold the product. This situation requires long-term rehabilitation, at least 90–120 days.
If the implant falls out due to an allergic reaction or individual intolerance to the raw materials of the device, a qualified doctor selects other materials and the installation is carried out again. Definitely, a rod that has not fused with the bone must be replaced! Contact experienced specialists who do not ignore the stages of preparation, as well as postoperative management. It's another matter when the problem concerns the crown. It is easier to solve. After firm fixation, the inconvenience is eliminated.
An implant with a pin fell out and you don’t know what to do? The specialists of our center will definitely help you! While the new device is being manufactured, a temporary system may be proposed. Often a nylon or clasp prosthesis is used. As practice has shown, only 2% of patients can count on saving the old structure. It is very important to carry out complex therapy that will eliminate inflammation and prevent further infection. The temporary plug of the device is also cleaned. Of course, a lot depends on the patient himself. After all, strict adherence to the rules and compliance with all the dentist’s advice eliminates the lion’s share of possible problems and complications.
Systemic diseases and body conditions affecting the fixation of implants
These include chronic diseases that make up the list of contraindications for implantation. They may go unnoticed or deliberately hidden by the patient, or appear much later, when the implant has been standing for several years.
Read about indications and contraindications for implantation in the feature article on the website “When you can or cannot place dental implants - a complete list of tolerances and prohibitions.”
Dental implant failure can occur due to the following diseases:
- diabetes mellitus in a long stage of decompensation,
- pathologies of the central nervous system,
- disruptions in the body's immune system,
- development of oncological tumors of any localization and subsequent therapy,
- allergic reactions in the oral cavity to the components of an implant or prosthesis,
- trauma of the maxillofacial apparatus,
- oral diseases
To avoid unexpected consequences of these diseases, experts recommend regular preventive oral examinations and monitoring of chronic diseases.
Prevention measures
Cleanliness of the oral cavity is of utmost importance to prevent postoperative complications. Good dental hygiene is so important that in some cases, doctors refuse implantation to patients who, in their opinion, are unable to properly care for implant-mounted prostheses.
Poor oral hygiene can not only act as the only cause of complications, but most often it is the provocateur of rejection.
There are special programs that are designed to educate patients about post-implant care. Key points that should be given particular attention include the following recommendations:
- You should brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush at least 2 times a day before bed and after breakfast.
But it is better to brush your teeth after every meal. This ensures the removal of soft plaque from the supragingival areas of implants, superstructures and teeth. You can use electrical appliances. Brushes need to be changed every 2 months. - It is highly advisable to clean the necks of implants and the gingival areas of superstructures with superfloss - dental floss with a porous fleecy working part.
This product allows you to completely remove plaque from the neck of implants, where its presence is critical for the condition of the infrastructure of the prosthesis. - It is recommended to use conical and cylindrical interdental brushes and monotuft brushes. In the gingival area, they are more effective than conventional brushes. Their size and shape are selected individually.
- Experts recommend antiseptic rinses as additional means of cleaning the oral cavity. They are usually used for a short time - immediately after surgery, and for inflammation of microbial etiology.
- For areas closed to other hygiene products, it is useful to use irrigators.
Important. After implantation, you should not use whitening toothpastes containing chlorine or soda.
A preventative visit to the doctor is considered mandatory every 6 months, but more often is better. If, after examining your mouth, your dentist suggests you have a professional cleaning, do not refuse.
The occurrence of implant mobility due to patient negligence
Here it mainly concerns oral hygiene and the rules of care for implants and prostheses installed on them. If the doctor performed the operation competently, taking into account all the patient’s characteristics, then the responsibility for the rehabilitation period falls 90% on the patient’s shoulders. If a dental implant wobbles due to gum inflammation, this indicates an extreme degree of peri-implantitis. Complications at this time and much later are possible for a number of reasons:
- refusal to take medications prescribed by a doctor to restore tissue, prevent inflammation, etc.,
- smoking and drinking alcohol after surgery, unwillingness to give up bad habits in the future. It is known that smokers experience implant rejection twice as often[2] (7% of cases) than those who are not exposed to the bad habit.
- insufficient daily care of dentures and implants, lack of proper hygiene, accumulation of bacterial plaque around implants,
- overload of implants when chewing too hard food, untimely (too early) load on the rods.
All this leads to the development of inflammation and, without treatment, to implant mobility and, ultimately, to rejection of the structure.
Read about the organization of comprehensive oral care after implantation in the thematic material on the website “Care for the oral cavity and dentures after implantation.”
What to do in case of rejection?
If the rod falls out of the bone or there are symptoms that indicate rejection, then you need to visit an implantologist as soon as possible. The doctor will try to find out the cause of the complication and offer options for solving the problem.
The warranty period for implantation systems is 10-20 years or more, and for doctor’s services – 1-2 years. This is explained by the fact that implants are stable, and the human body is constantly changing and is exposed to new diseases, irritants, etc. As a rule, if there are problems with installation, a violation of the implant’s engraftment occurs in the first 6 months or its rejection is observed over the course of 1-2 years.
If rejection occurs due to the doctor’s fault, if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed, or if the body is ill, then re-implantation is performed. In case of insufficient bone tissue, bone augmentation surgery may be performed. In case of severe deterioration of health, significant damage to bone tissue, treatment is carried out using removable prosthetics.