If your teeth involuntarily clench and grind during your sleep, you need to understand that these are clear signs of a disease such as bruxism.
Timely treatment is necessary to prevent the development of other diseases and complications. Bruxism can cause: tooth wear, dysfunction of the temporomandibular system, periodontitis, frequent headaches, etc.
The difficulty here is that such treatment will only be effective if there is an integrated approach. In addition to dental treatment, psychotherapeutic and physiotherapeutic treatment will be required, as well as massage and the use of protective caps.
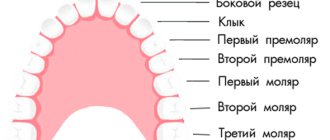
Causes of Bruxism
There are several theories about the appearance of bruxism in adults. Psychological theory attaches great importance to the emotional state of a person in the development of the disease. Thus, factors favoring the development of bruxism may be the following:
- stress;
- high psycho-emotional stress;
- social and everyday disorder, troubles;
- frequent affective states.
The disease is called the disease of businessmen. People who undergo high psycho-emotional stress and take on great responsibility experience tension, which leads to involuntary muscle spasms during sleep. But it is important to understand that positive-minded patients can also suffer from this disease.
According to the neurogenic theory, the causes of bruxism in adults lie in disruption of the central and peripheral nervous system. This leads to neurological and movement disorders, muscle spasms. The validity of this theory is confirmed by the fact that, along with bruxism, sleep disorders (apnea, snoring, somnambulism) are often observed; tremor, epilepsy, enuresis - bedwetting. Tonic muscle tension can also be associated with damage to the trigeminal nerve.
Dental theory is based on the assumption that bruxism develops as a result of disturbances in the structure and function of the dental system. These include the following:
- bite defects;
- incorrect position of teeth;
- supernumerary teeth;
- crowded teeth;
- violation of the integrity of the dentition (partial adentia);
- incorrectly selected dentures and orthodontic structures;
- overestimation of fillings according to the bite;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
Dental diseases lead to uneven distribution of the chewing load, and therefore the chewing muscles do not work properly. Her overexertion leads to nighttime cramps.
According to osteopathic theory, muscle contraction is an attempt by the neuromuscular system to eliminate blockage of the cranial sutures and restore craniosacral rhythm. This may be the result of birth trauma, malocclusion and posture, diseases of the cervical spine, etc.
Other theories about the origin of bruxism are not widely accepted, but some researchers link the problem to impaired nasal breathing, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), parasitosis, frequent chewing of plates or pads, and other factors.
In any case, the causes of bruxism in an adult can be different, so it is difficult to do without a comprehensive diagnosis and the involvement of several specialized specialists.
Ask a Question
What is bruxism
Clenching your teeth while sleeping is called bruxism. The attack, during which the jaws clench tightly, friction occurs and grinding sounds, lasts from a few seconds to 10 minutes and is repeated periodically throughout the night. Usually the phenomenon is accompanied by changes in blood pressure, breathing problems, and increased heart rate.
Bruxism is observed in 50% of children; as they grow older, in most cases, teeth grinding at night stops. But it’s better to find out the reasons right away in order to avoid health problems in the future. In adults, the phenomenon is less common and is not considered an independent disease, but this is a clear signal that not everything is in order with the body.
There are two types of bruxism:
- Day. It does not occur as often, it is easier to recognize. Periodically during the day, during tense moments, a spasm of the jaw occurs, which takes on an unusual, abnormal position. In most cases, self-control will help you cope with daytime bruxism.
- Night. It is much more dangerous, because during deep sleep a person does not control his actions.
At the time of an attack, pressure is applied to the jaw that is 10 times greater than the load during chewing.
Signs of Bruxism
An episode of nighttime teeth grinding lasts about 10 seconds. The number of episodes may vary and they may occur every night or occasionally. A characteristic symptom is grinding or clicking of teeth, but the patient himself rarely notices this feature, because sleep is not interrupted. Usually the patient learns about the problem from the lips of relatives and people living with him.
Associated symptoms of bruxism are the following:
- pain in the jaw, teeth;
- headache;
- pain in the facial muscles;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness.
What are the symptoms of bruxism and its impact on health?
Unfortunately, symptoms include repeated teeth grinding or clicking during sleep. All this can cause difficulty breathing and affect changes in blood pressure and heart rate.
After sleep, you may experience toothache and headache, symptoms of dizziness and a feeling of drowsiness during the day. You need to know and understand that if you do not treat bruxism in a timely manner, there can be such serious consequences as tooth wear, the appearance of various chips and cracks on them, and possible fractures in the places where crowns are installed.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of bruxism involves studying the patient’s complaints, as well as assessing indirect signs based on the results of a routine visual examination. The leading method of objective diagnosis is the use of Brux Checkers - special mouthguards that are made on the basis of a plaster cast of the patient’s jaw. These aligners allow the detection of occlusal obstructions. The doctor issues brux checkers to wear overnight, after which the patient submits them to the clinic for analysis. Using diagnostic aligners, a specialist determines which teeth bear the greatest load.
