A patient complaining that his neck hurts in front under the chin is not such a rare case in the practice of modern doctors. Patients themselves, faced with unpleasant or painful sensations in the throat area, often begin to panic and draw terrible pictures of possible ailments. The difficulty is that not every person is familiar with the structure of the neck in detail and has no idea what systems located inside this part of the body can fail and lead to pain.
Causes of pain in the neck muscles
There are several types of pathological conditions that, among other unpleasant symptoms, can lead to pain in the front of the neck under the chin.
Spinal diseases
This includes, first of all, osteochondrosis - one of the most common painful conditions affecting a huge number of the population. At risk are office workers, older people, women during and after menopause. Other common pathologies are spinal disc herniation or protrusion. They are a consequence of rupture of the fibrous ring surrounding each individual vertebra. These diseases cause a person severe constant pain (sometimes not even relieved by anti-inflammatory drugs), and if left untreated, they quickly progress and lead to disability.
Inflammatory diseases of the neck
Inflammation that occurs in the organs located under the muscular frame of the neck is one of the most common reasons why a person has pain in the neck in front under the chin. Usually, malaise is a consequence of viral diseases that affect the trachea and other organs of the upper respiratory tract, but sometimes the disease develops as a result of the pathogenic activity of infectious microorganisms.
Poor blood supply to the neck muscles
The reasons for this condition can be very diverse: sometimes it is only a temporary disorder (as people say, “the neck gets stiff” when being in the same position). In other situations, normal blood circulation becomes impossible due to the appearance of plaques on the inner surface of the vessels (atherosclerosis), and in some cases, pain in the neck under the chin is a consequence of pinched nerve endings.
Hereditary diseases of the muscular system
Diseases transmitted by inheritance often manifest themselves in early childhood and, in the absence of therapy, can “grow” with new symptoms. For example, muscular torticollis, a congenital disease, is diagnosed in infants already at the age of several weeks and is characterized by asymmetry of the face and head, and skeletal deformation. Often, as a result of torticollis, the neck hurts under the chin.
Why does my neck swell?
Traumatic injuries
Soft tissue bruises are accompanied by moderate local swelling and pain that intensifies during neck movements.
The swelling disappears within a few days. Subluxation of the cervical vertebra occurs as a result of a sharp turn of the head, and is more often detected in children. Asymmetrical swelling of the back of the neck is complemented by a forced position of the head, pain, and muscle tension. In case of fractures, local swelling is determined in the projection of the spinous process of the damaged vertebra. In victims with laryngeal injuries, external swelling is usually minor. Severe swelling can be a consequence of severe complications: internal bleeding into soft tissues, subcutaneous emphysema that occurs against the background of a rupture or penetrating wound of the larynx. Difficulty breathing, aphonia, and pain are noted. Hemoptysis and asphyxia are possible.
With uncomplicated laryngeal foreign bodies, there is no symptom. Against the background of inflammation in the area where a foreign object is located, swelling of varying severity occurs, combined with pain, hyperthermia, and symptoms of intoxication. A life-threatening condition is perforation of the larynx by a sharp foreign body with the development of subcutaneous emphysema.
Diseases of the lymphatic system
Swelling of the neck is often associated with inflammation of the regional lymph nodes. The following diseases can cause lymphadenitis:
- Purulent lesions of soft tissues
: infected wounds, boils, carbuncles, abscesses, phlegmon of the face, head and neck. - Dental problems
: caries, pulpitis, gumboil, stomatitis, purulent mumps, maxillary abscess, abscesses of the tongue, oral cavity, osteomyelitis of the jaw. - ENT pathologies
: tonsillitis, chronic tonsillitis, paratonsillar, parapharyngeal, intratonsilal abscesses, otitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis. - Children's infectious diseases
: diphtheria, scarlet fever, mumps. - Dangerous infections
: plague, anthrax.
In children with chronic skin diseases, lymphadenitis of the cervical, submandibular, and occipital lymph nodes occurs with the development of Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis. Enlarged lymph nodes also become a consequence of the lymphogenous spread of malignant tumors: cancer of the tongue, lower and upper jaw, larynx, pharynx, nose, paranasal sinuses.
Swelling of the neck due to thyroiditis
Endocrine pathologies
The most pronounced diffuse swelling of the neck is observed with myxedema. Not only the neck, but also the face swells; in severe cases, the swelling spreads throughout the body. Distinctive features are the absence of redness, pallor, pitting when pressing on the skin, shortness of breath, lethargy, lethargy, and increased sensitivity to cold. Changes in the anterior surface of the neck are determined in all forms of goiter:
- Diffuse euthyroid goiter.
The general condition has not changed, sometimes weakness and headaches are observed. In mild cases, swelling is noticeable only when palpating, tilting the head back, in severe cases it reaches the level of a pronounced cosmetic defect. - Diffuse toxic goiter.