Electromyography and polysomnography methods make it possible to register the pathological activity of the masticatory muscles and confirm the diagnosis of bruxism.
But, as a rule, it is possible to understand the reasons only with the help of comprehensive diagnostics. So, in the case of bruxism in adults, psychosomatics may occur, so consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist will be required.
What consequences are possible?
At the initial stage, the disease is not even always noticed, since grinding teeth during sleep is not consciously realized. But if bruxism gets worse, it can lead to:
- Excessive tension in the jaws, lower face, temporomandibular joints.
- Headaches, the true cause of which is usually difficult to understand.
- Abrasion of tooth enamel, sometimes leading to a decrease in the height of dental crowns. This is possible with the correct bite. Excessively clenching teeth is a pathology, and it is harmful even with correct occlusion of the teeth. This can lead to increased sensitivity and faster development of caries.
Worn tooth crowns: consequences of improper closure and severe grinding of teeth
- If implants or bridges are installed, with severe bruxism their coronal part may also wear out and lose its shape. With bridges, the junction with the tooth becomes less strong.
All these complaints are nonspecific. Headaches are usually attributed to fatigue or a change in weather, and tension in the facial muscles is difficult to determine for yourself. An experienced doctor can help with the correct diagnosis - at the appointment, he may notice that the chewing muscles are in strong tone, and the tooth enamel is worn out.
Bruxism is quite common in children, including at an early age. It often leads to the formation of incorrect teeth position. Therefore, parents should not ignore this fact - the sooner treatment begins, the better it will be possible to maintain dental health.
Complications of bruxism
If the disease is observed for a long time, pathological abrasion of the tooth enamel, increased sensitivity of the enamel, and the appearance of a wedge-shaped defect, cracks and chips may develop. Constant trauma to the periodontal tissues can lead to periodontitis, loosening and loss of teeth. The service life of fillings and orthopedic structures (prostheses) in patients with bruxism is shorter due to high mechanical load.
The consequence of the disease can be dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, accompanied by pain in the jaw and neck, hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles.
Frequent injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity can lead to inflammatory diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis.
Pathological closing of the jaws during sleep complicates orthopedic and orthodontic treatment. Many dental restoration methods may not be available to patients, so it is important to pay attention to the disease in order to be able to receive comprehensive care in case of dental diseases or tooth loss.
Symptoms
Teeth grinding at night is the first and surest sign of bruxism.
But it is almost impossible to find out about it without outside help. To independently identify the disease, you should pay attention to the condition of the enamel, to the presence of an increased reaction to sweets, hot or cold. New holes, chips, or dentures may have become damaged for no apparent reason. All this is indirect evidence of the development of a movement disorder. There are a number of additional signs that may indicate the manifestation of night bruxism:
- throbbing pain in temples in the morning;
- dizziness and ringing in the ears;
- soreness of the jaw muscles;
- constant feeling of fatigue, drowsiness;
- discomfort in the sinuses;
- restless sleep and frequent awakenings.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Why do your legs twitch when you fall asleep?
Treatment methods for bruxism
Comprehensive treatment of bruxism may include medication, psychotherapy, physical therapy, and dental methods. This approach demonstrates the greatest efficiency.
The doctor will develop a treatment plan based on the severity of the disorder. It is very important to identify the causes in order to select adequate therapy.
In the case of exposure to psychogenic factors, the basis of treatment is cognitive behavioral therapy: the patient’s mastery of relaxation and self-control methods, psychotherapeutic trainings, art therapy, etc.
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing convulsive muscle activity. The main groups of funds include:
- magnesium, calcium preparations;
- B vitamins;
- mild sedatives;
- sleeping pills, etc.
Treatment of bruxism with botulinum toxin is also classified as a medicinal method. Botulinum toxin injections block nerve impulses entering the muscles, which relieves the muscles from involuntary spasms. The effect of botulinum toxin preparations is not permanent - after several months the injections are repeated. It is important to understand that this is rather a way to combat the symptom. Injections do not help eliminate the causes of the disease.
In some cases, osteopathic treatment may be recommended: manual therapy, massage, warming up the muscles with compresses.
The dental approach involves the participation of different specialists: periodontist, dental therapist, orthopedist, orthodontist. In the absence of pathologies in the dental system, protective rubber or plastic mouth guards are made, which helps prevent the consequences of bruxism in adults. According to indications, the following activities can be carried out:
- selective grinding of teeth;
- correction of bite by wearing mouthguards, braces;
- restoration of the integrity of the dentition: prosthetics and implantation.
Correction of bite defects is possible only after the patient’s condition improves. The installation of fillings and veneers, and splinting of teeth may be postponed due to the high risk of damage to structures.
Treatment and prevention
Dentistry suggests constantly wearing a mouthguard - a custom-made rubber structure that protects teeth from abrasion and loosening.
magnesium, calcium and B vitamins, light sedative and hypnotic infusions in order to calm the nervous system Before going to bed, you can apply a warm, damp towel to relieve tension, and undergo massage sessions of the chin and jaw system.