Detailed symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are detected. The thyroid gland is uniformly enlarged, the degree of swelling does not always correlate with the severity of the disease. - Nodular goiter.
The function of the gland is often preserved; some patients show signs of hypo- or hyperthyroidism. The swelling of the neck is uneven, one side is larger than the other.
In acute thyroiditis, swelling is combined with pain, local hyperthermia, hyperthermia. The onset of the purulent form of thyroiditis is marked by increased pain, severe fever, and lymphadenitis. In patients with subacute thyroiditis, the body temperature is subfebrile, there is swelling, moderate pain in the projection of the thyroid gland, in half of the cases symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are detected. Chronic thyroiditis develops gradually. The affected area is lumpy and painless.
Maxillofacial pathology
The cause of swelling is often diseases of the salivary glands and soft tissues. Swelling is observed in the following pathological conditions:
- Sialadenitis.
The parotid salivary gland most often suffers; a one-sided painful swelling is located on the border of the neck and lower jaw, next to the earlobe. Less commonly affected are the submandibular salivary glands, which are localized in the submandibular triangle of the neck. - Purulent parotitis.
With purulent inflammation, swelling spreads to the neck, cheek, and submandibular area on the affected side. A pronounced deformation occurs. Pain, general hyperthermia, severe weakness, weakness are noted. - Salivary gland abscess.
Along with the parotid, other salivary glands may be affected. In 50% of cases, inflammation affects the paired organ. The area of swelling corresponds to the location of the affected gland. There is severe pain, febrile body temperature, and severe intoxication syndrome. - Perimaxillary abscess.
Formed as a complication of tonsillitis, furunculosis, infected abrasions of the skin and oral mucosa. Unilateral swelling is detected in the area of the submandibular triangle. When the abscess ruptures, swelling spreads down the neck. - Cellulitis of the neck.
It is provoked by odontogenic or tonsillogenic infection, foreign bodies of the laryngopharynx. Swelling appears on one side, grows quickly, and diffusely covers a significant part of the neck. The skin over the area of swelling is red, hot, and tense. The general condition is serious.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Swelling of the neck in otolaryngological diseases is often caused by lymphadenitis. Diseases accompanied by swelling of the neck, not associated with enlarged lymph nodes, include:
- Chondroperichondritis of the larynx.
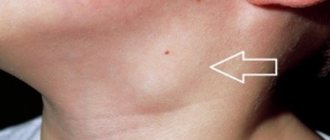
A limited area of swelling is located in the front of the lower or middle third of the neck. Combined with chills, weakness, hyperthermia, pain, aggravated by talking, coughing, swallowing. - Neck cyst.
The tumor-like formation is localized on the lateral or anterior surface, and is more clearly contoured when the head is turned in the opposite direction. In the absence of inflammation, it is asymptomatic. When infected, the skin turns red, the cyst enlarges, becomes painful, and swelling spreads beyond the affected area. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
Swelling of the neck behind the angle of the lower jaw, sore throat, breathing problems aggravated in an upright position, severe impairment of the general condition, and hyperthermia are detected. - Lemierre's syndrome.
Postanginal anaerobic sepsis is manifested by swelling of the lower part of the lateral surface of the neck (in the projection of the jugular vein), pain, progressive deterioration of the condition up to impairment of consciousness and speech, the development of pneumonia, arthritis, and osteomyelitis. - Ludwig's sore throat.
The disease is characterized by a rapid onset and severe course with fever, intoxication, severe sore throat, and diffuse swelling of the soft tissues of the neck. On palpation, the tissues are painful, dense, and “woody.”
Allergy
With angioedema, swelling of the neck, face, lips, eyelids, ears, limbs, and genital area is observed. The swelling is painless, accompanied by a feeling of tension and fullness, and pale skin. It is provoked by contact with allergens: drugs, food, insect poison. Sometimes it occurs due to pseudo-allergy. In addition, severe swelling of the face, neck, feet, and hands is found in the edematous type of allergy to salicylates.
Infectious diseases
The most common infectious cause of neck swelling is mumps. Swelling is detected in the area of the salivary glands, often bilateral, sometimes asymmetrical. Due to the enlargement of the upper parts of the neck, the face becomes pear-shaped. Severe swelling of the anterior parts of the neck is detected in the toxic form of diphtheria. 1st degree is characterized by swelling reaching the middle of the neck, 2nd – to the collarbones, 3rd – spreading to the face, chest, back, back of the neck.
In patients with typhus, redness and swelling of the face and neck are accompanied by injection of the conjunctiva, the appearance of a thick rash on the torso and limbs, hepatosplenomegaly, oliguria, neurological disorders, and severe intoxication.
Neoplasms
Local swelling of the neck may be due to the development of neoplasia, which includes:
- lipomas, fibromas;
- cancer of the pharynx and larynx;
- thyroid tumors.
Benign neoplasms are limited, painless swellings that do not increase or increase very slowly in size. Malignant neoplasia rapidly progresses, causes enlargement of lymph nodes, invades neighboring organs, and is accompanied by breathing and swallowing disorders, and voice changes.