You should avoid eating foods that stimulate the nervous system (chocolate, coffee, strong tea, energy drinks, chewing gum).
Psychological and physiological ways to overcome bruxism
- You can learn autogenic training methods, breathing exercises, meditation, relaxation and stress relief.
- You should make a list of your favorite calming activities that allow you to relax and switch your attention from worries (to form a so-called “ bank of positive emotions ”). This could be long walks in nature, playing a suitable sport (swimming, running, cycling, yoga or qigong), taking warm relaxing baths with herbal decoctions, listening to music, chatting in a pleasant company, watching interesting films or programs, reading books, traveling to new places.
- A visit to a psychologist or psychotherapist will help the patient speak out, understand himself, internal conflicts, frequent mood swings, overcome depression and find spiritual harmony and balance.
Patients with bruxism are often torn between reason and emotions, between “want” and “should.” As a result, a person seems to eat and strive to destroy himself, grinding his teeth in his sleep when control over the psyche is weakened. Bruxism manifests itself as a destructive form of auto-aggression (aggression that has not found a way out). And the task of the psychologist is to recognize and bring out, work through and make conscious to the patient these suppressed elements of his psyche (including through the use of hypnotic techniques). Find acceptable options for expressing suppressed emotions, allow the patient to realize himself, turning aggression into a constructive direction.
Also, with the help of a psychologist, you can learn useful relaxation skills, for example, according to Jacobson . This technique consists of alternately working with different parts of the body - tensing and then relaxing the muscles, including the maxillofacial muscles.
In case of an excess of sexual energy, it will be useful to think about having a partner and regularly realizing your sexual potential, which in itself brings positive emotions and relaxes.
Prevention of bruxism
Bruxism can be prevented by paying attention to oral health: it is important to see a dentist in a timely manner, treat diseases of the teeth and gums, and restore the integrity of the dentition if teeth are lost. If you have bite defects or crowded teeth, you should consult an orthodontist.
Prevention involves normalizing the psycho-emotional state, giving up bad habits, coffee and energy drinks; maintaining a daily routine and proper nutrition.
Specialists from STOMA clinics will help adult patients get rid of bruxism: with us you can get help from all specialized doctors - from dental therapists to periodontists and orthodontists.
Symptoms of Bruxism
All video presentations
A person with bruxism involuntarily grinds his teeth:
- If the cutting is observed during the day, it is called daytime bruxism,
- if at night, they speak, accordingly, about night bruxism.
Individuals suffering from bruxism often have problems relating to those with whom they sleep in the same bed or live in the same room because the symptoms prevent others from sleeping. Negative attitudes toward someone with bruxism create a vicious cycle, placing the person under even more stress, which only makes the symptoms worse.
How is bruxism treated?
If a problem occurs, you should contact an orthodontist. He will select a special mouth guard to wear while you sleep. It is an elastic dental splint made of biocompatible plastic. This orthodontic design responds to the load when the patient compresses the dentition, preventing the chewing muscles from overexerting. As a result, the lower jaw relaxes and muscle hypertonicity goes away. Treatment will be effective if you wear the mouth guard for at least 10 hours a day.
Causes of teeth grinding
Today, most experts identify two main causes of teeth grinding [1]:
Stress, emotional exhaustion
Austrian gnathologist professor Rudolf Slavicek calls bruxism a “stress release valve” that helps relieve psycho-emotional tension [3]. Bruxism can be caused by:
- taking antidepressants, sleeping pills;
- abuse of alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, drugs;
- constant psycho-emotional tension, accumulated stress;
- depression, recent traumatic brain injury, Parkinson's disease and other mental disorders, neurological and psychosomatic diseases;
- sleep disorder;
- damage to motor neurons of the trigeminal nerve.
The secondary importance of occlusal disorders in the pathogenesis of bruxism has been proven.
As the main reason, a number of works emphasize the role of the central nervous system and psycho-emotional stress in the development of bruxism. There is evidence from the authors that an unstable psycho-emotional state is one of the triggers for the occurrence of bruxism. Magomedgadzhiev Sh. A., Department of Pathophysiology with a course of Clinical Pathophysiology, First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova [3]
Occlusal disharmony
Occlusal disharmony is a violation of the contact (closing) of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw. May arise due to [4]:
- malocclusion;
- polyodontia - the presence of supernumerary teeth;
- partial edentia - the absence of several teeth;
- violations during dental prosthetics, installation of braces;
- pathologies of the temporomandibular joint and other causes.
Causes of involuntary teeth grinding
The most common and direct cause of the disease is considered to be excessive stress. People who cannot cope with it suppress stress during the day, and at night it makes itself felt through teeth grinding. From a psychological point of view, the cause of the disease may be agoraphobia, or fear of open spaces. Somatic causes include poor-quality dental fillings, malocclusion, diseases of the nervous system and hereditary predisposition.