Other reasons
The list of other causes of neck swelling includes a number of diseases of various etiologies:
- Rheumatology, orthopedics
: cervical myositis, Shulman's disease, scleroderma, dermatomyositis. - Cardiology, pulmonology
: exudative pericarditis, pleurisy, mediastinitis, superior vena cava syndrome. - Dermatology
: furunculosis, bullous dermatitis. - Neurology
: Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome. - Nephrology
: membranous glomerulonephritis. - Emergency conditions
: cytokine storm.
Elimination of pain in the muscles of the neck in front
Since this condition is classified as pathological, it requires the most prompt treatment possible. The best option is to consult a doctor, since this specialist has all the necessary knowledge regarding the fight against inflammatory and other diseases that occur in the cervical region. If you have neck pain in the front under your chin, call and make an appointment with the highly qualified, experienced doctors at the Energo Clinic. The telephone number for contact is indicated on the website in the “Contacts” section; registration is carried out on any day and time of day convenient for you.
Drug treatment
After collecting anamnesis, conducting an examination and finding out why your neck hurts in front under the chin, our neurologist
will write out the most detailed treatment plan for the disease and instruct what needs to be done to prevent the disease from worsening again. The most important point will be taking medications - painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs whose action is aimed at maintaining the optimal condition of the muscular frame and skeletal system.
Massage and physical therapy
Conducted strictly in the presence of a chiropractor
,
massage therapist
or doctor at a physical therapy room. The neck is a rather delicate organ; it should not be pressed, and often not heated intensely, as this can cause a deterioration in the condition. At the same time, a soft, relaxing massage will help relieve muscle tension and normalize blood flow.
Surgery
It is necessary in situations where the condition threatens the normal course of a person’s life. For example, if the thyroid gland is enlarged and there is no effect from medications, the affected organ is removed in a surgical hospital. After the operation, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the attending physician, undergo regular examinations by an endocrinologist, and take hormones.
ethnoscience
Effective for inflammatory diseases, but should only be used as an additional treatment measure. A proven folk remedy is a decoction of chamomile or calendula - it is used for colds and to relieve throat spasms. In situations where a person has pain in the neck under the chin as a result of thyroid pathologies, herbal medicine brings good results: certain medicinal plants contain components that have a positive effect on the state of the hormonal system.
Diagnostics
Therapists are involved in determining the cause of neck swelling. According to indications, patients are referred to otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, maxillofacial surgeons, and other specialists. The examination includes objective, instrumental, and laboratory techniques. The following diagnostic procedures are carried out:
- Questioning, general examination
. A basic study that allows you to establish a preliminary diagnosis and draw up a plan for further examination. Involves studying symptoms, medical history, and assessing external changes. - Sonography
. Ultrasound of the neck is informative when studying the condition of organs and soft tissues, it allows you to identify tumors, areas of inflammation, determine the localization and boundaries of pathological processes. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed if an endocrine cause of neck swelling is suspected. Ultrasound of the lymph nodes is recommended for lymphadenitis and cancerous tumors. - Radiography
. To exclude subluxations and vertebral fractures, X-rays of C1 or the cervical spine are prescribed. If there are symptoms of damage to the ENT organs, an x-ray of the larynx is performed. - Other visualization techniques
. CT and MRI of the neck are performed to detail the information obtained during sonography or radiography and make it possible to clarify the location, volume, and nature of the pathological process. - Radioisotope scintigraphy.
Effective in studying the thyroid gland, visualizes nodes, confirms the presence of diffuse changes. - Endoscopic examination of the throat.
Direct and indirect laryngoscopy, microlaryngoscopy, fibrolaryngoscopy are prescribed for lesions of the larynx. According to indications, a biopsy is performed during the study. - Lab tests
. Depending on the existing symptoms, general and biochemical blood tests, examination of the level of thyroid hormones and antibodies to them, microbiological analysis of swabs, punctures, blood samples, cytological or histological examination of a biopsy specimen can be performed.
Neck palpation
Prevention
A variety of preventive measures will help prevent the disease from exacerbating and returning. First of all, it is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Engage in moderate physical activity and avoid eating unhealthy foods in excess. If you periodically have pain in your neck under your chin, then do not forget to visit a doctor and consult with him before you feel another pain syndrome. Stop smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day. Try not to abuse alcohol or take medications not directly prescribed by your doctor.
Tumor classifications
Tumors in the neck vary depending on where they originate.
Table No. 1. Types of tumors
| View | Description |
| Organ tumors | They keep the elements of the organ structure intact. There are benign and malignant. Appear from organs that are located in the neck. |
| Extraorgan tumors | Do not come into contact with organs located in the neck area. They can be either benign or malignant. Affects muscle and nerve tissue. |
| Tumor lesions | The lymph nodes located in the neck are affected. May be primary or secondary. |